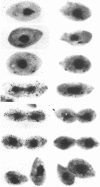
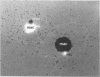
Abstract
Transcriptionally active macronuclei and transcriptionally inert micronuclei of the ciliated protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila contain similar DNA sequences but have very different histones associated with the linker regions of chromatin. In situ hybridization showed that a gene coding for micronuclear linker histone is expressed only in association with micronuclear DNA replication, whereas the gene for macronuclear H1 histone is expressed during macronuclear (but not during micronuclear) S phase. These results indicate that cell-cycle regulation plays an important role in directing proteins to the appropriate nucleus in Tetrahymena and that the replication-expression model [Gottesfeld, J. & Bloomer, L. S. (1982) Cell 28, 781-791; Wormington, W. M., Schlissel, M. & Brown, D. D. (1983) Cold Spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 47, 879-884] for establishing appropriate transcriptionally active or repressed chromatin complexes during DNA replication is generally applicable.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allis C. D., Allen R. L., Wiggins J. C., Chicoine L. G., Richman R. Proteolytic processing of h1-like histones in chromatin: a physiologically and developmentally regulated event in Tetrahymena micronuclei. J Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;99(5):1669–1677. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.5.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allis C. D., Colavito-Shepanski M., Gorovsky M. A. Scheduled and unscheduled DNA synthesis during development in conjugating Tetrahymena. Dev Biol. 1987 Dec;124(2):469–480. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90500-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allis C. D., Glover C. V., Gorovsky M. A. Micronuclei of Tetrahymena contain two types of histone H3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4857–4861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannon G. A., Calzone F. J., Bowen J. K., Allis C. D., Gorovsky M. A. Multiple, independently regulated, polyadenylated messages for histone H3 and H4 in Tetrahymena. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):3903–3917. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D. The role of stable complexes that repress and activate eucaryotic genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Robertis E. M. Nucleocytoplasmic segregation of proteins and RNAs. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1021–1025. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90285-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert D. M. Temporal order of replication of Xenopus laevis 5S ribosomal RNA genes in somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2924–2928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. A., Holmquist G. P., Gray M. C., Caston L. A., Nag A. Replication timing of genes and middle repetitive sequences. Science. 1984 May 18;224(4650):686–692. doi: 10.1126/science.6719109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A. Genome organization and reorganization in Tetrahymena. Annu Rev Genet. 1980;14:203–239. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.14.120180.001223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Yao M. C., Keevert J. B., Pleger G. L. Isolation of micro- and macronuclei of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;9(0):311–327. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60080-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesfeld J., Bloomer L. S. Assembly of transcriptionally active 5S RNA gene chromatin in vitro. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):781–791. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90057-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinta D. R., Korn L. J. Differential order of replication of Xenopus laevis 5S RNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2536–2542. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinta D. R., Tso J. Y., Narayanswami S., Hamkalo B. A., Korn L. J. Early replication and expression of oocyte-type 5S RNA genes in a Xenopus somatic cell line carrying a translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5150–5154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz S., Gorovsky M. A. An unusual genetic code in nuclear genes of Tetrahymena. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2452–2455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson V., Chalkley R. Histone synthesis and deposition in the G1 and S phases of hepatoma tissue culture cells. Biochemistry. 1985 Nov 19;24(24):6921–6930. doi: 10.1021/bi00345a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L. Protooncogene expression during the cell cycle. Lab Invest. 1986 Apr;54(4):365–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Razvi F., Worcel A. The role of DNA-mediated transfer of TFIIIA in the concerted gyration and differential activation of the Xenopus 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):209–218. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90385-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A repetitive DNA sequence that confers cell-cycle START (CDC28)-dependent transcription of the HO gene in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old R. W., Woodland H. R. Histone genes: not so simple after all. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):624–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90256-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Brown D. D. The transcriptional regulation of Xenopus 5s RNA genes in chromatin: the roles of active stable transcription complexes and histone H1. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schümperli D. Cell-cycle regulation of histone gene expression. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):471–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90277-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. H., Barker D. G., Nurse P., Johnston L. H. Periodic transcription as a means of regulating gene expression during the cell cycle: contrasting modes of expression of DNA ligase genes in budding and fission yeast. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1705–1709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04414.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Andrews M. T., Crawford E., Losa R., Brown D. D. Negative supercoiling is not required for 5S RNA transcription in vitro. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):301–303. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90279-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Brown D. D. DNA replication in vitro erases a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):217–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodard J., Kaneshiro E., Gorovsky M. A. Cytochemical studies on the problem of macronuclear subnuclei in tetrahymena. Genetics. 1972 Feb;70(2):251–260. doi: 10.1093/genetics/70.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M., Schlissel M., Brown D. D. Developmental regulation of Xenopus 5S RNA genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):879–884. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. H., Kuehl L., Rechsteiner M. Dynamic behavior of histone H1 microinjected into HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):465–474. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Allis C. D., Richman R., Cook R. G., Gorovsky M. A. An intervening sequence in an unusual histone H1 gene of Tetrahymena thermophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8674–8678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Gorovsky M. A. Comparison of the sequences of macro- and micronuclear DNA of Tetrahymena pyriformis. Chromosoma. 1974;48(1):1–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00284863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]