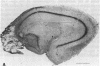
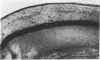
Abstract
The role of the Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent, diacylglycerol-activated enzyme protein kinase C (PKC) in rabbit eyelid conditioning was examined. PKC was partially purified from the CA1 region of hippocampal slices from naive, pseudoconditioned, and conditioned rabbits 24 hr after the rabbits were well conditioned. Crude membrane and cytosol fractions were prepared. In conditioned rabbits, significantly more PKC activity (63.3%) was associated with the membrane fraction (and significantly less with the cytosol fraction) compared to naive (42.0%) and pseudoconditioned (44.7%) animals. These differences in distribution of enzyme activity were paralleled by differences in stimulation of enzyme activity by Ca2+, phospholipid, and diacylglycerol. There were no between-group differences in basal protein kinase activity. These results suggest that there is a long-term translocation of PKC from cytosol to membrane as a result of conditioning. Autoradiographic binding of radioactive phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate to PKC demonstrated that almost all specific binding was in the stratum radiatum, a region containing the proximal apical dendrites of CA1 pyramidal neurons. Therefore, this may be the site of the conditioning-specific PKC translocation, a locus well-suited to underlie the biophysical effects of conditioning.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akers R. F., Lovinger D. M., Colley P. A., Linden D. J., Routtenberg A. Translocation of protein kinase C activity may mediate hippocampal long-term potentiation. Science. 1986 Feb 7;231(4738):587–589. doi: 10.1126/science.3003904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L. Calcium-mediated reduction of ionic currents: a biophysical memory trace. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1037–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.6093258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Kubota M., Neary J. T., Naito S., Coulter D., Rasmussen H. C-kinase activation prolongs Ca2+-dependent inactivation of K+ currents. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1245–1253. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Lederhendler I., Shoukimas J. J. Primary changes of membrane currents during retention of associative learning. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):693–695. doi: 10.1126/science.7058334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Sakakibara M., Forman R., Harrigan J., Lederhendler I., Farley J. Reduction of two voltage-dependent K+ currents mediates retention of a learned association. Behav Neural Biol. 1985 Sep;44(2):278–300. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(85)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H., Alger B. E. Protein kinase C regulates ionic conductance in hippocampal pyramidal neurons: electrophysiological effects of phorbol esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2538–2542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger T. W., Orr W. B. Hippocampectomy selectively disrupts discrimination reversal conditioning of the rabbit nictitating membrane response. Behav Brain Res. 1983 Apr;8(1):49–68. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(83)90171-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger T. W., Rinaldi P. C., Weisz D. J., Thompson R. F. Single-unit analysis of different hippocampal cell types during classical conditioning of rabbit nictitating membrane response. J Neurophysiol. 1983 Nov;50(5):1197–1219. doi: 10.1152/jn.1983.50.5.1197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRiemer S. A., Strong J. A., Albert K. A., Greengard P., Kaczmarek L. K. Enhancement of calcium current in Aplysia neurones by phorbol ester and protein kinase C. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):313–316. doi: 10.1038/313313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disterhoft J. F., Coulter D. A., Alkon D. L. Conditioning-specific membrane changes of rabbit hippocampal neurons measured in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2733–2737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grab D. J., Carlin R. K., Siekevitz P. Function of a calmodulin in postsynaptic densities. II. Presence of a calmodulin-activatable protein kinase activity. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):440–448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafsson B., Wigström H., Abraham W. C., Huang Y. Y. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus using depolarizing current pulses as the conditioning stimulus to single volley synaptic potentials. J Neurosci. 1987 Mar;7(3):774–780. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-03-00774.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Go M., Koumoto J., Nishizuka Y. Rapid purification of protein kinase C by high performance liquid chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):636–643. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima I., Kojima K., Rasmussen H. Role of calcium fluxes in the sustained phase of angiotensin II-mediated aldosterone secretion from adrenal glomerulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9177–9184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LoTurco J. L., Coulter D. A., Alkon D. L. Enhancement of synaptic potentials in rabbit CA1 pyramidal neurons following classical conditioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1672–1676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Madison D. V., Andrade R., Nicoll R. A. Phorbol esters mimic some cholinergic actions in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 Feb;6(2):475–480. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-02-00475.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Madison D. V., Nicoll R. A. Potentiation of synaptic transmission in the hippocampus by phorbol esters. Nature. 1986 May 8;321(6066):175–177. doi: 10.1038/321175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloni E., Pontremoli S., Michetti M., Sacco O., Sparatore B., Salamino F., Horecker B. L. Binding of protein kinase C to neutrophil membranes in the presence of Ca2+ and its activation by a Ca2+-requiring proteinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6435–6439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neary J. T., Crow T., Alkon D. L. Change in a specific phosphoprotein band following associative learning in Hermissenda. Nature. 1981 Oct 22;293(5834):658–660. doi: 10.1038/293658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Port R. L., Patterson M. M. Fimbrial lesions and sensory preconditioning. Behav Neurosci. 1984 Aug;98(4):584–589. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.98.4.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOVILLE W. B., MILNER B. Loss of recent memory after bilateral hippocampal lesions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1957 Feb;20(1):11–21. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.20.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakakibara M., Alkon D. L., DeLorenzo R., Goldenring J. R., Neary J. T., Heldman E. Modulation of calcium-mediated inactivation of ionic currents by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Biophys J. 1986 Aug;50(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83465-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaltz L. W., Theios J. Acquisition and extinction of a classically conditioned response in hippocampectomized rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus). J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1972 May;79(2):328–333. doi: 10.1037/h0032531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon P. R., Moore J. W. Latent inhibition and stimulus generalization of the classically conditioned nictitating membrane response in rabbits (Oryctolagus cuniculus) following dorsal hippocampal ablation. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1975 Dec;89(10):1192–1203. doi: 10.1037/h0077183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon P. R. Role of the hippocampus in blocking and conditioned inhibition of the rabbit's nictitating membrane response. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1977 Apr;91(2):407–417. doi: 10.1037/h0077330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solomon P. R., Solomon S. D., Schaaf E. V., Perry H. E. Altered activity in the hippocampus is more detrimental to classical conditioning than removing the structure. Science. 1983 Apr 15;220(4594):329–331. doi: 10.1126/science.6836277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka Y., Miyake R., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Rapid assay of binding of tumor-promoting phorbol esters to protein kinase C1. J Biochem. 1986 Jan;99(1):257–261. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teyler T. J. Brain slice preparation: hippocampus. Brain Res Bull. 1980 Jul-Aug;5(4):391–403. doi: 10.1016/s0361-9230(80)80009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. Interaction of protein kinase C with membranes is regulated by Ca2+, phorbol esters, and ATP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15718–15722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf M., LeVine H., 3rd, May W. S., Jr, Cuatrecasas P., Sahyoun N. A model for intracellular translocation of protein kinase C involving synergism between Ca2+ and phorbol esters. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):546–549. doi: 10.1038/317546a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Heterogeneous localization of protein kinase C in rat brain: autoradiographic analysis of phorbol ester receptor binding. J Neurosci. 1986 Jan;6(1):199–207. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-01-00199.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]