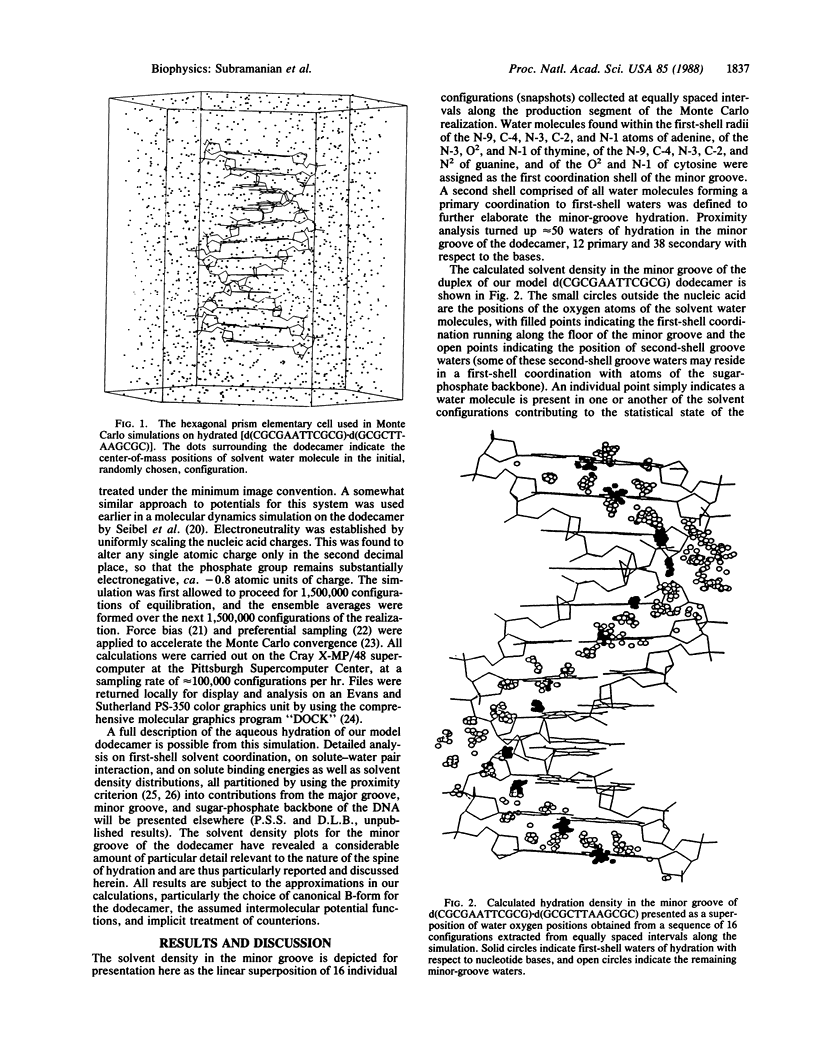
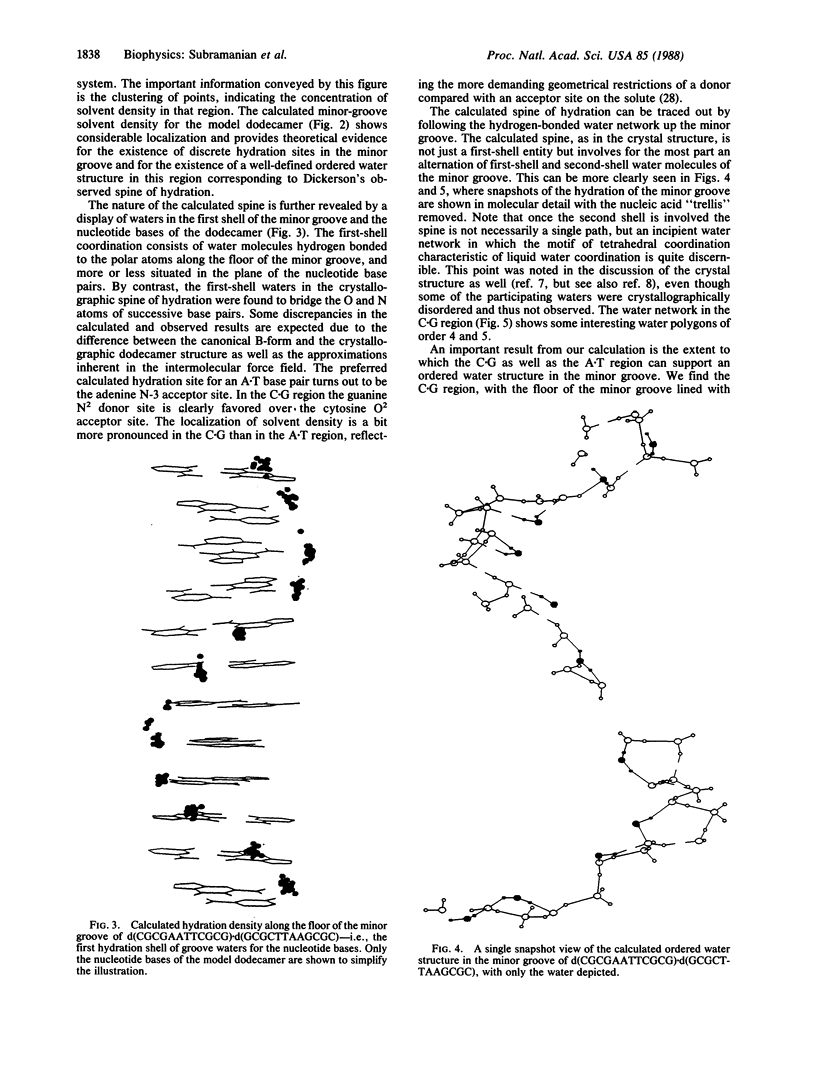
Abstract
A theoretical description of aqueous hydration in the minor groove of a B-form DNA is presented on the basis of a liquid-state Monte Carlo computer simulation on a system consisting of the oligonucleotide duplex d(CGCGAATTCGCG).d(GCGCTTAAGCGC) in a canonical B-form together with 1777 water molecules contained in a hexagonal prism cell and treated under periodic boundary conditions. The results are analyzed in terms of solvent density distributions. The calculated minor-groove solvent density shows considerable localization, indicative of discrete solvation sites and providing theoretical evidence for a well-defined ordered water structure. In the AATT sequence, this corresponds to the "spine of hydration" described by H. R. Drew and R. E. Dickerson [(1981) J. Mol. Biol. 151, 535-556] based on the x-ray crystal structure of the dodecamer hydrate. We find, however, that the calculated ordered water structure also extends into the CGCG flanking sequences, supported by the N2 hydrogen bond donors of the guanine residues and indicating that the spine of hydration could thus extend throughout the minor groove of a B-form DNA. This provides a possible explanation of the positive binding entropies observed by L. A. Marky and K. J. Breslauer [(1984) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 4359-4363] for both A.T and C.G sequences on the complexation of netropsin to the minor groove of DNAs. Implications of these results with regard to the thermodynamic stability of DNA in water and the sequence specificity of the minor groove hydration are discussed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman H. M. Hydration of nucleic acid crystals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;482:166–178. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb20948.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge D. L., Maye P. V., Jayaram B., Ravishanker G., Mezei M. Aqueous hydration of nucleic acid constituents: Monte Carlo computer simulation studies. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1984 Oct;2(2):261–270. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1984.10507565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer. III. Geometry of hydration. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):535–556. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Samson S., Dickerson R. E. Structure of a B-DNA dodecamer at 16 K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4040–4044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov V. I., Minchenkova L. E., Minyat E. E., Frank-Kamenetskii M. D., Schyolkina A. K. The B to A transition of DNA in solution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 25;87(4):817–833. