Abstract
We describe a regulatory function of the terminal cytolytic C5b-9 complex [C5b-9(m)] of human complement. Purified C5b-9(m) complexes isolated from target membranes, whether in solution or bound to liposomes, inhibited lysis of sensitized sheep erythrocytes by whole human serum in a dose-dependent manner. C9 was not required for the inhibitory function since C5b-7 and C5b-8 complexes isolated from membranes were also effective. No effect was found with the cytolytically inactive, fluid-phase SC5b-9 complex. However, tryptic modification of SC5b-9 conferred an inhibitory capacity to the complex, due probably to partial removal of the S protein. Experiments using purified components demonstrated that C5b-9(m) exerts a regulatory effect on the formation of the classical- and alternative-pathway C3 convertases and on the utilization of C5 by cell-bound C5 convertases. C5b-9(m) complexes were unable to inhibit the lysis of cells bearing C5b-7(m) by C8 and C9. Addition of C5b-9(m) to whole human serum abolished its bactericidal effect on the serum-sensitive Escherichia coli K-12 strain W 3110 and suppressed its hemolytic function on antibody-sensitized, autologous erythrocytes. Feedback inhibition by C5b-9(m) represents a biologically relevant mechanism through which complement may autoregulate its effector functions.
Full text
PDF

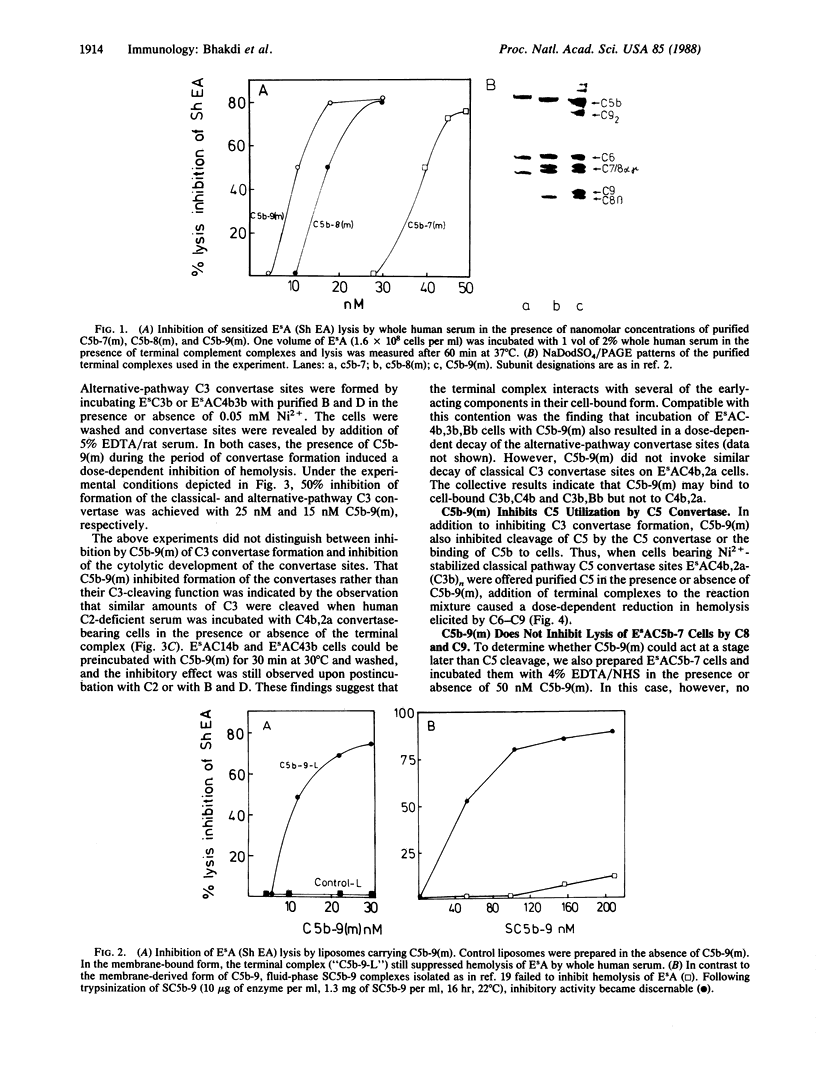
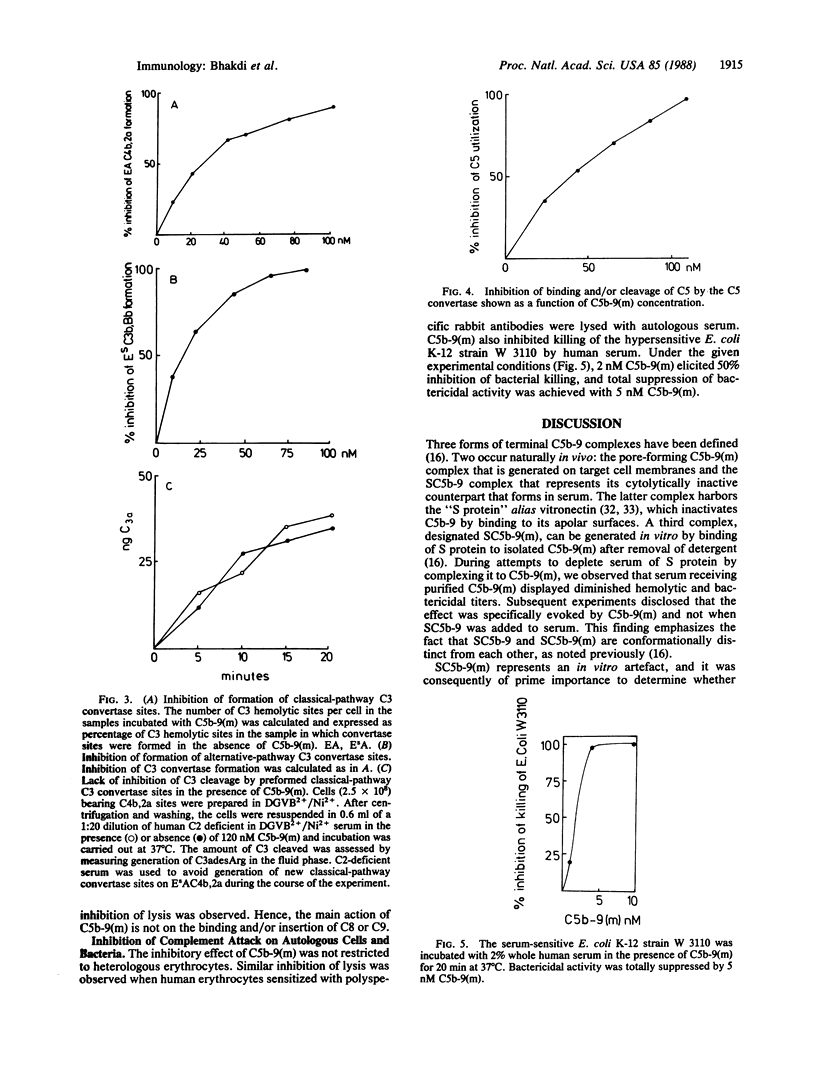

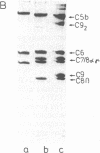
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bhakdi S., Roth M. Fluid-phase SC5b-8 complex of human complement: generation and isolation from serum. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):576–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. C5b-9 assembly: average binding of one C9 molecule to C5b-8 without poly-C9 formation generates a stable transmembrane pore. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2999–3005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Damage to mammalian cells by proteins that form transmembrane pores. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1987;107:147–223. doi: 10.1007/BFb0027646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Hydrophilic-amphiphilic transition of the terminal SC5b-8 complement complex through tryptic modification: biochemical and ultrastructural studies. Mol Immunol. 1982 Sep;19(9):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90327-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Membrane damage by complement. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Aug 11;737(3-4):343–372. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Molecular nature of the complement lesion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5655–5659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. On the cause and nature of C9-related heterogeneity of terminal complement complexes generated on target erythrocytes through the action of whole serum. