Abstract
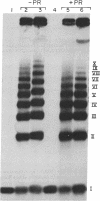
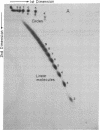
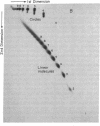
A 32-base-pair DNA fragment containing a thymine photodimer was constructed and ligated head-to-tail to obtain multimers of this sequence in which thymine dimers were in phase with the helix screw axis (approximately equal to 3 turns apart). The ligation products were analyzed by one- and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and quantitative electron microscopy. These analyses show that the thymine photodimer introduces a bend of approximately equal to 30 degrees in DNA, which causes anomalously slow migration of DNA fragments in polyacrylamide gels and facilitates the formation of small covalent circles. Repair of thymine dimers by DNA photolyase abolishes the anomalous migration.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Camerman N., Camerman A. Crystal and molecular structure of photodimer A of 1,3-dimethylthymine (the isomer in irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid). J Am Chem Soc. 1970 Apr 22;92(8):2523–2527. doi: 10.1021/ja00711a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciarrocchi G., Pedrini A. M. Determination of pyrimidine dimer unwinding angle by measurement of DNA electrophoretic mobility. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 25;155(2):177–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90445-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D., Christiansen G. Electron microscope visualization of chromatin and other DNA-protein complexes. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1978;7:19–35. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.07.060178.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J., Bleyman M., Rauch C. A., Kitchin P. A., Englund P. T. Visualization of the bent helix in kinetoplast DNA by electron microscopy. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):717–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90347-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes F. N., Williams D. L., Ratlift R. L., Varghese A. J., Rupert C. S. Effect of a single thymine photodimer on the oligodeoxythymidylate-polydeoxyadenylate interaction. J Am Chem Soc. 1971 Sep;93(19):4940–4942. doi: 10.1021/ja00748a065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Sancar A. Binding of E. coli DNA photolyase to a defined substrate containing a single T mean value of T dimer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1109–1120. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemmink J., Boelens R., Koning T., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Kaptein R. 1H NMR study of the exchangeable protons of the duplex d(GCGTTGCG).d(CGCAACGC) containing a thymine photodimer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4645–4653. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini J. C., Levene S. D., Crothers D. M., Englund P. T. Bent helical structure in kinetoplast DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7664–7668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlman D. A., Holbrook S. R., Pirkle D. H., Kim S. H. Molecular models for DNA damaged by photoreaction. Science. 1985 Mar 15;227(4692):1304–1308. doi: 10.1126/science.3975615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peckler S., Graves B., Kanne D., Rapoport H., Hearst J. E., Kim S. H. Structure of a psoralen-thymine monoadduct formed in photoreaction with DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 25;162(1):157–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao S. N., Keepers J. W., Kollman P. The structure of d(CGCGAAT[]TCGCG) . d(CGCGAATTCGCG); the incorporation of a thymine photodimer into a B-DNA helix. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4789–4807. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Smith F. W., Sancar G. B. Purification of Escherichia coli DNA photolyase. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):6028–6032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman S. E., Gibson D., Wang A. H., Lippard S. J. X-ray structure of the major adduct of the anticancer drug cisplatin with DNA: cis-[Pt(NH3)2(d(pGpG))]. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):412–417. doi: 10.1126/science.4048939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Langowski J., Baldwin R. L. DNA flexibility studied by covalent closure of short fragments into circles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4833–4837. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. C., Kunkel T. A., Casna N. J., Ford J. P., Sancar A. Activities and incision patterns of ABC excinuclease on modified DNA containing single-base mismatches and extrahelical bases. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14496–14505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulanovsky L., Bodner M., Trifonov E. N., Choder M. Curved DNA: design, synthesis, and circularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):862–866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahn K., Blattner F. R. Direct evidence for DNA bending at the lambda replication origin. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):416–422. doi: 10.1126/science.2951850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]