Abstract
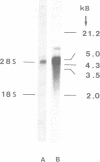
We have isolated and sequenced a cDNA encoding the alpha subunit of phosphorylase kinase from rabbit fast-twitch skeletal muscle. The cDNA molecule consists of 388 nucleotides of 5'-nontranslated sequence, the complete coding sequence of 3711 nucleotides, and 342 nucleotides of 3'-nontranslated sequence followed by a poly(dA) tract. It encodes a polypeptide of 1237 amino acids and a deduced molecular mass of 138,422 Da. Nearly half of the deduced amino acid sequence is confirmed by peptide sequencing. Seven positions of endogenously phosphorylated serine residues and autophosphorylation sites, identified by peptide sequencing, could be assigned. They cluster in a segment of only 60 amino acids. RNA blot hybridization analysis demonstrates a predominant RNA species of approximately equal to 4500 nucleotides and a less abundant RNA of 8700 nucleotides.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender P. K., Emerson C. P., Jr Skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase catalytic subunit mRNAs are expressed in heart tissue but not in liver. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8799–8805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschmeier B., Meyer H. E., Mayr G. W. Characterization of the calmodulin-binding sites of muscle phosphofructokinase and comparison with known calmodulin-binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 15;262(20):9454–9462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., VanTuinen P., Reeves A. A., Philip B. A., Caskey C. T. Isolation of cDNA clones for the catalytic gamma subunit of mouse muscle phosphorylase kinase: expression of mRNA in normal and mutant Phk mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2886–2890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chrisman T. D., Jordan J. E., Exton J. H. Purification of rat liver phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10798–10804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Burchell A., Foulkes J. G., Cohen P. T., Vanaman T. C., Nairn C. Identification of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein as the fourth subunit of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):287–293. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80772-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Picton C., Klee C. B. Activation of phosphorylase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle by calmodulin and troponin. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81078-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in the hormonal control of enzyme activity. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 16;151(3):439–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The subunit structure of rabbit-skeletal-muscle phosphorylase kinase, and the molecular basis of its activation reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Watson D. C., Dixon G. H. The hormonal control of activity of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. Amino-acid sequences at the two sites of action of adenosine-3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 3;51(1):79–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. H., Sul H. S., McCullough T. E., Walsh D. A. Purification and properties of the cardiac isoenzyme of phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11794–11801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb J. W., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr High performance liquid chromatography purification and structural characterization of the subunits of rabbit muscle phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6346–6350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb J. W., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Micropreparative protein purification by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr. 1984 Jul 27;296:129–141. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)96407-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daegelen-Proux D., Alexandre Y., Dreyfus J. C. Phosphorylase kinase isoenzymes in deficient ICR/IAn mice. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct;90(2):369–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12613.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickneite G., Jennissen H. P., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Differentiation of two catalytic sites on phosphorylase kinase for phosphorylase b and troponin T phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 1978 Mar 15;87(2):297–302. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross S. R., Bromwell K. Postnatal development of phosphorylase kinase in mouse skeletal muscle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 Nov;184(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guliaeva N. V., Vul'fson P. L., Severin E. S. Ingibirovanie aktivnosti kinazy fosforilazy analogami ATP i sviazvanie ikh s sub'edinitsami fermenta. Biokhimiia. 1978 Feb;43(2):373–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Meredith S. C. Amino acid analysis by reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography: precolumn derivatization with phenylisothiocyanate. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):65–74. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessová Z., Thieleczek R., Varsányi M., Falkenberg F. W., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Monoclonal antibodies to rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. Probes for studies of subunit function. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10111–10117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennissen H. P., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr General aspects of hydrophobic chromatography. Adsorption and elution characteristics of some skeletal muscle enzymes. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 25;14(4):754–760. doi: 10.1021/bi00675a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennissen H. P., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Multiple forms of phosphorylase kinase in red and white skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 15;42(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., FISCHER E. H. The phosphorylase b to a converting enzyme of rabbit skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1956 Apr;20(1):150–157. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(56)90273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilimann M. W., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Multiple activities on phosphorylase kinase. 1. Characterization of three partial activities by their response to calcium ion, magnesium ion, pH, and ammonium chloride and effect of activation by phosphorylation and proteolysis. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 13;21(8):1727–1734. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilimann M. W., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Multiple activities on phosphorylase kinase. 2. Different specificities toward the protein substrates phosphorylase b, troponin, and phosphorylase kinase. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 13;21(8):1735–1739. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilimann M. W., Schnackerz K. D., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Nonactivated phosphorylase kinase is a phosphoprotein: differentiation of two classes of endogenous phosphoserine residues by phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and phosphatase sensitivity. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 3;23(1):112–117. doi: 10.1021/bi00296a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King M. M., Carlson G. M. Interaction of phosphorylase kinase with the 2',3'-dialdehyde derivative of adenosine triphosphate. 2. Differential inactivation measured with various protein substrates. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 21;20(15):4387–4393. doi: 10.1021/bi00518a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Nishiyama K., Nakanishi H., Uratsuji Y., Nomura H., Takeyama Y., Nishizuka Y. Studies on the phosphorylation of myelin basic protein by protein kinase C and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12492–12499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon J. B., Jr The X-chromosome and the enzymes controlling muscle glycogen: phosphorylase kinase. Biochem Genet. 1970 Feb;4(1):169–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00484028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malthus R., Clark D. G., Watts C., Sneyd J. G. Glycogen-storage disease in rats, a genetically determined deficiency of liver phosphorylase kinase. Biochem J. 1980 Apr 15;188(1):99–106. doi: 10.1042/bj1880099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H. E., Hoffmann-Posorske E., Korte H., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Sequence analysis of phosphoserine-containing peptides. Modification for picomolar sensitivity. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 11;204(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H. E., Swiderek K., Hoffmann-Posorske E., Korte H., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Quantitative determination of phosphoserine by high-performance liquid chromatography as the phenylthiocarbamyl-S-ethylcysteine. Application to picomolar amounts of peptides and proteins. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jun 26;397:113–121. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)84994-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newgard C. B., Nakano K., Hwang P. K., Fletterick R. J. Sequence analysis of the cDNA encoding human liver glycogen phosphorylase reveals tissue-specific codon usage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8132–8136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picton C., Klee C. B., Cohen P. Phosphorylase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle: identification of the calmodulin-binding subunits. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(2):553–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04971.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann E. M., Titani K., Ericsson L. H., Wade R. D., Fischer E. H., Walsh K. A. Homology of the gamma subunit of phosphorylase b kinase with cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4185–4192. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. K., Tam S. W., Waisman D. M., Wang J. H. Differential interaction of rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase isozymes with calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11102–11103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skuster J. R., Chan K. F., Graves D. J. Isolation and properties of the catalytically active gamma subunit of phosphorylase b kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2203–2210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varsányi M., Vrbica A., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr X-linked dominant inheritance of partial phosphorylase kinase deficiency in mice. Biochem Genet. 1980 Apr;18(3-4):247–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00484240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Cruz e Silva E. F., Cohen P. T. Isolation and sequence analysis of a cDNA clone encoding the entire catalytic subunit of phosphorylase kinase. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 10;220(1):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80871-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]