Abstract
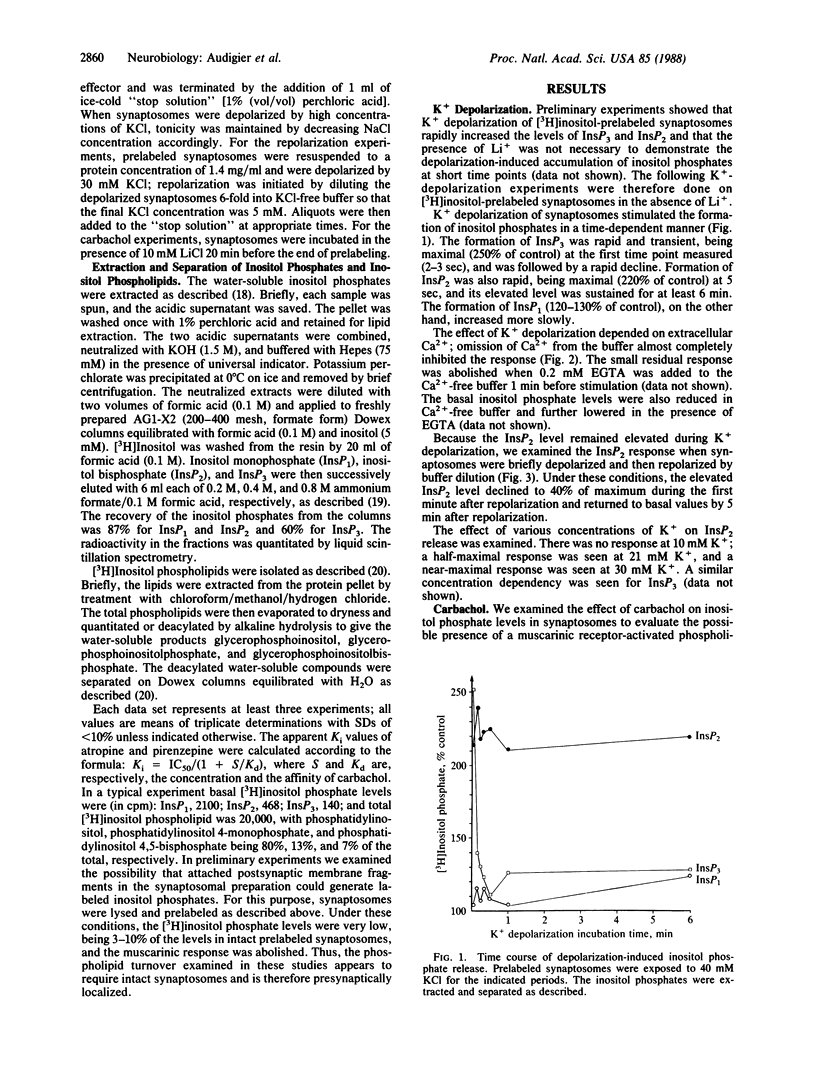
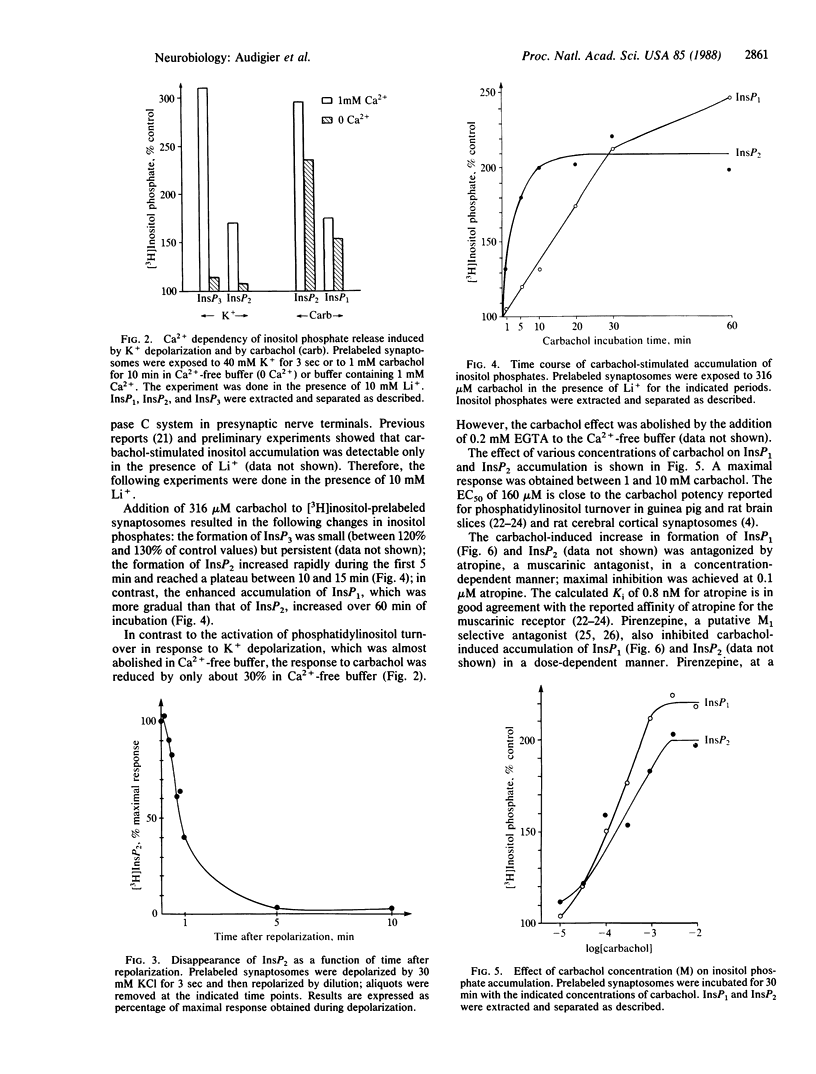
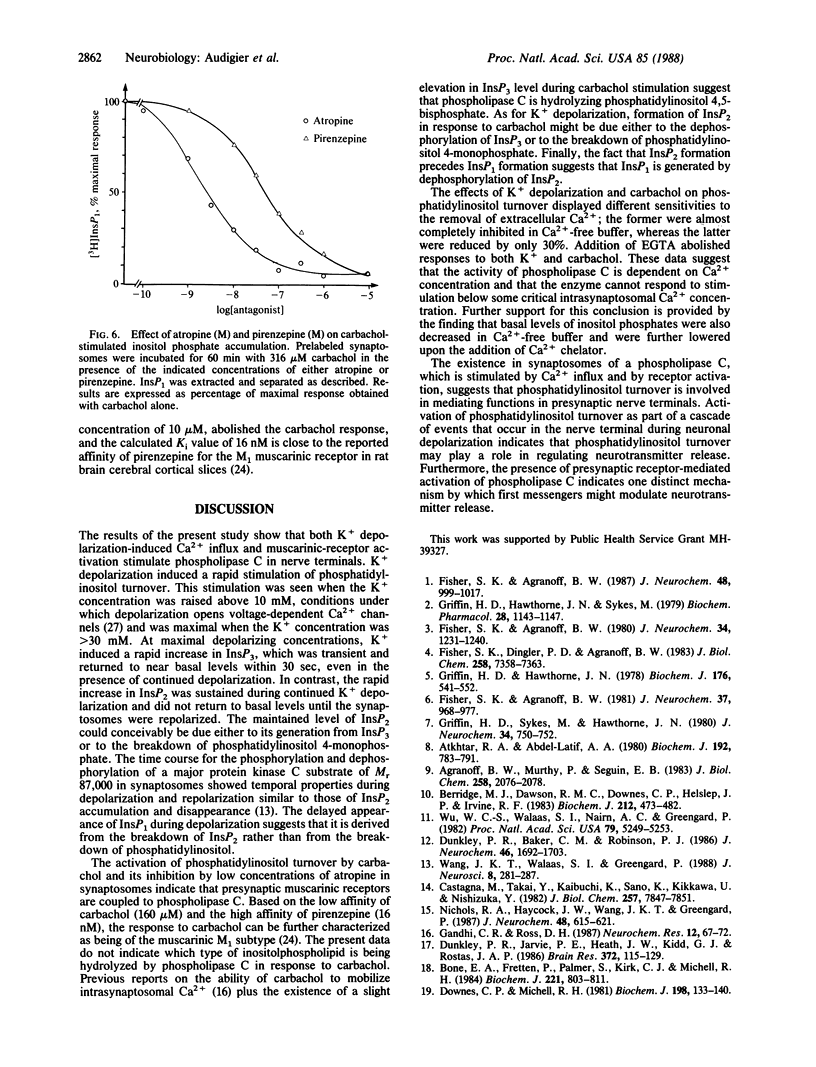
Synaptosomes, purified from rat cerebral cortex, were prelabeled with [3H]inositol to study phosphatidylinositol turnover in nerve terminals. Labeled synaptosomes were either depolarized with 40 mM K+ or exposed to carbamoylcholine (carbachol). K+ depolarization increased the level of inositol phosphates in a time-dependent manner. The inositol trisphosphate concentration increased rapidly and transiently, reaching maximum (250% of control) in less than 3 sec and returning to near basal levels by 30 sec. The inositol bisphosphate level also increased rapidly, but its elevated level (220% of control) was sustained during continued depolarization. The elevated level of inositol bisphosphate was reversed upon repolarization of the synaptosomes. The level of inositol monophosphate increased slowly to 120-130% of control. These effects of K+ depolarization depended on the presence of Ca2+ in the incubation medium. Carbachol stimulated the turnover of phosphatidylinositol in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The level of inositol trisphosphate increased only slightly (120-130% of control) during carbachol stimulation. The level of inositol bisphosphate increased to 210% of control, and this maximal response was seen from 15 to 60 min. Accumulation of inositol monophosphate (250% of control) was larger than that of inositol bisphosphate, but its time course was slower. Atropine and pirenzepine inhibited the carbachol effect with high affinities of 0.8 nM and 16 nM, respectively, indicating that the effect of carbachol was mediated by activation of a M1 muscarinic receptor. Incubation of synaptosomes in Ca2+-free buffer reduced the response to carbachol by 30%, and addition of EGTA abolished it. These data show that both Ca2+ influx and M1 muscarinic receptor activation stimulate phospholipase C activity in synaptosomes, suggesting that phosphatidylinositol turnover may be involved in regulating neurotransmitter release from nerve terminals.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam-Vizi V., Ashley R. H. Relation of acetylcholine release to Ca2+ uptake and intraterminal Ca2+ concentration in guinea-pig cortex synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1987 Oct;49(4):1013–1021. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb09988.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agranoff B. W., Murthy P., Seguin E. B. Thrombin-induced phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2076–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar R. A., Abdel-Latif A. A. Requirement for calcium ions in acetylcholine-stimulated phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidyl-myo-inositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rabbit iris smooth muscle. Biochem J. 1980 Dec 15;192(3):783–791. doi: 10.1042/bj1920783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Downes C. P., Hanley M. R. Lithium amplifies agonist-dependent phosphatidylinositol responses in brain and salivary glands. