Abstract
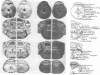
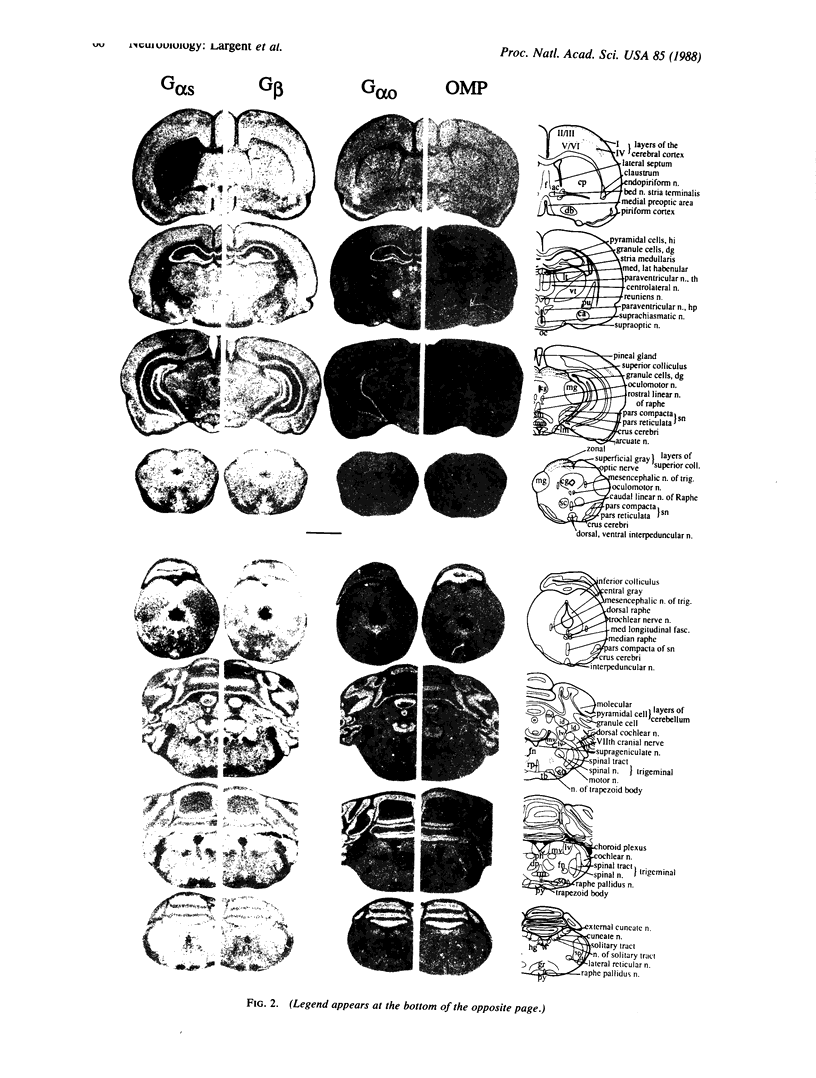
Guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) mediate many receptor-coupled signal transduction events. We have localized in rat brain by in situ hybridization the mRNA for the G protein subunits--G alpha s, G alpha o, and G beta. Oligonucleotide probes were radiolabeled by a technique that resulted in a probe of defined specific activity and uniform length. mRNA species encoding G alpha s and G beta occur in high densities heterogeneously throughout the brain, especially in large neuronal cell bodies--e.g., hippocampal pyramidal cells, granule cells of the dentate gyrus, hypothalamic nuclei, and neurons of brainstem nuclei and the reticular formation. G alpha o mRNA has a more limited distribution and abundance, being detectable in the claustrum, endopiriform nucleus, habenula, hippocampal pyramidal cells, granule cells of the dentate gyrus, and cerebellar Purkinje cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akam M. E., Martinez-Arias A. The distribution of Ultrabithorax transcripts in Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1689–1700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brann M. R., Collins R. M., Spiegel A. Localization of mRNAs encoding the alpha-subunits of signal-transducing G-proteins within rat brain and among peripheral tissues. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 28;222(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80218-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong H. K., Amatruda T. T., 3rd, Birren B. W., Simon M. I. Distinct forms of the beta subunit of GTP-binding regulatory proteins identified by molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3792–3796. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung B. K., Hurley J. B., Stryer L. Flow of information in the light-triggered cyclic nucleotide cascade of vision. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):152–156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierschik P., Milligan G., Pines M., Goldsmith P., Codina J., Klee W., Spiegel A. Use of specific antibodies to quantitate the guanine nucleotide-binding protein Go in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff R. M., Axton J. M., Neer E. J. Physical and immunological characterization of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein purified from bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10864–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Smigel M. D., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Subunit dissociation and the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in S49 lymphoma cyc- and wild type membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3586–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Ui M. Mechanisms for inhibition of the catalytic activity of adenylate cyclase by the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins serving as the substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5215–5221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logothetis D. E., Kurachi Y., Galper J., Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. The beta gamma subunits of GTP-binding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):321–326. doi: 10.1038/325321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. The subunits of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Resolution of the activated 45,000-dalton (alpha) subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11369–11376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers K. E., Dasgupta P., Gubler U., Grillo M., Khew-Goodall Y. S., Margolis F. L. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a cDNA for olfactory marker protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1704–1708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Bourne H. R. G proteins: a family of signal transducers. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:391–419. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trussell L. O., Jackson M. B. Dependence of an adenosine-activated potassium current on a GTP-binding protein in mammalian central neurons. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3306–3316. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03306.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., De Souza E. B., Snyder S. H. Mapping second messenger systems in the brain: differential localizations of adenylate cyclase and protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4053–4057. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Van Dop C., Neer E. J., Snyder S. H. Go, a guanine nucleotide-binding protein: immunohistochemical localization in rat brain resembles distribution of second messenger systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4561–4565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Direct activation of mammalian atrial muscarinic potassium channels by GTP regulatory protein Gk. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):207–211. doi: 10.1126/science.2432660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Imoto Y., Reeves J. P., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. A G protein directly regulates mammalian cardiac calcium channels. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2446390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]