Abstract
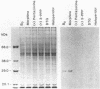
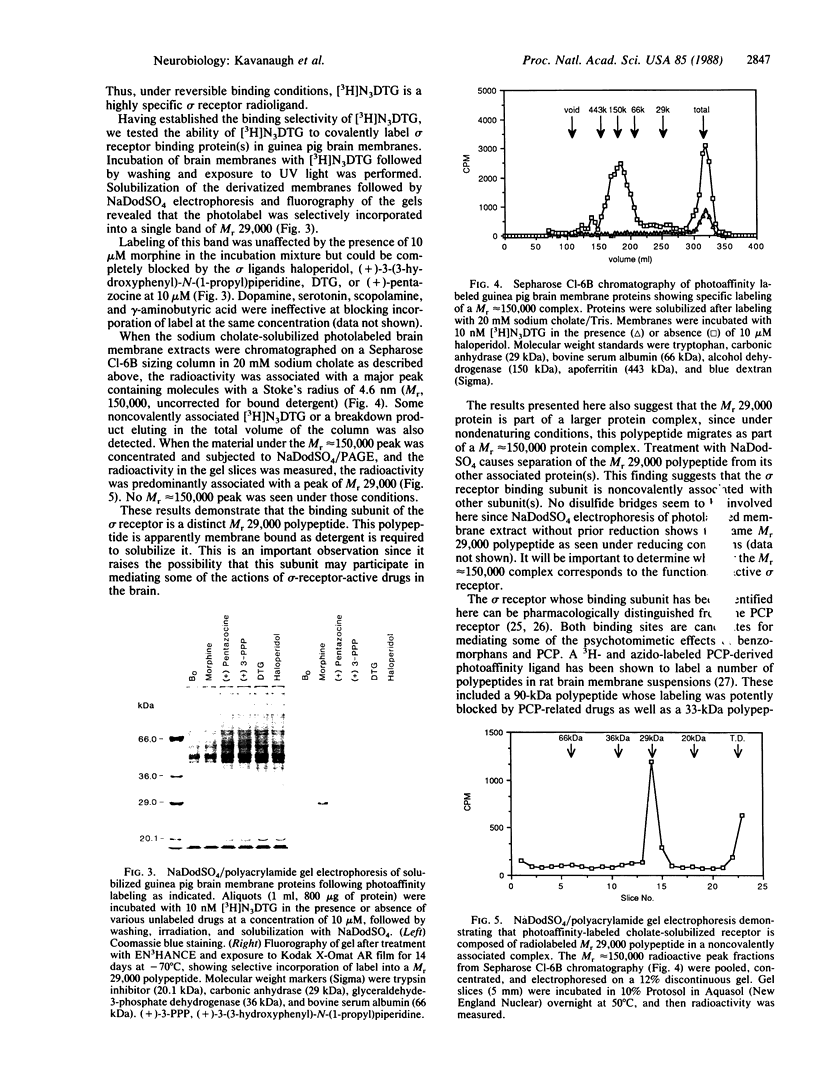
The sigma-type opiate receptor is a distinct binding site in the brain that may mediate some of the psychotomimetic effects caused by benzomorphan opiates and phencyclidine in humans. We have developed a synthetic, highly selective ligand for this receptor, 1,3-di-o-tolylguanidine (DTG). To identify the binding protein(s) of the sigma receptor, we have now synthesized a radiolabeled azide derivative of DTG, 1-(4-azido-2-methyl[6-3H]phenyl)-3-(2-methyl[4,6-3H]phenyl)-guanidine ([3H]N3DTG). In guinea pig brain membrane binding assays conducted in the dark, [3H]N3DTG bound reversibly, selectively, and with high affinity (Kd = 10 nM) to sigma receptors. The drug specificity profile of reversible [3H]-N3DTG binding was identical to that of [3H]DTG and 3H-labeled (+)-3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(1-propyl)piperidine binding indicating that [3H]N3DTG is a selective sigma receptor ligand. Guinea pig brain membranes were photoaffinity-labeled with [3H]N3DTG. NaDodSO4/PAGE of detergent-solubilized membrane extract identified a single 29-kDa radioactive band. Sepharose Cl-6B gel chromatography of photolabeled brain membranes solubilized with the nondenaturing detergent sodium cholate showed a radioactive complex with a Stoke's radius of 4.6 nm (Mr, 150,000) that may represent the intact sigma receptor complex. NaDodSO4/PAGE of this complex showed that the radiolabeled material was a 29-kDa polypeptide that may be the binding subunit of the sigma receptor. The specific sigma receptor photoaffinity ligand described here should be a useful tool for purifying and characterizing the sigma receptor.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J. T., Teal P. M., Sonders M. S., Tester B., Esherick J. S., Scherz M. W., Keana J. F., Weber E. Synthesis and characterization of an affinity label for brain receptors to psychotomimetic benzomorphans: differentiation of sigma-type and phencyclidine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Oct 6;142(1):61–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90654-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aniline O., Pitts F. N., Jr Phencyclidine (PCP): a review and perspectives. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1982 Apr;10(2):145–177. doi: 10.3109/10408448209041322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anis N. A., Berry S. C., Burton N. R., Lodge D. The dissociative anaesthetics, ketamine and phencyclidine, selectively reduce excitation of central mammalian neurones by N-methyl-aspartate. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):565–575. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady K. T., Balster R. L., May E. L. Stereoisomers of N-allylnormetazocine: phencyclidine-like behavioral effects in squirrel monkeys and rats. Science. 1982 Jan 8;215(4529):178–180. doi: 10.1126/science.6274022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell B. G., Bobker D. H., Leslie F. M., Mefford I. N., Weber E. Both the sigma receptor-specific ligand (+)3-PPP and the PCP receptor-specific ligand TCP act in the mouse vas deferens via augmentation of electrically evoked norepinephrine release. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jun 26;138(3):447–449. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90487-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowan A. Simple in vivo tests that differentiate prototype agonists at opiate receptors. Life Sci. 1981 Apr 6;28(14):1559–1570. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90310-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haertzen C. A. Subjective effects of narcotic antagonists cyclazocine and nalorphine on the Addiction Research Center Inventory (ARCI). Psychopharmacologia. 1970;18(4):366–377. doi: 10.1007/BF00402763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haring R., Kloog Y., Sokolovsky M. Identification of polypeptides of the phencyclidine receptor of rat hippocampus by photoaffinity labeling with [3H]azidophencyclidine. Biochemistry. 