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):587–595. doi: 10.1042/bj2060587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone E. A., Fretten P., Palmer S., Kirk C. J., Michell R. H. Rapid accumulation of inositol phosphates in isolated rat superior cervical sympathetic ganglia exposed to V1-vasopressin and muscarinic cholinergic stimuli. Biochem J. 1984 Aug 1;221(3):803–811. doi: 10.1042/bj2210803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Michell R. H. The polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase of erythrocyte membranes. Biochem J. 1981 Jul 15;198(1):133–140. doi: 10.1042/bj1980133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley P. R., Baker C. M., Robinson P. J. Depolarization-dependent protein phosphorylation in rat cortical synaptosomes: characterization of active protein kinases by phosphopeptide analysis of substrates. J Neurochem. 1986 Jun;46(6):1692–1703. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb08486.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunkley P. R., Jarvie P. E., Heath J. W., Kidd G. J., Rostas J. A. A rapid method for isolation of synaptosomes on Percoll gradients. Brain Res. 1986 Apr 30;372(1):115–129. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. K., Agranoff B. W. Calcium and the muscarinic synaptosomal phospholipid labeling effect. J Neurochem. 1980 May;34(5):1231–1240. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb09964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. K., Agranoff B. W. Enhancement of the muscarinic synaptosomal phospholipid labeling effect by the ionophore A23187. J Neurochem. 1981 Oct;37(4):968–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. K., Agranoff B. W. Receptor activation and inositol lipid hydrolysis in neural tissues. J Neurochem. 1987 Apr;48(4):999–1017. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05618.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. K., Bartus R. T. Regional differences in the coupling of muscarinic receptors to inositol phospholipid hydrolysis in guinea pig brain. J Neurochem. 1985 Oct;45(4):1085–1095. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05527.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. K., Klinger P. D., Agranoff B. W. Muscarinic agonist binding and phospholipid turnover in brain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7358–7363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gandhi C. R., Ross D. H. Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate induced mobilization of Ca2+ from rat brain synaptosomes. Neurochem Res. 1987 Jan;12(1):67–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00971366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil D. W., Wolfe B. B. Pirenzepine distinguishes between muscarinic receptor-mediated phosphoinositide breakdown and inhibition of adenylate cyclase. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Mar;232(3):608–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales R. A., Crews F. T. Characterization of the cholinergic stimulation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat brain slices. J Neurosci. 1984 Dec;4(12):3120–3127. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-12-03120.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin H. D., Hawthorne J. N., Sykes M., Orlacchio A. A calcium requirement for the phosphatidylinositol response following activation of presynaptic muscarinic receptors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979 Apr 1;28(7):1143–1147. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin H. D., Sykes M., Hawthorne J. N. Effects of neomycin on calcium and polyphosphoinositide metabolism of guinea pig synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1980 Mar;34(3):750–752. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb11209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R., Berrie C. P., Birdsall N. J., Burgen A. S., Hulme E. C. Pirenzepine distinguishes between different subclasses of muscarinic receptors. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):90–92. doi: 10.1038/283090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer R., Giachetti A. Muscarinic receptor subtypes: M1 and M2 biochemical and functional characterization. Life Sci. 1982 Dec 27;31(26):2991–2998. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. A., Haycock J. W., Wang J. K., Greengard P. Phorbol ester enhancement of neurotransmitter release from rat brain synaptosomes. J Neurochem. 1987 Feb;48(2):615–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb04137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. K., Walaas S. I., Greengard P. Protein phosphorylation in nerve terminals: comparison of calcium/calmodulin-dependent and calcium/diacylglycerol-dependent systems. J Neurosci. 1988 Jan;8(1):281–288. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-01-00281.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu W. C., Walaas S. I., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Calcium/phospholipid regulates phosphorylation of a Mr "87k" substrate protein in brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5249–5253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



