Abstract
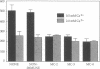
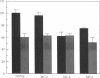
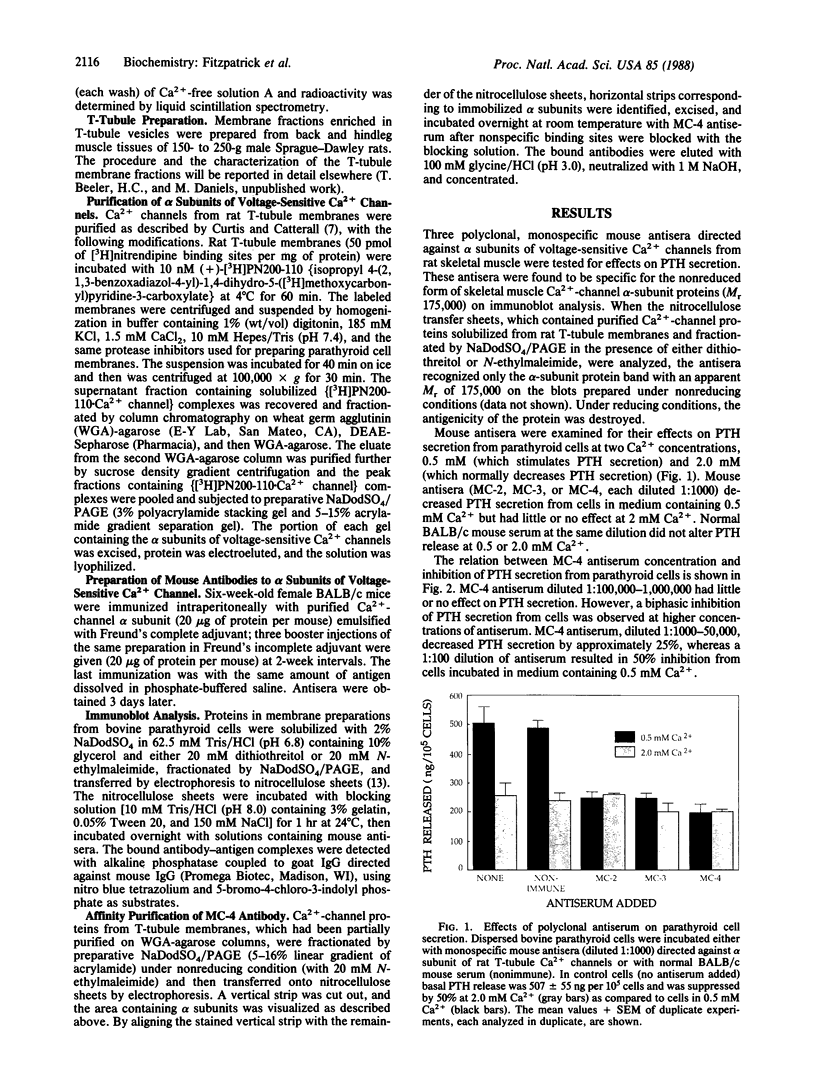
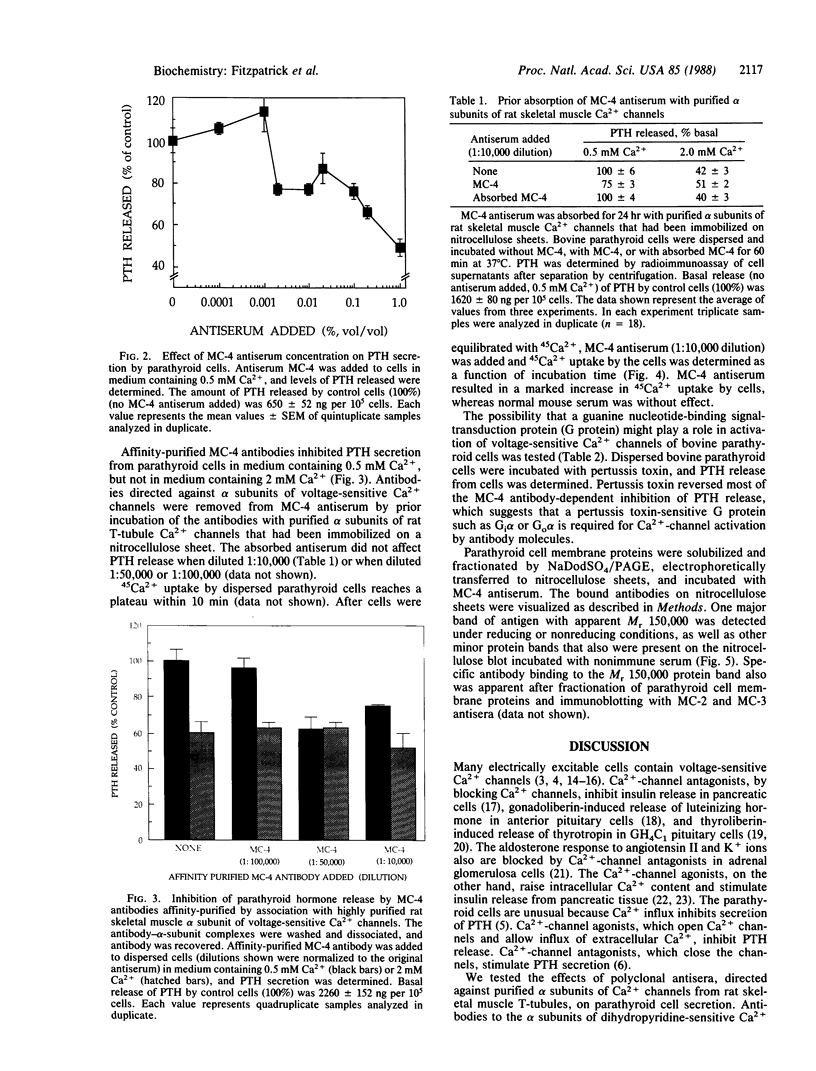
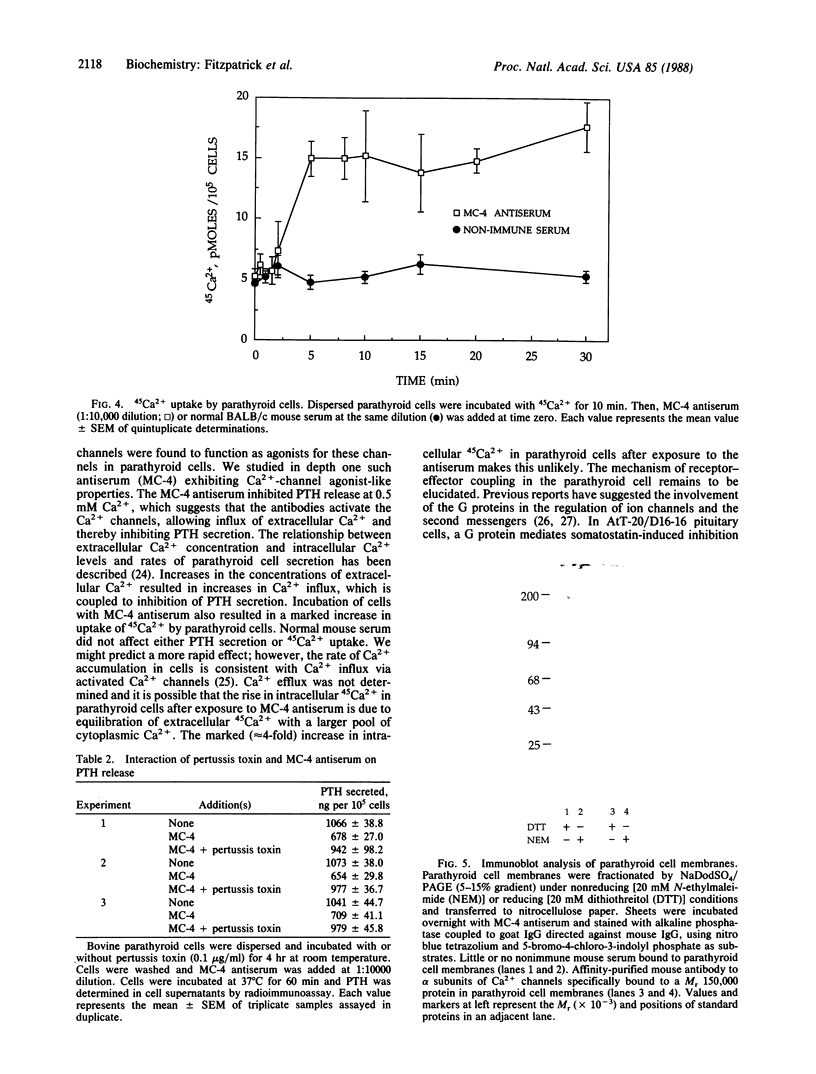
We have shown previously that Ca2+-channel agonists, which open Ca2+ channels, inhibit parathyroid hormone (PTH) secretion from dispersed bovine parathyroid cells, whereas Ca2+-channel antagonists, which close Ca2+ channels, stimulate PTH release. We now have tested the effects of mouse antibodies specific for purified alpha subunits of rat skeletal muscle Ca2+-channel proteins on PTH secretion by bovine parathyroid cells in vitro. Mouse antisera (MC-2, MC-3, MC-4) blocked the secretion of PTH from parathyroid cells incubated with 0.5 mM Ca2+ ions. Affinity-purified MC-4 antibodies inhibited PTH release in a concentration-dependent manner. Incubation of parathyroid cells with pertussis toxin markedly reduced MC-4-dependent inhibition of PTH secretion. Parathyroid cell membrane proteins were fractionated by NaDodSO4/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under either reducing or nonreducing conditions and immunoblotted with MC-4 antiserum. Antibodies bound to one major band of protein with Mr approximately equal to 150,000. These results suggest that the antibodies bind to Ca2+-channel alpha subunits and act as agonists that open the channels and inhibit PTH release.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguilera G., Catt K. J. Participation of voltage-dependent calcium channels in the regulation of adrenal glomerulosa function by angiotensin II and potassium. Endocrinology. 1986 Jan;118(1):112–118. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-1-112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Eckert R. Voltage-activated calcium channels that must be phosphorylated to respond to membrane depolarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2518–2522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. M. PTH secretion in vivo and in vitro. Regulation by calcium and other secretagogues. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1982 Sep-Oct;8(3-4):130–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J. P., McCoy E. E., Graeter J., Tasaka K., Catt K. J. Participation of voltage-dependent calcium channels in the action of gonadotropin-releasing hormone. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9105–9108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Phosphorylation of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Purification of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2113–2118. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Reconstitution of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel purified from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3077–3083. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean W. L., Adunyah S. E., Cohn D. V. Calcium uptake and inositol trisphosphate-induced calcium release from parathyroid gland membranes. Bone Miner. 