Abstract
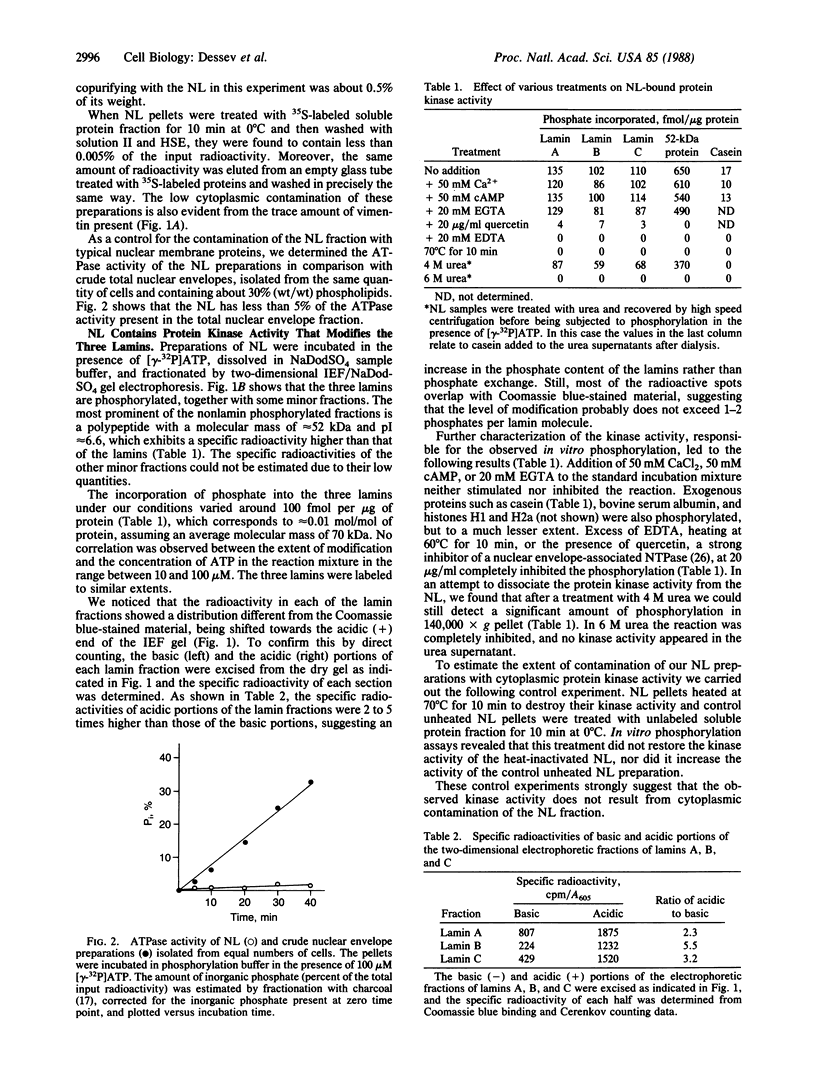
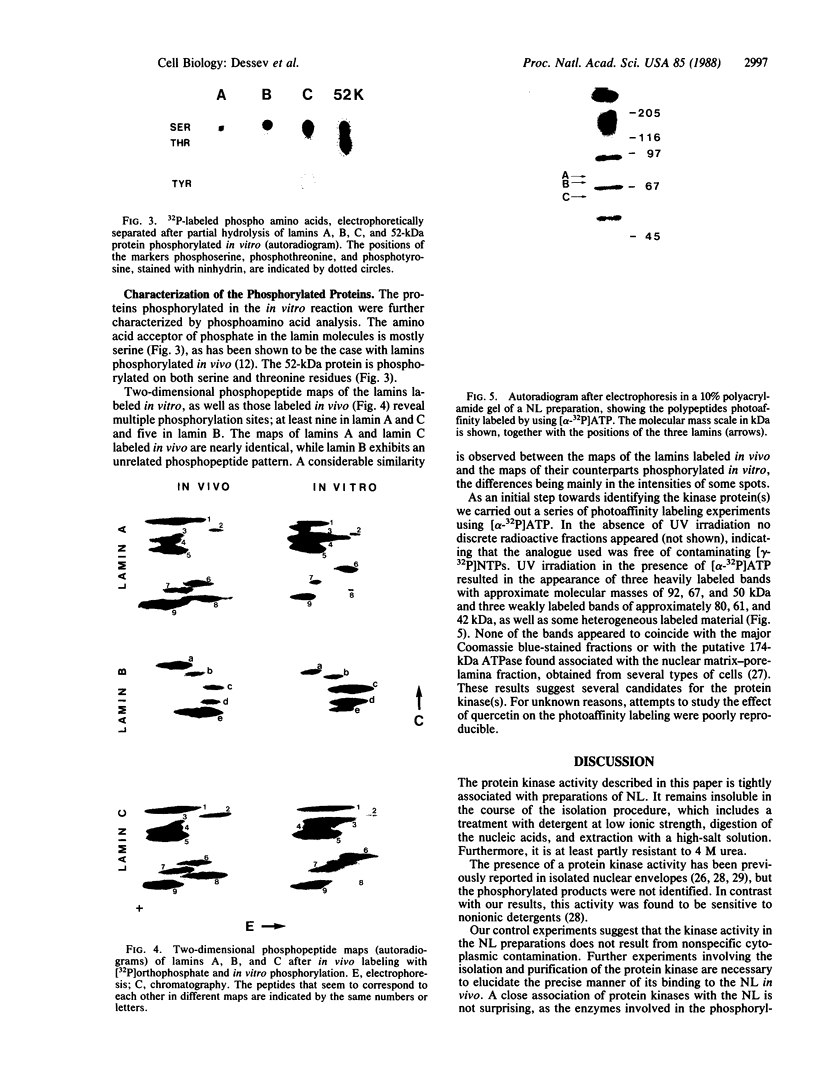
A nuclear lamina-enriched fraction from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells contains a tightly bound protein kinase activity, which phosphorylates in vitro the nuclear lamins, a 52-kilodalton protein, and several unknown minor components. The enzyme(s) is thermolabile, independent of Ca2+ and cAMP, and inhibited by quercetin. After treatment with 4 M urea it remains bound to the nuclear lamina in an active state, but it is irreversibly inactivated in 6 M urea. The lamin proteins are phosphorylated on serine residues. Their two-dimensional phosphopeptide maps show multiple phosphorylation sites and a considerable similarity to the phosphopeptide maps of lamins labeled in vivo. Photoaffinity labeling experiments revealed several polypeptide fractions in the nuclear lamina fraction that are candidates for the protein kinase(s).
