Abstract
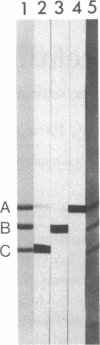
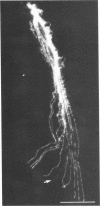
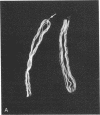
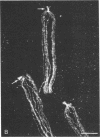
Affinity purified, polyclonal antibodies were prepared against three tektins (tektins A, B, and C) isolated from sea urchin sperm axonemal microtubules. These antibodies (anti-tektins) were used to localize tektins in axonemes, basal bodies, and centrioles. By immunofluorescence microscopy it could be demonstrated that in sperm tails from Lytechinus pictus all three anti-tektins stain all nine axonemal doublet microtubules and A-tubule extensions along their entire length. In addition to staining doublet microtubules, anti-tektin C weakly labeled the central-pair microtubules in sperm tails from Patiria miniata. The anti-tektin staining revealed also a clear cross-reaction with basal bodies of sea urchin sperm and with centrioles of cells from hamsters, humans, and pigs. These data provide evidence of tektin or tektin-like proteins in basal bodies and centrioles and suggest that centriole microtubules are constructed according to the same principles as flagellar microtubules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amos L., Klug A. Arrangement of subunits in flagellar microtubules. J Cell Sci. 1974 May;14(3):523–549. doi: 10.1242/jcs.14.3.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amos W. B., Amos L. A., Linck R. W. Proteins closely similar to flagellar tektins are detected in cilia but not in cytoplasmic microtubules. Cell Motil. 1985;5(3):239–249. doi: 10.1002/cm.970050306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amos W. B., Amos L. A., Linck R. W. Studies of tektin filaments from flagellar microtubules by immunoelectron microscopy. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1986;5:55–68. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_5.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang X. J., Piperno G. Cross-reactivity of antibodies specific for flagellar tektin and intermediate filament subunits. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1563–1568. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly J. A., Kalnins V. I. Visualization of centrioles and basal bodies by fluorescent staining with nonimmune rabbit sera. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):526–532. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M. Growth factors involved in haemopoiesis. J Cell Sci. 1987 Aug;88(Pt 1):1–6. doi: 10.1242/jcs.88.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBBONS I. R., GRIMSTONE A. V. On flagellar structure in certain flagellates. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Jul;7:697–716. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.4.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimstone A. V., Klug A. Observations on the substructure of flagellar fibres. J Cell Sci. 1966 Sep;1(3):351–362. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1.3.351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson G. K., Starkebaum G. A., Benditt E. P., Schwartz S. M. Fc-mediated binding of IgG to vimentin-type intermediate filaments in vascular endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3103–3107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W., Fung B., Shyamala M., Kasamatsu H. Identification of antigenically related polypeptides at centrioles and basal bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2373–2377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linck R. W., Amos L. A., Amos W. B. Localization of tektin filaments in microtubules of sea urchin sperm flagella by immunoelectron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):126–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linck R. W. Flagellar doublet microtubules: fractionation of minor components and alpha-tubulin from specific regions of the A-tubule. J Cell Sci. 1976 Mar;20(2):405–439. doi: 10.1242/jcs.20.2.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linck R. W., Langevin G. L. Reassembly of flagellar B (alpha beta) tubulin into singlet microtubules: consequences for cytoplasmic microtubule structure and assembly. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):323–337. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linck R. W., Langevin G. L. Structure and chemical composition of insoluble filamentous components of sperm flagellar microtubules. J Cell Sci. 1982 Dec;58:1–22. doi: 10.1242/jcs.58.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linck R. W., Olson G. E., Langevin G. L. Arrangement of tubulin subunits and microtubule-associated proteins in the central-pair microtubule apparatus of squid (Loligo pealei) sperm flagella. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):309–322. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linck R. W., Stephens R. E. Biochemical characterization of tektins from sperm flagellar doublet microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1069–1075. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mage M. G. Preparation of Fab fragments from IgGs of different animal species. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):142–150. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70045-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandelkow E. M., Schultheiss R., Rapp R., Müller M., Mandelkow E. On the surface lattice of microtubules: helix starts, protofilament number, seam, and handedness. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):1067–1073. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. M., Osborne W. R., Pfeiffer J. R., Child F. M., Berlin R. D. Purine nucleoside phosphorylase is associated with centrioles and basal bodies. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):837–847. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum J. L., Binder L. I., Granett S., Dentler W. L., Snell W., Sloboda R., Haimo L. Directionality and rate of assembly of chick brain tubulin onto pieces of neurotubules, flagellar axonemes, and basal bodies. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;253:147–177. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb19198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorokin S. P. Reconstructions of centriole formation and ciliogenesis in mammalian lungs. J Cell Sci. 1968 Jun;3(2):207–230. doi: 10.1242/jcs.3.2.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. Differential protein synthesis and utilization during cilia formation in sea urchin embryos. Dev Biol. 1977 Dec;61(2):311–329. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90301-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Bryan J., Bush D. J., Fujiwara K., Mooseker M. S., Murphy D. B., Snyder D. H. Microtubules: evidence for 13 protofilaments. J Cell Biol. 1973 Nov;59(2 Pt 1):267–275. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turksen K., Aubin J. E., Kalnins V. I. Identification of a centriole-associated protein by antibodies present in normal rabbit sera. Nature. 1982 Aug 19;298(5876):763–765. doi: 10.1038/298763a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wais-Steider C., White N. S., Gilbert D. S., Eagles P. A. X-ray diffraction patterns from microtubules and neurofilaments in axoplasm. J Mol Biol. 1987 Sep 20;197(2):205–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]