1986 Feb;1(1):59–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyeart J. J., Aizawa T., Hinkle P. M. Dihydropyridine Ca2+ antagonists: potent inhibitors of secretion from normal and transformed pituitary cells. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):C510–C519. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.5.C510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick L. A., Brandi M. L., Aurbach G. D. Calcium-controlled secretion is effected through a guanine nucleotide regulatory protein in parathyroid cells. Endocrinology. 1986 Dec;119(6):2700–2703. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-6-2700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick L. A., Brandi M. L., Aurbach G. D. Control of PTH secretion is mediated through calcium channels and is blocked by pertussis toxin treatment of parathyroid cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 31;138(2):960–965. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80589-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Ferry D. R., Goll A., Striessnig J., Zernig G. Calcium channels and calcium channel drugs: recent biochemical and biophysical findings. Arzneimittelforschung. 1985;35(12A):1917–1935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima K., Kojima I., Rasmussen H. Dihydropyridine calcium agonist and antagonist effects on aldosterone secretion. Am J Physiol. 1984 Nov;247(5 Pt 1):E645–E650. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1984.247.5.E645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung A. T., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P. Structural characterization of the 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel from rabbit skeletal muscle. Evidence for two distinct high molecular weight subunits. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):7943–7946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. L., Weight F. F., Luini A. A guanine nucleotide-binding protein mediates the inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current by somatostatin in a pituitary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9035–9039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logothetis D. E., Kurachi Y., Galper J., Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. The beta gamma subunits of GTP-binding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):321–326. doi: 10.1038/325321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse-Lagae F., Mathias P. C., Malaisse W. J. Gating and blocking of calcium channels by dihydropyridines in the pancreatic B-cell. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Sep 28;123(3):1062–1068. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80241-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Mathias P. C. Stimulation of insulin release by an organic calcium agonist. Diabetologia. 