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agutter P. S., Cockrill J. B., Lavine J. E., McCaldin B., Sim R. B. Properties of mammalian nuclear-envelope nucleoside triphosphatase. Biochem J. 1979 Sep 1;181(3):647–658. doi: 10.1042/bj1810647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios M., Blobel G., Fisher P. A. Characterization of an ATPase/dATPase activity associated with the Drosophila nuclear matrix-pore complex-lamina fraction. Identification of the putative enzyme polypeptide by direct ultraviolet photoaffinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4548–4555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. Peptide mapping of phosphorylated vimentin. Evidence for a site-specific alteration in mitotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5372–5375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenner C., Traut R. R., Mason D. T., Wikman-Coffelt J. Quantification of Coomassie Blue stained proteins in polyacrylamide gels based on analyses of eluted dye. Anal Biochem. 1975 Feb;63(2):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90386-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. Z., Chaudhary N., Blobel G. cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockhart D. A., Corbin J. D. Regulatory mechanisms in the control of protein kinases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982 Feb;12(2):133–186. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Scheer U., Krohne G., Jarasch E. D. The nuclear envelope and the architecture of the nuclear periphery. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):39s–50s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.39s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. Nuclear lamina and the structural organization of the nuclear envelope. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):967–978. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. The nuclear envelope lamina is reversibly depolymerized during mitosis. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blum A., Blobel G. Immunocytochemical localization of the major polypeptides of the nuclear pore complex-lamina fraction. Interphase and mitotic distribution. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):546–566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman A. E., Maul G., Steinert P. M., Yang H. Y., Goldman R. D. Keratin-like proteins that coisolate with intermediate filaments of BHK-21 cells are nuclear lamins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3839–3843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman R. D., Goldman A. E., Green K. J., Jones J. C., Jones S. M., Yang H. Y. Intermediate filament networks: organization and possible functions of a diverse group of cytoskeletal elements. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1986;5:69–97. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_5.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry S. M., Hodge L. D. Nuclear matrix: a cell-cycle-dependent site of increased intranuclear protein phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jun 1;133(1):23–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krachmarov C., Tasheva B., Markov D., Hancock R., Dessev G. Isolation and characterization of nuclear lamina from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Cell Biochem. 1986;30(4):351–359. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240300408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam K. S., Kasper C. B. Selective phosphorylation of a nuclear envelope polypeptide by an endogenous protein kinase. Biochemistry. 1979 Jan 23;18(2):307–311. doi: 10.1021/bi00569a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., Laemmli U. K. Non-histone proteins and long-range organization of HeLa interphase DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):325–344. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90332-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maul G. G., Maul H. M., Scogna J. E., Lieberman M. W., Stein G. S., Hsu B. Y., Borun T. W. Time sequence of nuclear pore formation in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated lymphocytes and in HeLa cells during the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1972 Nov;55(2):433–447. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.2.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):463–468. doi: 10.1038/319463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottaviano Y., Gerace L. Phosphorylation of the nuclear lamins during interphase and mitosis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):624–632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder H. C., Rottmann M., Bachmann M., Müller W. E. Purification and characterization of the major nucleoside triphosphatase from rat liver nuclear envelopes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):663–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer R. C., Wilson M. J., Ahmed K. Protein phosphokinase activity of rat liver nuclear membrane. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Mar 15;119(2):403–406. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90372-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue V. T., Schimmel P. R. Direct and specific photochemical cross-linking of adenosine 5'-triphosphate to an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4678–4684. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zackroff R. V., Goldman A. E., Jones J. C., Steinert P. M., Goldman R. D. Isolation and characterization of keratin-like proteins from cultured cells with fibroblastic morphology. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1231–1237. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