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1453–1463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. Terminal membrane C5b-9 complex of human complement: transition from an amphiphilic to a hydrophilic state through binding of the S protein from serum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):755–759. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. L., Housley G. A., Jr, Dykman T. R., MacDermott R. P., Atkinson J. P. Identification of an additional class of C3-binding membrane proteins of human peripheral blood leukocytes and cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):859–863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R., Müller-Eberhard H. J. The reaction mechanism of human C5 in immune hemolysis. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):775–793. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper N. R. The classical complement pathway: activation and regulation of the first complement component. Adv Immunol. 1985;37:151–216. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60340-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Properdin: binding to C3b and stabilization of the C3b-dependent C3 convertase. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):856–863. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T. Regulation of the amplification C3 convertase of human complement by an inhibitory protein isolated from human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5867–5871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E., Kazatchkine M. D., Mecarelli-Halbwachs L. Protection of the classical and alternative complement pathway C3 convertases, stabilized by nephritic factors, from decay by the human C3b receptor. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Dec;14(12):1111–1114. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer E., Kazatchkine M. D. Surface-dependent modulation by H of C5 cleavage by the cell-bound alternative pathway C5 convertase of human complement. J Immunol. 1983 Jun;130(6):2821–2824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giavedoni E. B., Chow Y. M., Dalmasso A. P. The functional size of the primary complement lesion in resealed erythrocyte membrane ghosts. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Fujita T., Nussenzweig V. Modulation of the classical pathway C3 convertase by plasma proteins C4 binding protein and C3b inactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6596–6600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunsicker L. G., Ruddy S., Austen K. F. Alternate complement pathway: factors involved in cobra venom factor (CoVF) activation of the third component of complement (C3). J Immunol. 1973 Jan;110(1):128–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänsch G. M., Seitz M., Martinotti G., Betz M., Rauterberg E. W., Gemsa D. Macrophages release arachidonic acid, prostaglandin E2, and thromboxane in response to late complement components. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):2145–2150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa D. K., Osifchin N. E., Paznekas W. A., Shin M. L., Mayer M. M. Consequences of cell membrane attack by complement: release of arachidonate and formation of inflammatory derivatives. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6647–6651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenne D., Stanley K. K. Molecular cloning of S-protein, a link between complement, coagulation and cell-substrate adhesion. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3153–3157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazatchkine M. D., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Human alternative complement pathway: membrane-associated sialic acid regulates the competition between B and beta1 H for cell-bound C3b. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazatchkine M. D., Nydegger U. E. The human alternative complement pathway: biology and immunopathology of activation and regulation. Prog Allergy. 1982;30:193–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroll H. P., Bhakdi S., Taylor P. W. Membrane changes induced by exposure of Escherichia coli to human serum. Infect Immun. 1983 Dec;42(3):1055–1066. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.3.1055-1066.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachmann P. J., Thompson R. A. Reactive lysis: the complement-mediated lysis of unsensitized cells. II. The characterization of activated reactor as C56 and the participation of C8 and C9. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):643–657. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Eberhard H. J. The membrane attack complex. Springer Semin Immunopathol. 1984;7(2-3):93–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01893017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. A., Jr, Jensen J., Gigli I., Tamura N. Methods for the separation, purification and measurement of nine components of hemolytic complement in guinea-pig serum. Immunochemistry. 1966 Mar;3(2):111–135. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(66)90292-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., Burge J., Fearon D. T., Weller P. F., Austen K. F. Isolation of a human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein with decay-accelerating activity for C3 convertases of the complement system. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):184–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger W., Suttorp N., Hellwig A., Bhakdi S. Noncytolytic terminal complement complexes may serve as calcium gates to elicit leukotriene B4 generation in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1286–1293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strunk R. C., Giclas P. C. Modulation of the activity of the classical complement pathway C3 convertase by surface-bound C3 or C5. J Immunol. 1980 Feb;124(2):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack B. D., Prahl J. W. Third component of human complement: purification from plasma and physicochemical characterization. Biochemistry. 1976 Oct 5;15(20):4513–4521. doi: 10.1021/bi00665a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]