Abstract
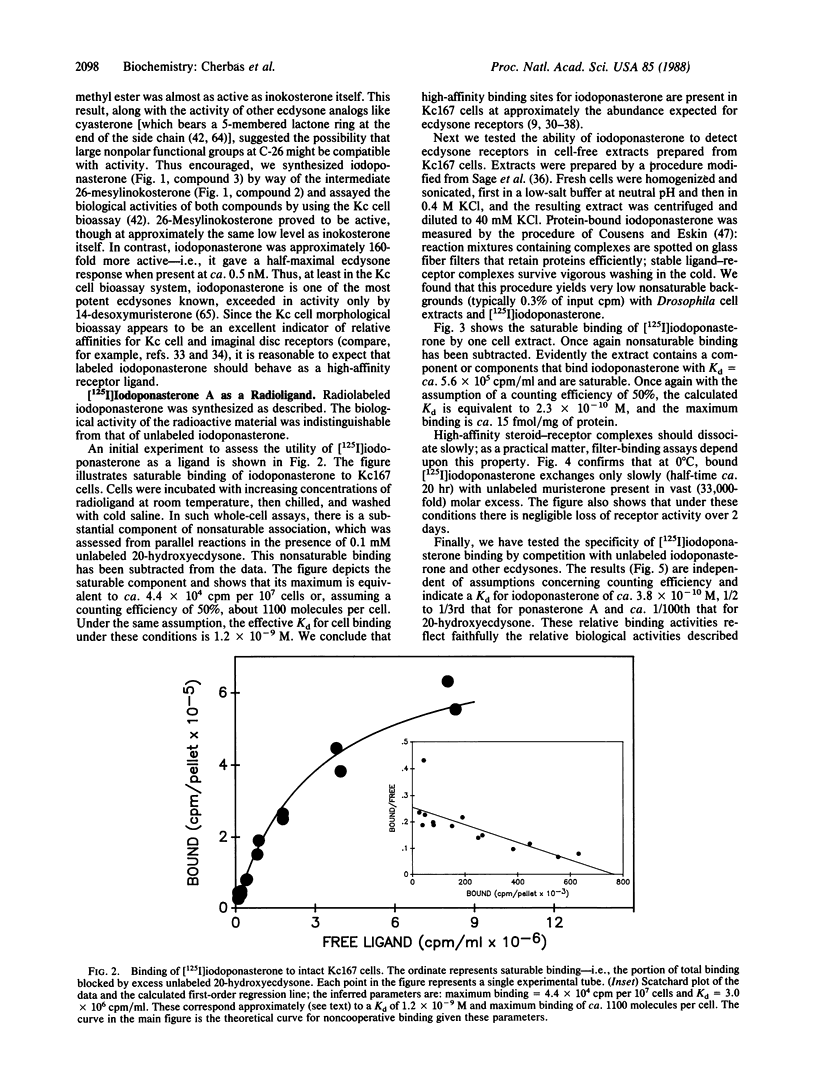
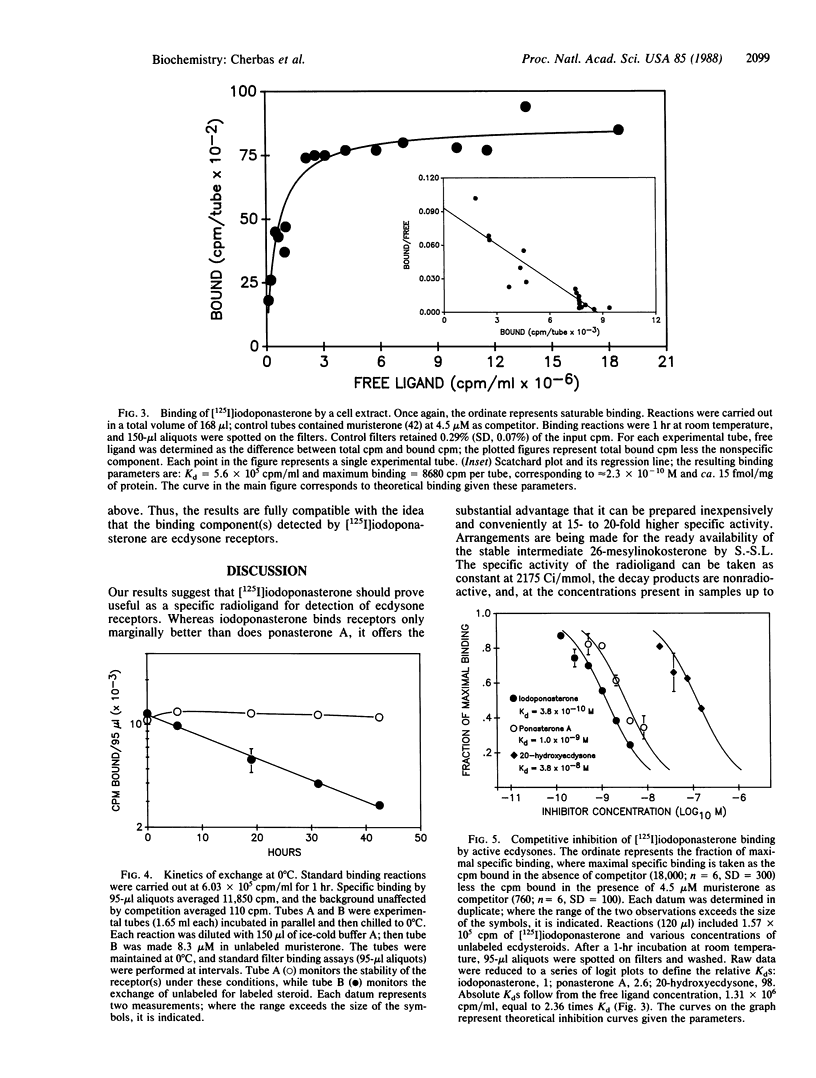
The effects of ecdysone, the steroid molting hormone of arthropods, are of considerable interest both to insect physiologists and to those studying steroid-regulated gene expression. Yet progress in understanding ecdysone receptors has been inhibited by the lack of a suitable highly radioactive hormone analog with high affinity for the receptor. Here we report that the synthetic ecdysteroid 26-iodoponasterone A is one of the most active ecdysones known, inducing half-maximal morphological transformation in Drosophila Kc167 cells when present at 0.5 nM. 26-[125I]Iodoponasterone A can be prepared at a specific activity of 2175 Ci/mmol (1 Ci = 37 GBq) by reaction of the precursor 26-mesylinokosterone with carrier-free Na125I. The radiolabeled material binds to Kc167 cell ecdysone receptors specifically and with affinity (Kd ca. 3.8 X 10(-10) M). Thus, 26-[125I]iodoponasterone A appears to be a superior radioligand for ecdysone receptors on grounds both of affinity and of specific activity. Its ready availability should greatly facilitate studies of these receptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M. Induction of puffs in polytene chromosomes of in vitro cultured salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster by ecdysone and echysone analogues. Nat New Biol. 1971 Apr 14;230(15):222–224. doi: 10.1038/newbio230222a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckers C., Maróy P., Dennis R., O'Connor J. D., Emmerich H. The uptake and release of ponasterone A by the Kc cell line of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1980 Jan;17(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(80)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. J. An assessment of the ecdysteroid receptor of Drosophila. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourouis M., Jarry B. Vectors containing a prokaryotic dihydrofolate reductase gene transform Drosophila cells to methotrexate-resistance. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1099–1104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01552.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherbas L., Schulz R. A., Koehler M. M., Savakis C., Cherbas P. Structure of the Eip28/29 gene, an ecdysone-inducible gene from Drosophila. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jun 20;189(4):617–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90492-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark W. C., Doctor J., Fristrom J. W., Hodgetts R. B. Differential responses of the dopa decarboxylase gene to 20-OH-ecdysone in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1986 Mar;114(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90390-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couderc J. L., Sobrier M. L., Giraud G., Becker J. L., Dastugue B. Actin gene expression is modulated by ecdysterone in a Drosophila cell line. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 5;164(3):419–430. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courgeon A. M. Action of insect hormones at the cellular level. Morphological changes of a diploid cell line of Drosophila melanogaster, treated with ecdysone and several analogues in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Oct;74(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90384-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousens L., Eskin B. Filter assay method for the estrogen receptor protein: detection of both filled and unfilled estrogen binding sites. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 15;121(1):39–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosby M. A., Meyerowitz E. M. Drosophila glue gene Sgs-3: sequences required for puffing and transcriptional regulation. Dev Biol. 1986 Dec;118(2):593–607. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90029-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J., Toft D., Shyamala G., Smith D., Notides A. Hormone receptors: studies on the interaction of estrogen with the uterus. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1968;24:45–80. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9827-9.50008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandics P., Miller A., Schmidt T. J., Mittman D., Litwack G. Purification of the unactivated glucocorticoid receptor and its subsequent in vitro activation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3173–3180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochberg R. B. Iodine-125--labeled estradiol: a gamma-emitting analog of estradiol that binds to the estrogen receptor. Science. 1979 Sep 14;205(4411):1138–1140. doi: 10.1126/science.472733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Gerring S. L., Corces V. G. The ovarian, ecdysterone, and heat-shock-responsive promoters of the Drosophila melanogaster hsp27 gene react very differently to perturbations of DNA sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):973–981. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Suzuki T., Kawashima T., Stumpf W. E., Jungblut P. W., DeSombre E. R. A two-step mechanism for the interaction of estradiol with rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):632–638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenellenbogen J. A., Johnson H. J., Jr, Carlson K. E. Studies on the uterine, cytoplasmic estrogen binding protein. Thermal stability and ligand dissociation rate. An assay of empty and filled sites by exchange. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 9;12(21):4092–4099. doi: 10.1021/bi00745a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larocca D. Ecdysterone and heat shock induction of transfecting and endogenous heat shock genes in cultured Drosophila cells. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):563–567. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londershausen M., Spindler K. D. Characterization of cytoplasmic ecdysteroid receptors in the hypodermis of the crayfish, Orconectes limosus. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Dec;24(3):253–265. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroy P., Dennis R., Beckers C., Sage B. A., O'Connor J. D. Demonstration of an ecdysteroid receptor in a cultured cell line of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6035–6038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maschat F., Roux J., Benes H., Pictet R., Jami J., Lepesant J. A. Hormonal and developmental specificities of transcription lie within a 1.5 kb region 5' to the ecdysone inducible Drosophila P1 gene. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):583–588. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestril R., Schiller P., Amin J., Klapper H., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Heat shock and ecdysterone activation of the Drosophila melanogaster hsp23 gene; a sequence element implied in developmental regulation. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1667–1673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi K. The ecdysones. Pure Appl Chem. 1971;25(1):167–195. doi: 10.1351/pac197125010167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natzle J. E., Hammonds A. S., Fristrom J. W. Isolation of genes active during hormone-induced morphogenesis in Drosophila imaginal discs. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5575–5583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S., Nishimoto N. [Isolation of the moulting hormones of insects from Achyranthis radix]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1967 Mar;87(3):325–327. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.87.3_325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtaki T., Milkman R. D., Williams C. M. ECDYSONE AND ECDYSONE ANALOGUES: THEIR ASSAY ON THE FLESHFLY Sarcophaga peregrina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Sep;58(3):981–984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.3.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osterbur D. L., Yund M. A. Ecdysteroid binding activity in embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biochem. 1982;20(3):277–282. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240200307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Pelham H. R. Activation of the Drosophila hsp27 promoter by heat shock and by ecdysone involves independent and remote regulatory sequences. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1653–1658. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb J. A. Maintenance of imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster in chemically defined media. J Cell Biol. 1969 Jun;41(3):876–885. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.3.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins W. E., Kaplanis J. N., Thompson M. J., Shortino T. J., Joyner S. C. Ecdysones and synthetic analogs: Molting hormone activity and inhibitive effects on insect growth, metamorphosis and reproduction. Steroids. 1970 Jul;16(1):105–125. doi: 10.1016/s0039-128x(70)80100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J., Pipa R. Metamorphic shortening of interganglionic connectives of Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera) in vitro: stimulation by ecdysone analogues. J Insect Physiol. 1973 Mar;19(3):673–679. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(73)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sage B. A., Tanis M. A., O'Connor J. D. Characterization of ecdysteroid receptors in cytosol and naive nuclear preparations of Drosophila Kc cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6373–6379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanborn B. M., Rao B. R., Korenman S. G. Interaction of 17 -estradiol and its specific uterine receptor. Evidence for complex kinetic and equilibrium behavior. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4955–4962. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sater A. K., Woods D. F., Poodry C. A. Cell surface proteins of Drosophila. II. A comparison of embryonic and ecdysone-induced proteins. Dev Biol. 1984 Jul;104(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaltmann K., Pongs O. Identification and characterization of the ecdysterone receptor in Drosophila melanogaster by photoaffinity labeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):6–10. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirk P. D., Minoo P., Postlethwait J. H. 20-Hydroxyecdysone stimulates the accumulation of translatable yolk polypeptide gene transcript in adult male Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):186–190. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler K. D., Hamann A., Spindler-Barth M., Ihne A., Beckers C., Emmerich H. Derivatives of the insect moulting hormone for affinity chromatography, and their biological activities. Steroids. 1976 Apr;27(4):553–565. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(76)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swiderski R. E., O'Connor J. D. Modulation of novel-length DOPA decarboxylase transcripts by 20-OH-ecdysone in a Drosophila melanogaster Kc cell subline. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4433–4439. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto T., Ogawa S., Nishimoto N., Mue K. [Studies on the contituents of achyranthis radix. V. Insect hormone activity of ecdysterone and inokosterone on the flies]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1967 Dec;87(12):1481–1483. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.87.12_1481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemoto T., Ogawa S., Nishimoto N. [Studies on the constituents of Achyranthis radix. 3. Structure of inokosterone]. Yakugaku Zasshi. 1967 Dec;87(12):1474–1477. doi: 10.1248/yakushi1947.87.12_1474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. R., Lengyel J. A. Ecdysteroid-regulated heat-shock gene expression during Drosophila melanogaster development. Dev Biol. 1986 Jun;115(2):434–438. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90263-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker V. K., Ashburner M. The control of ecdysterone-regulated puffs in Drosophila salivary glands. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90309-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrange O., Okret S., Radojćić M., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A. Characterization of the purified activated glucocorticoid receptor from rat liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4534–4541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yund M. A., King D. S., Fristrom J. W. Ecdysteroid receptors in imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6039–6043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yund M. A. Specific binding of 20-hydroxyecdysone to nuclei of imaginal discs of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1979 Apr;14(1):19–35. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(79)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