1985 Mar;28(3):153–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00273863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malouf N. N., Coronado R., McMahon D., Meissner G., Gillespie G. Y. Monoclonal antibody specific for the transverse tubular membrane of skeletal muscle activates the dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca2+ channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):5019–5023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.5019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleskey E. W., Fox A. P., Feldman D., Tsien R. W. Different types of calcium channels. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:177–190. doi: 10.1242/jeb.124.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rane S. G., Dunlap K. Kinase C activator 1,2-oleoylacetylglycerol attenuates voltage-dependent calcium current in sensory neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):184–188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Properties of two inward membrane currents in the heart. Annu Rev Physiol. 1979;41:413–424. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.41.030179.002213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp A. H., Imagawa T., Leung A. T., Campbell K. P. Identification and characterization of the dihydropyridine-binding subunit of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12309–12315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp M. E., Marx S. J. Radioimmunoassay for the middle region of human parathyroid hormone: comparison of two radioiodinated synthetic peptides. Clin Chim Acta. 1985 Jan 15;145(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(85)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoback D. M., Thatcher J., Leombruno R., Brown E. M. Relationship between parathyroid hormone secretion and cytosolic calcium concentration in dispersed bovine parathyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3113–3117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. Voltage-dependent calcium channels of excitable membranes. Br Med Bull. 1986 Oct;42(4):359–367. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Striessnig J., Knaus H. G., Grabner M., Moosburger K., Seitz W., Lietz H., Glossmann H. Photoaffinity labelling of the phenylalkylamine receptor of the skeletal muscle transverse-tubule calcium channel. FEBS Lett. 1987 Feb 23;212(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81354-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Seagar M. J., Jones J. F., Reber B. F., Catterall W. A. Subunit structure of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels from skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5478–5482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. N., Tashjian A. H., Jr Voltage-dependent calcium channels in pituitary cells in culture. II. Participation in thyrotropin-releasing hormone action on prolactin release. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):427–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Direct activation of mammalian atrial muscarinic potassium channels by GTP regulatory protein Gk. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):207–211. doi: 10.1126/science.2432660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]