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90086-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopka M. L., Fratini A. V., Drew H. R., Dickerson R. E. Ordered water structure around a B-DNA dodecamer. A quantitative study. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jan 5;163(1):129–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumry R., Rajender S. Enthalpy-entropy compensation phenomena in water solutions of proteins and small molecules: a ubiquitous property of water. Biopolymers. 1970;9(10):1125–1227. doi: 10.1002/bip.1970.360091002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marky L. A., Blumenfeld K. S., Breslauer K. J. Calorimetric and spectroscopic investigation of drug-DNA interactions. I. The binding of netropsin to poly d(AT). Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2857–2870. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marky L. A., Breslauer K. J. Origins of netropsin binding affinity and specificity: correlations of thermodynamic and structural data. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4359–4363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marky L. A., Snyder J. G., Remeta D. P., Breslauer K. J. Thermodynamics of drug-DNA interactions. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(2):487–507. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mezei M., Beveridge D. L. Structural chemistry of biomolecular hydration via computer simulation: the proximity criterion. Methods Enzymol. 1986;127:21–47. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)27005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seibel G. L., Singh U. C., Kollman P. A. A molecular dynamics simulation of double-helical B-DNA including counterions and water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6537–6540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Prangé T., Chevrier B., Moras D. Solvent distribution in crystals of B- and Z-oligomers. Biochimie. 1985 Jul-Aug;67(7-8):811–817. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80172-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing R., Drew H., Takano T., Broka C., Tanaka S., Itakura K., Dickerson R. E. Crystal structure analysis of a complete turn of B-DNA. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):755–758. doi: 10.1038/287755a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


