Abstract
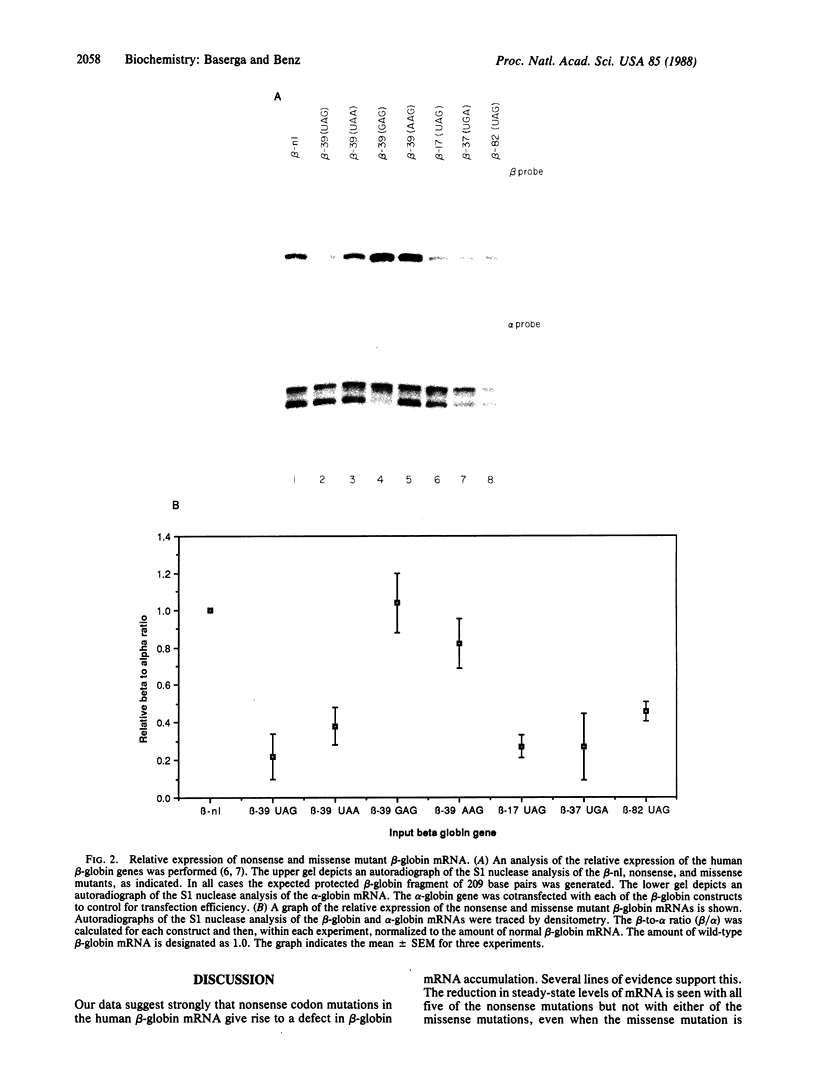
A number of premature translation termination mutations (nonsense mutations) have been described in the human alpha- and beta-globin genes. Studies on mRNA isolated from patients with beta zero-thalassemia have shown that for both the beta-17 and the beta-39 mutations less than normal levels of beta-globin mRNA accumulate in peripheral blood cells. (The codon at which the mutation occurs designates the name of the mutation; there are 146 codons in human beta-globin mRNA.) In vitro studies using the cloned beta-39 gene have reproduced this effect in a heterologous transfection system and have suggested that the defect resides in intranuclear metabolism. We have asked if this phenomenon of decreased mRNA accumulation is a general property of nonsense mutations and if the effect depends on the location or the type of mutation. Toward this end, we have studied the effect of five nonsense mutations and two missense mutations on the expression of human beta-globin mRNA in a heterologous transfection system. In all cases studied, the presence of a translation termination codon correlates with a decrease in the steady-state level of mRNA. The data suggest that the metabolism of a mammalian mRNA is affected by the presence of a mutation that affects translation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M. Control of transcription termination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:967–996. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.004535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz E. J., Forget B. G., Hillman D. G., Cohen-Solal M., Pritchard J., Cavallesco C., Prensky W., Housman D. Variability in the amount of beta-globin mRNA in beta0 thalassemia. Cell. 1978 Jun;14(2):299–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm C. D., Dowling C. E., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J., Kazazian H. H., Jr Use of oligonucleotide hybridization in the characterization of a beta zero-thalassemia gene (beta 37 TGG----TGA) in a Saudi Arabian family. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):1185–1188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimhall B., Jones R. T., Schneider R. G., Hosty T. S., Tomlin G., Atkins R. Two new hemoglobins. Hemoglobin Alabama (beta39(C5)Gln leads to Lys) and hemoglobin Montgomery (alpha 48(CD 6) Leu leads to Arg). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 30;379(1):28–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. beta 0 thalassemia, a nonsense mutation in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2886–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J., Fiori M., Mach B. A new nonsense mutation as the molecular basis for beta thalassaemia. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 25;154(3):537–540. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Pandey N. B., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. Translation is required for regulation of histone mRNA degradation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphries R. K., Ley T. J., Anagnou N. P., Baur A. W., Nienhuis A. W. Beta O-39 thalassemia gene: a premature termination codon causes beta-mRNA deficiency without affecting cytoplasmic beta-mRNA stability. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):23–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall A. G., ten Pas A., Wilson J. B., Cope N., Bolch K., Huisman T. H. Hb Vaasa or alpha2beta2 (39(C5)Gln replaced by Glu), a mildly unstable variant found in a Finnish family. Hemoglobin. 1977;1(3):292–295. doi: 10.3109/03630267709003413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J. Internalization-defective LDL receptors produced by genes with nonsense and frameshift mutations that truncate the cytoplasmic domain. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):735–743. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Schneider W. J., Brown M. S., Davis C. G., Elhammer A., Russell D. W., Goldstein J. L. The Lebanese allele at the low density lipoprotein receptor locus. Nonsense mutation produces truncated receptor that is retained in endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):401–410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebhaber S. A., Coleman M. B., Adams J. G., 3rd, Cash F. E., Steinberg M. H. Molecular basis for nondeletion alpha-thalassemia in American blacks. Alpha 2(116GAG----UAG). J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):154–159. doi: 10.1172/JCI113041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metherall J. E., Collins F. S., Pan J., Weissman S. M., Forget B. G. Beta zero thalassemia caused by a base substitution that creates an alternative splice acceptor site in an intron. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2551–2557. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moschonas N., de Boer E., Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., Wright S., Shewmaker C. K., Flavell R. A. Structure and expression of a cloned beta o thalassaemic globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4391–4401. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Goff S. C. Nonsense and frameshift mutations in beta 0-thalassemia detected in cloned beta-globin genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9782–9784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pergolizzi R., Spritz R. A., Spence S., Goossens M., Kan Y. W., Bank A. Two cloned beta thalassemia genes are associated with amber mutations at codon 39. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):7065–7072. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.7065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita K., Forget B. G., Scarpa A., Benz E. J., Jr Intranuclear defect in beta-globin mRNA accumulation due to a premature translation termination codon. Blood. 1984 Jul;64(1):13–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trecartin R. F., Liebhaber S. A., Chang J. C., Lee K. Y., Kan Y. W., Furbetta M., Angius A., Cao A. beta zero thalassemia in Sardinia is caused by a nonsense mutation. J Clin Invest. 1981 Oct;68(4):1012–1017. doi: 10.1172/JCI110323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winslow R. M., Swenberg M. L., Gross E., Chervenick P. A., Buchman R. R., Anderson W. F. Hemoglobin McKees Rocks (alpha2beta2145Tyr leads to Term). A human "nonsense" mutation leading to a shortened beta-chain. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):772–781. doi: 10.1172/JCI108336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]