Abstract
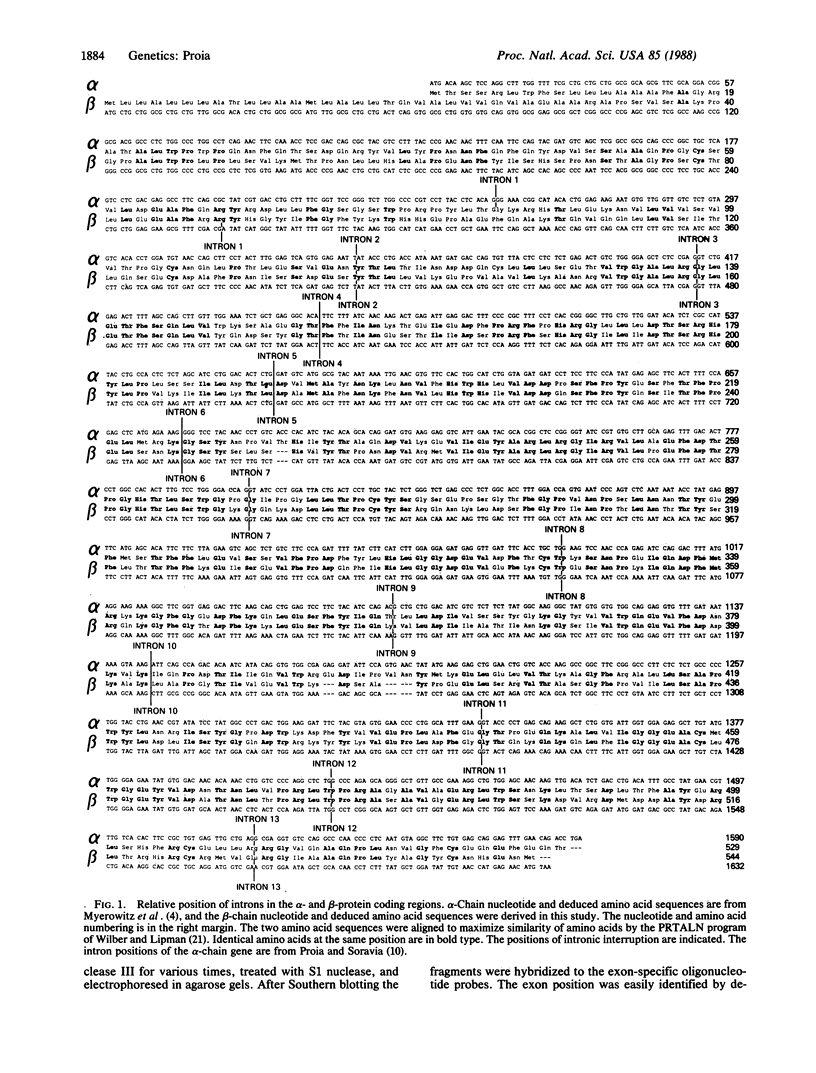
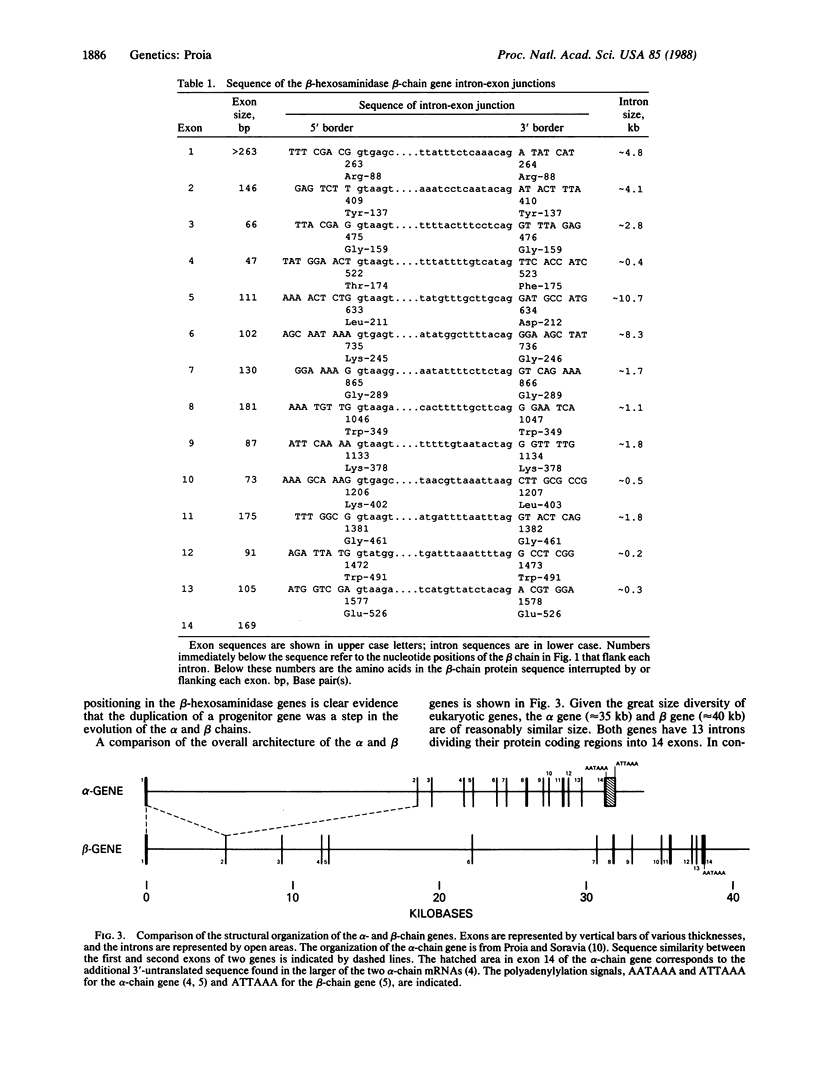
Lysosomal beta-hexosaminidase (EC 3.2.1.52) is composed of two structurally similar chains, alpha and beta, that are the products of different genes. Mutations in either gene causing beta-hexosaminidase deficiency result in the lysosomal storage disease GM2-gangliosidosis. To enable the investigation of the molecular lesions in this disorder and to study the evolutionary relationship between the alpha and beta chains, the beta-chain gene was isolated, and its organization was characterized. The beta-chain coding region is divided into 14 exons distributed over approximately 40 kilobases of DNA. Comparison with the alpha-chain gene revealed that 12 of the 13 introns interrupt the coding regions at homologous positions. This extensive sharing of intron placement demonstrates that the alpha and beta chains evolved by way of the duplication of a common ancestor.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andermann E., Scriver C. R., Wolfe L. S., Dansky L., Andermann F. Genetic variants of Tay-Sachs disease: Tay-Sachs disease and Sandhoff's disease in French Canadians, juvenile Tay-Sachs disease in Lebanese Canadians, and a Tay-Sachs screening program in the French-Canadian population. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1977;18:161–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Choo Q. L., Swift G. H., Quinto C., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Structure of two related rat pancreatic trypsin genes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14255–14264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craik C. S., Rutter W. J., Fletterick R. Splice junctions: association with variation in protein structure. Science. 1983 Jun 10;220(4602):1125–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.6344214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garger S. J., Griffith O. M., Grill L. K. Rapid purification of plasmid DNA by a single centrifugation in a two-step cesium chloride-ethidium bromide gradient. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91672-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautron S., Poenaru L., Boue J., Puissant H., Lisman J. J., Dreyfus J. C. Evidence for the presence of beta-subunit of hexosaminidase in a case of Sandhoff disease using a blotting technique. Hum Genet. 1983;63(3):258–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00284660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Genes-in-pieces revisited. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):823–824. doi: 10.1126/science.4001923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson K., Widmark E., Jonsson A. K., Servenius B., Sachs D. H., Larhammar D., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Class II genes of the human major histocompatibility complex. Evolution of the DP region as deduced from nucleotide sequences of the four genes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8778–8786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Neufeld E. F. Biosynthesis of lysosomal enzymes in fibroblasts. Synthesis as precursors of higher molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4937–4945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneluk R. G., Mahuran D. J., Neote K., Klavins M. H., O'Dowd B. F., Tropak M., Willard H. F., Anderson M. J., Lowden J. A., Gravel R. A. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the alpha-subunit of human beta-hexosaminidase. Extensive homology between the alpha- and beta-subunits and studies on Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8407–8413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kytzia H. J., Sandhoff K. Evidence for two different active sites on human beta-hexosaminidase A. Interaction of GM2 activator protein with beta-hexosaminidase A. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7568–7572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahuran D., Novak A., Lowden J. A. The lysosomal hexosaminidase isozymes. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1985;12:229–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Fritsch E. F., Lauer J., Lawn R. M. The molecular genetics of human hemoglobins. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:145–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Hogikyan N. D. A deletion involving Alu sequences in the beta-hexosaminidase alpha-chain gene of French Canadians with Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15396–15399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Piekarz R., Neufeld E. F., Shows T. B., Suzuki K. Human beta-hexosaminidase alpha chain: coding sequence and homology with the beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7830–7834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Teranishi Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Notake M., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Isolation and structural organization of the human preproenkephalin gene. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):431–434. doi: 10.1038/297431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Klavins M. H., Willard H. F., Gravel R., Lowden J. A., Mahuran D. J. Molecular heterogeneity in the infantile and juvenile forms of Sandhoff disease (O-variant GM2 gangliosidosis). J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12680–12685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Quan F., Willard H. F., Lamhonwah A. M., Korneluk R. G., Lowden J. A., Gravel R. A., Mahuran D. J. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the beta subunit of human beta-hexosaminidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen G. M., Rotter J. I., Cantor R. M., Field L. L., Greenwald S., Lim J. S., Roy C., Schoenfeld V., Lowden J. A., Kaback M. M. The Tay-Sachs disease gene in North American Jewish populations: geographic variations and origin. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Nov;35(6):1258–1269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Neufeld E. F. Synthesis of beta-hexosaminidase in cell-free translation and in intact fibroblasts: an insoluble precursor alpha chain in a rare form of Tay-Sachs disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6360–6364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Soravia E. Organization of the gene encoding the human beta-hexosaminidase alpha-chain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5677–5681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rackwitz H. R., Zehetner G., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H. Rapid restriction mapping of DNA cloned in lambda phage vectors. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. Exon shuffling and intron insertion in serine protease genes. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):458–459. doi: 10.1038/315458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K., Christomanou H. Biochemistry and genetics of gangliosidoses. Hum Genet. 1979;50(2):107–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00390234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K., Conzelmann E. The biochemical basis of gangliosidoses. Neuropediatrics. 1984 Sep;15 (Suppl):85–92. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess M., Schwartz A. L., Lodish H. F. Sequence of human asialoglycoprotein receptor cDNA. An internal signal sequence for membrane insertion. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):1979–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Wyler T., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Comparative analysis of the structural organization of two closely related vitellogenin genes in X. laevis. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