1986 Feb 11;25(3):612–620. doi: 10.1021/bi00351a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwamoto E. T. Locomotor activity and antinociception after putative mu, kappa and sigma opioid receptor agonists in the rat: influence of dopaminergic agonists and antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 May;217(2):451–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khazan N., Young G. A., El-Fakany E. E., Hong O., Calligaro D. Sigma receptors mediated the psychotomimetic effects of N-allylnormetazocine (SKF-10,047), but not its opioid agonistic-antagonistic properties. Neuropharmacology. 1984 Aug;23(8):983–987. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(84)90015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Largent B. L., Gundlach A. L., Snyder S. H. Pharmacological and autoradiographic discrimination of sigma and phencyclidine receptor binding sites in brain with (+)-[3H]SKF 10,047, (+)-[3H]-3-[3-hydroxyphenyl]-N-(1-propyl)piperidine and [3H]-1-[1-(2-thienyl)cyclohexyl]piperidine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Aug;238(2):739–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Largent B. L., Gundlach A. L., Snyder S. H. Psychotomimetic opiate receptors labeled and visualized with (+)-[3H]3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-(1-propyl)piperidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4983–4987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maragos W. F., Chu D. C., Greenamyre J. T., Penney J. B., Young A. B. High correlation between the localization of [3H]TCP binding and NMDA receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Apr 9;123(1):173–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W. R., Eades C. G., Thompson J. A., Huppler R. E., Gilbert P. E. The effects of morphine- and nalorphine- like drugs in the nondependent and morphine-dependent chronic spinal dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Jun;197(3):517–532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. A practical computer-based approach to the analysis of radioligand binding experiments. Comput Programs Biomed. 1983 Aug-Oct;17(1-2):107–113. doi: 10.1016/0010-468x(83)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Hammer R. P., Jr, Herkenham M., Pert C. B. Phencyclidine (angel dust)/sigma "opiate" receptor: visualization by tritium-sensitive film. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5881–5885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonders M. S., Keana J. F., Weber E. Phencyclidine and psychotomimetic sigma opiates: recent insights into their biochemical and physiological sites of action. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jan;11(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su T. P. Evidence for sigma opioid receptor: binding of [3H]SKF-10047 to etorphine-inaccessible sites in guinea-pig brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):284–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam S. W., Cook L. Sigma opiates and certain antipsychotic drugs mutually inhibit (+)-[3H] SKF 10,047 and [3H]haloperidol binding in guinea pig brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5618–5621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaupel D. B. Naltrexone fails to antagonize the sigma effects of PCP and SKF 10,047 in the dog. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Sep 2;92(3-4):269–274. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaupel D. B., Su T. P. Guinea-pig vas deferens preparation may contain both receptors and phencyclidine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Jul 2;139(1):125–128. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90507-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincent J. P., Kartalovski B., Geneste P., Kamenka J. M., Lazdunski M. Interaction of phencyclidine ("angel dust") with a specific receptor in rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4678–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Sonders M., Quarum M., McLean S., Pou S., Keana J. F. 1,3-Di(2-[5-3H]tolyl)guanidine: a selective ligand that labels sigma-type receptors for psychotomimetic opiates and antipsychotic drugs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8784–8788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zukin S. R., Zukin R. S. Specific [3H]phencyclidine binding in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5372–5376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]