Abstract
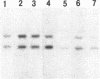
Nucleotide sequence analysis of a genomic clone from an Ashkenazic Jewish patient with type 1 Gaucher disease revealed a single-base mutation (adenosine to guanosine transition) in exon 9 of the glucocerebrosidase gene. This change results in the amino acid substitution of serine for asparagine. Transient expression studies following oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of the normal cDNA confirmed that the mutation results in loss of glucocerebrosidase activity. Allele-specific hybridization with oligonucleotide probes demonstrated that this mutation was found exclusively in the type 1 phenotype. None of the 6 type 2 patients, 11 type 3 patients, or 12 normal controls had this allele. In contrast, 15 of 24 type 1 patients had one allele with this mutation, and 3 others were homozygous for the mutation. Furthermore, some of the Ashkenazic Jewish type 1 patients had only one allele with this mutation, suggesting that even in this population there is allelic heterozygosity. These findings indicate that there are multiple allelic mutations responsible for type 1 Gaucher disease in both the Jewish and non-Jewish populations. Allelic-specific hybridization demonstrating this mutation in exon 9, used in conjunction with the Nci I restriction fragment length polymorphism described as a marker for neuronopathic Gaucher disease, provides a tool for diagnosis and genetic counseling that is approximately equal to 80% informative in all Gaucher patients studied.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRADY R. O., KANFER J. N., SHAPIRO D. METABOLISM OF GLUCOCEREBROSIDES. II. EVIDENCE OF AN ENZYMATIC DEFICIENCY IN GAUCHER'S DISEASE. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Jan 18;18:221–225. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90743-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler E., Kuhl W., Sorge J. Cross-reacting material in Gaucher disease fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6506–6510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Ginns E. I., Barranger J. A. Biosynthesis of the lysosomal enzyme glucocerebrosidase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14319–14324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginns E. I., Brady R. O., Pirruccello S., Moore C., Sorrell S., Furbish F. S., Murray G. J., Tager J., Barranger J. A. Mutations of glucocerebrosidase: discrimination of neurologic and non-neurologic phenotypes of Gaucher disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5607–5610. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginns E. I., Tegelaers F. P., Barneveld R., Galjaard H., Reuser A. J., Brady R. O., Tager J. M., Barranger J. A. Determination of Gaucher's disease phenotypes with monoclonal antibody. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Jul 15;131(3):283–287. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90097-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravel R. A., Leung A. Complementation analysis in Gaucher disease using single cell microassay techniques. Evidence for a single "Gaucher gene". Hum Genet. 1983;65(2):112–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00286645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson L. M., Murray G. J., Sorrell S. H., Strijland A., Aerts J. F., Ginns E. I., Barranger J. A., Tager J. M., Schram A. W. Biosynthesis and maturation of glucocerebrosidase in Gaucher fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 1;164(1):171–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nukiwa T., Brantly M., Garver R., Paul L., Courtney M., LeCocq J. P., Crystal R. G. Evaluation of "at risk" alpha 1-antitrypsin genotype SZ with synthetic oligonucleotide gene probes. J Clin Invest. 1986 Feb;77(2):528–537. doi: 10.1172/JCI112333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge J., Gelbart T., West C., Westwood B., Beutler E. Heterogeneity in type I Gaucher disease demonstrated by restriction mapping of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5442–5445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studencki A. B., Wallace R. B. Allele-specific hybridization using oligonucleotide probes of very high specific activity: discrimination of the human beta A- and beta S-globin genes. DNA. 1984;3(1):7–15. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji S., Choudary P. V., Martin B. M., Stubblefield B. K., Mayor J. A., Barranger J. A., Ginns E. I. A mutation in the human glucocerebrosidase gene in neuronopathic Gaucher's disease. N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 5;316(10):570–575. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703053161002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenger D. A., Roth S., Kudoh T., Grover W. D., Tucker S. H., Kaye E. M., Ullman M. D. Biochemical studies in a patient with subacute neuropathic Gaucher disease without visceral glucosylceramide storage. Pediatr Res. 1983 May;17(5):344–348. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198305000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:468–500. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]