Abstract
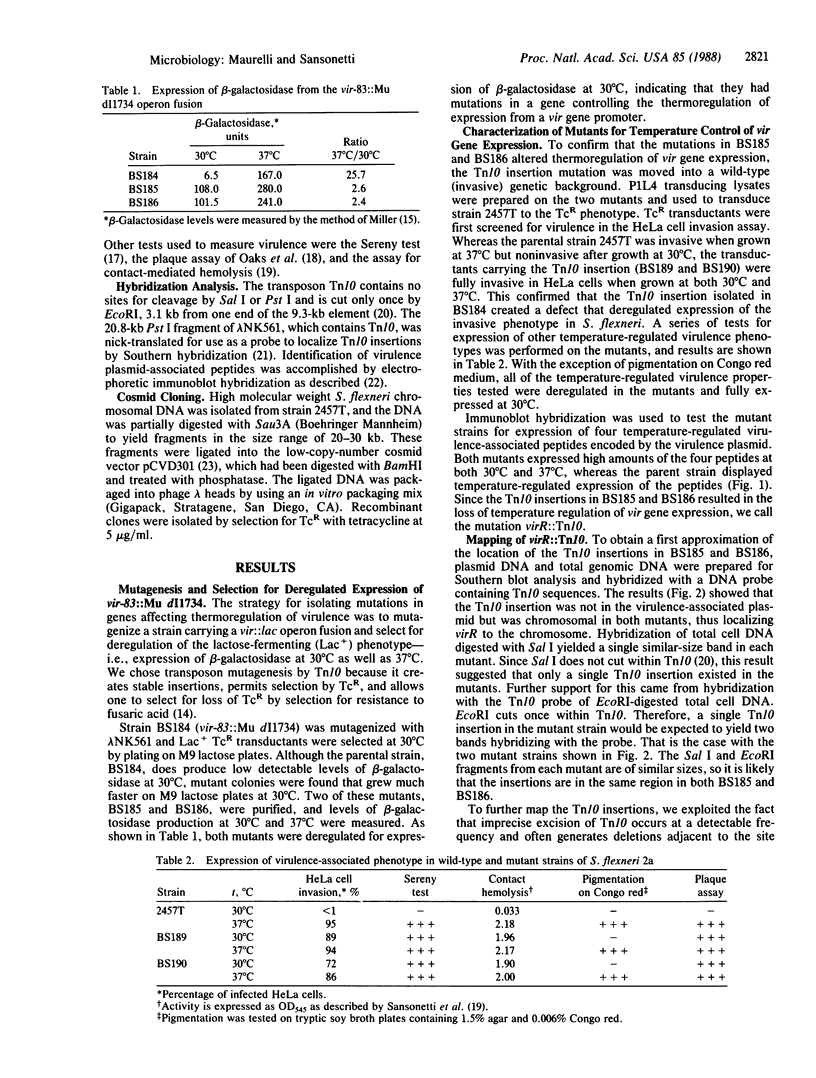
Genes required for the full expression of Shigella virulence are on both the chromosome and a large virulence-associated plasmid. Expression of one or more virulence (vir) genes is temperature-regulated, wild-type strains being virulent (invasive) when grown at 37 degrees C but phenotypically avirulent (noninvasive) at 30 degrees C. A vir::lac operon fusion located on the virulence plasmid, which brings the lac genes under control of a temperature-regulated vir gene promoter, was used to select regulatory mutants constitutive for the Lac+ phenotype at the nonpermissive temperature. A transposon Tn10-induced mutant that was Lac+ at 30 degrees C and 37 degrees C was isolated, and the Tn10 insertion was transduced into a wild-type strain. The transductants all simultaneously became deregulated for virulence and invaded HeLa cells equally well at 30 degrees C and 37 degrees C. Other virulence-associated phenotypes were also deregulated and expressed at 30 degrees C. Southern hybridization with a probe for Tn10 determined the insertion to be on the chromosome. Fine mapping by transduction with phage P1L4 positioned the mutation between the galU and trp genes. A cosmid cloned fragment of Shigella chromosomal DNA containing the region around galU was used in complementation studies and showed that the closely linked regulatory gene was able to complement, in trans, the Tn10-induced mutation. We propose that this mutation defines a regulatory gene, virR, and that insertion of Tn10 into this gene inactivates a repressor that normally blocks expression of vir genes at 30 degrees C.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bölin I., Portnoy D. A., Wolf-Watz H. Expression of the temperature-inducible outer membrane proteins of yersiniae. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):234–240. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.234-240.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castilho B. A., Olfson P., Casadaban M. J. Plasmid insertion mutagenesis and lac gene fusion with mini-mu bacteriophage transposons. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):488–495. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.488-495.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciampi M. S., Schmid M. B., Roth J. R. Transposon Tn10 provides a promoter for transcription of adjacent sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5016–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta A. R., Kaper J. B., MacQuillan A. M. Shuttle cloning vectors for the marine bacterium Vibrio parahaemolyticus. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):808–811. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.808-811.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORMAL S. B., DAMMIN G. J., LABREC E. H., SCHNEIDER H. Experimental Shigella infections: characteristics of a fatal infection produced in guinea pigs. J Bacteriol. 1958 May;75(5):604–610. doi: 10.1128/jb.75.5.604-610.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Formal S. B., Hornick R. B. Invasive Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis. 1978 May;137(5):641–644. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.5.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster T. J., Lundblad V., Hanley-Way S., Halling S. M., Kleckner N. Three Tn10-associated excision events: relationship to transposition and role of direct and inverted repeats. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):215–227. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90286-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goguen J. D., Yother J., Straley S. C. Genetic analysis of the low calcium response in Yersinia pestis mu d1(Ap lac) insertion mutants. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):842–848. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.842-848.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R. Biochemical and genetic studies with nitrate reductase C-gene mutants of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1969;105(4):285–297. doi: 10.1007/BF00277583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göransson M., Uhlin B. E. Environmental temperature regulates transcription of a virulence pili operon in E. coli. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2885–2888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02225.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Formal S. B. Protein synthesis in HeLa or Henle 407 cells infected with Shigella dysenteriae 1, Shigella flexneri 2a, or Salmonella typhimurium W118. Infect Immun. 1981 Apr;32(1):137–144. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.1.137-144.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Oaks E. V., Formal S. B. Identification and antigenic characterization of virulence-associated, plasmid-coded proteins of Shigella spp. and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):620–629. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.620-629.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Berg D. E., Allet B., Reznikoff W. S. Restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn10, a transposon which encodes tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):681–685. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.681-685.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Barker D. F., Ross D. G., Botstein D. Properties of the translocatable tetracycline-resistance element Tn10 in Escherichia coli and bacteriophage lambda. Genetics. 1978 Nov;90(3):427–461. doi: 10.1093/genetics/90.3.