Abstract
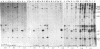
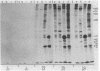
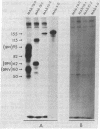
Lysates of radiolabeled explants from four human trigeminal ganglia were immunoprecipitated with antibodies to varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and to herpes simplex virus. Both herpes simplex virus- and VZV-specific proteins were detected in lysates of all four ganglia. Absence of reactivity in ganglion explants with monoclonal antibodies suggested that herpes simplex virus and VZV were not reactivated during the culture period. In situ hybridization studies demonstrated the presence of RNA transcripts from the VZV immediate early gene 63. This approach to the detection of herpes simplex virus and VZV expression in human ganglia should facilitate analysis of viral RNA and proteins in human sensory ganglia.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baringer J. R., Swoveland P. Recovery of herpes-simplex virus from human trigeminal ganglions. N Engl J Med. 1973 Mar 29;288(13):648–650. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197303292881303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastian F. O., Rabson A. S., Yee C. L., Tralka T. S. Herpesvirus varicellae isolated from human dorsal root ganglia. Arch Pathol. 1974 May;97(5):331–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Faber S., Wilcox K. W., Pizer L. I. Herpes simplex virus immediate early infected-cell polypeptide 4 binds to DNA and promotes transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4016–4020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., McGeoch D. J. Evolutionary comparisons of the S segments in the genomes of herpes simplex virus type 1 and varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Apr;67(Pt 4):597–611. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-4-597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstathiou S., Minson A. C., Field H. J., Anderson J. R., Wildy P. Detection of herpes simplex virus-specific DNA sequences in latently infected mice and in humans. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):446–455. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.446-455.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. A detailed analysis of an HSV-1 early promoter: sequences involved in trans-activation by viral immediate-early gene products are not early-gene specific. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3037–3056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Rozenman Y., Murray R., Devlin M., Vafai A. Detection of varicella-zoster virus nucleic acid in neurons of normal human thoracic ganglia. Ann Neurol. 1987 Sep;22(3):377–380. doi: 10.1002/ana.410220315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Shtram Y., Friedmann A., Wellish M., Devlin M., Cohen A., Fraser N., Becker Y. Extraction of cell-associated varicella-zoster virus DNA with triton X-100-NaCl. J Virol Methods. 1982 May;4(4-5):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Vafai A., Shtram Y., Becker Y., Devlin M., Wellish M. Varicella-zoster virus DNA in human sensory ganglia. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):478–480. doi: 10.1038/306478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. T., Courtney R. J., Dunkel E. C. Detection of an immediate early herpes simplex virus type 1 polypeptide in trigeminal ganglia from latently infected animals. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):987–992. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.987-992.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman R. W., Ecker J. R., Tenser R. B. Varicella-zoster virus RNA in human trigeminal ganglia. Lancet. 1983 Oct 8;2(8354):814–816. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90736-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Evidence for a direct role for both the 175,000- and 110,000-molecular-weight immediate-early proteins of herpes simplex virus in the transactivation of delayed-early promoters. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):751–760. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.751-760.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plotkin S. A., Stein S., Snyder M., Immesoete P. Attempts to recover varicella virus from ganglia. Ann Neurol. 1977 Sep;2(3):249–249. doi: 10.1002/ana.410020313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puga A., Notkins A. L. Continued expression of a poly(A)+ transcript of herpes simplex virus type 1 in trigeminal ganglia of latently infected mice. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1700–1703. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1700-1703.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Wagner E. K., Devi-Rao G. B., Cook M. L., Feldman L. T. RNA complementary to a herpesvirus alpha gene mRNA is prominent in latently infected neurons. Science. 1987 Feb 27;235(4792):1056–1059. doi: 10.1126/science.2434993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vafai A., Wellish M., Gilden D. Polypeptides encoded by varicella-zoster virus unique short sequences. Virus Res. 1986 Jul;5(1):67–76. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(86)90066-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vafai A., Wellish M., Wroblewska Z., Cisco M., Gilden D. Induction of antibody against in vitro translation products encoded by varicella-zoster virus glycoprotein genes. Virus Res. 1987 Jun;7(4):325–333. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(87)90046-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vafai A., Wroblewska Z., Wellish M., Green M., Gilden D. Analysis of three late varicella-zoster virus proteins, a 125,000-molecular-weight protein and gp1 and gp3. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):953–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.953-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren K. G., Devlin M., Gilden D. H., Wroblewska Z., Brown S. M., Subak-Sharpe J., Koprowski H. Isolation of Herpes simplex virus from human trigeminal ganglia, including ganglia from one patient with multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 1977 Sep 24;2(8039):637–639. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92501-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]