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labrec E. H., Schneider H., Magnani T. J., Formal S. B. EPITHELIAL CELL PENETRATION AS AN ESSENTIAL STEP IN THE PATHOGENESIS OF BACILLARY DYSENTERY. J Bacteriol. 1964 Nov;88(5):1503–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.5.1503-1518.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird W. J., Cavanaugh D. C. Correlation of autoagglutination and virulence of yersiniae. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Apr;11(4):430–432. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.4.430-432.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlor K. M., Daskaleros P. A., Robinson R. E., Payne S. M. Virulence of iron transport mutants of Shigella flexneri and utilization of host iron compounds. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):594–599. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.594-599.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Nunn W. D. Selection for loss of tetracycline resistance by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1110–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1110-1111.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Baudry B., d'Hauteville H., Hale T. L., Sansonetti P. J. Cloning of plasmid DNA sequences involved in invasion of HeLa cells by Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Jul;49(1):164–171. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.1.164-171.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Loss of pigmentation in Shigella flexneri 2a is correlated with loss of virulence and virulence-associated plasmid. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):397–401. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.397-401.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Blackmon B., Curtiss R., 3rd Temperature-dependent expression of virulence genes in Shigella species. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.195-201.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurelli A. T., Curtiss R., 3rd Bacteriophage Mu d1(Apr lac) generates vir-lac operon fusions in Shigella flexneri 2a. Infect Immun. 1984 Sep;45(3):642–648. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.3.642-648.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassif X., Mazert M. C., Mounier J., Sansonetti P. J. Evaluation with an iuc::Tn10 mutant of the role of aerobactin production in the virulence of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):1963–1969. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.1963-1969.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., VanBogelen R. A., Vaughn V. The genetics and regulation of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:295–329. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Thompson M. R., Gemski P., Doctor B. P., Formal S. B. Biological properties of Shigella flexneri 2A toxin and its serological relationship to Shigella dysenteriae 1 toxin. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):796–798. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.796-798.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oaks E. V., Wingfield M. E., Formal S. B. Plaque formation by virulent Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1985 Apr;48(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.1.124-129.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne S. M. Synthesis and utilization of siderophores by Shigella flexneri. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1420–1424. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1420-1424.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SERENY B. Experimental shigella keratoconjunctivitis; a preliminary report. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;2(3):293–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Hale T. L., Dammin G. J., Kapfer C., Collins H. H., Jr, Formal S. B. Alterations in the pathogenicity of Escherichia coli K-12 after transfer of plasmid and chromosomal genes from Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1983 Mar;39(3):1392–1402. doi: 10.1128/iai.39.3.1392-1402.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Involvement of a plasmid in the invasive ability of Shigella flexneri. Infect Immun. 1982 Mar;35(3):852–860. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.3.852-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Kopecko D. J., Formal S. B. Shigella sonnei plasmids: evidence that a large plasmid is necessary for virulence. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):75–83. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.75-83.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., Ryter A., Clerc P., Maurelli A. T., Mounier J. Multiplication of Shigella flexneri within HeLa cells: lysis of the phagocytic vacuole and plasmid-mediated contact hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):461–469. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.461-469.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansonetti P. J., d'Hauteville H., Ecobichon C., Pourcel C. Molecular comparison of virulence plasmids in Shigella and enteroinvasive Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 May-Jun;134A(3):295–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Graaf F. K., Wientjes F. B., Klaasen-Boor P. Production of K99 antigen by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strains of antigen groups o8, o9, o20, and o101 grown at different conditions. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):216–221. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.216-221.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





