Abstract
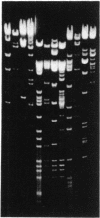
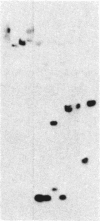
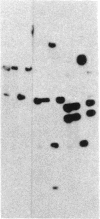
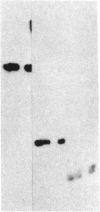
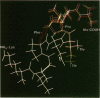
A full-length placental alkaline phosphatase (PLAP) cDNA was used to identify and clone the PLAP-like Nagao isozyme gene from human genomic libraries. The entire nucleotide sequence of the gene reveals the existence of 11 exons interrupted by 10 small introns (76-427 base pairs). Putative regulatory sequences have been identified in the promoter regions as well as dispersed in the introns. The deduced amino acid sequence of the Nagao isozyme indicates that the mature molecule is composed of 513 amino acids, of which 12 residues are different from the sequence of PLAP (98% homology). A sequence derived from exon III of the Nagao isozyme gene was used to synthesize a peptide (NH2-Lys-Leu-Gly-Pro-Glu-Thr-Phe-Leu-Ala-COOH) that contains two mutations with respect to the corresponding PLAP sequence. This peptide elicited rabbit polyclonal antibodies that reacted specifically with the seminoma Nagao isozyme but not with PLAP in electrophoretic transfer blots. These results indicate that the tumor, and possibly the normal testis, Nagao isozyme is encoded by a gene referred to as germ-cell alkaline phosphatase gene that differs from the PLAP gene expressed by syncitiotrophoblastic cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avrameas S. Coupling of enzymes to proteins with glutaraldehyde. Use of the conjugates for the detection of antigens and antibodies. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Garattini E., Hua J. C., Udenfriend S. Cloning and sequencing of human intestinal alkaline phosphatase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):695–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Angellis D., Fishman W. H. Presence of the rare D-variant heat-stable, placental-type alkaline phosphatase in normal human testis. Cancer Res. 1980 May;40(5):1506–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald L. J., Robson E. B. Rare variants of placental alkaline phosphatase. Ann Hum Genet. 1974 Jan;37(3):303–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1974.tb01837.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epenetos A. A., Snook D., Durbin H., Johnson P. M., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Limitations of radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies for localization of human neoplasms. Cancer Res. 1986 Jun;46(6):3183–3191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman L., Miyayama H., Driscoll S. G., Fishman W. H. Developmental phase-specific alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes of human placenta and their occurrence in human cancer. Cancer Res. 1976 Jul;36(7 Pt 1):2268–2273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H., Inglis N. I., Stolbach L. L., Krant M. J. A serum alkaline phosphatase isoenzyme of human neoplastic cell origin. Cancer Res. 1968 Jan;28(1):150–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman W. H. Oncotrophoblast gene expression: placental alkaline phosphatase. Adv Cancer Res. 1987;48:1–35. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Rogers C., Harris H. A search for trace expression of placental-like alkaline phosphatase in non-malignant human tissues: demonstration of its occurrence in lung, cervix, testis and thymus. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Oct 13;125(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P. S., Knoll B. J., Raducha M., Rothblum K. N., Slaughter C., Weiss M., Lafferty M. A., Fischer T., Harris H. Products of two common alleles at the locus for human placental alkaline phosphatase differ by seven amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5597–5601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P. S., Raducha M., Edwards Y. H., Weiss M. J., Slaughter C., Lafferty M. A., Harris H. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of human intestinal alkaline phosphatase: close homology to placental alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1234–1238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppsson A., Wahren B., Brehmer-Andersson E., Silfverswärd C., Stigbrand T., Millán J. L. Eutopic expression of placental-like alkaline phosphatase in testicular tumors. Int J Cancer. 1984 Dec 15;34(6):757–761. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910340604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppsson A., Wahren B., Millán J. L., Stigbrand T. Tumour and cellular localization by use of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies to placental alkaline phosphatase. Br J Cancer. 1984 Feb;49(2):123–128. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppsson A., Wahren B., Stigbrand T., Edsmyr F., Andersson L. A clinical evaluation of serum placental alkaline phosphatase in seminoma patients. Br J Urol. 1983 Feb;55(1):73–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410x.1983.tb07083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kam W., Clauser E., Kim Y. S., Kan Y. W., Rutter W. J. Cloning, sequencing, and chromosomal localization of human term placental alkaline phosphatase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8715–8719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange P. H., Millan J. L., Stigbrand T., Vessella R. L., Ruoslahti E., Fishman W. H. Placental alkaline phosphatase as a tumor marker for seminoma. Cancer Res. 1982 Aug;42(8):3244–3247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDicken I. W., McLaughlin P. J., Tromans P. M., Luesley D. M., Johnson P. M. Detection of placental-type alkaline phosphatase in ovarian cancer. Br J Cancer. 1985 Jul;52(1):59–64. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellon P., Parker V., Gluzman Y., Maniatis T. Identification of DNA sequences required for transcription of the human alpha 1-globin gene in a new SV40 host-vector system. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):279–288. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90411-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L., Beckman G., Jeppsson A., Stigbrand T. Genetic variants of placental alkaline phosphatase as detected by a monoclonal antibody. Hum Genet. 1982;60(2):145–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00569701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L., Eriksson A., Stigbrand T. A possible new locus of alkaline phosphatase expressed in human testis. Hum Genet. 1982;62(4):293–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00304541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L. Promoter structure of the human intestinal alkaline phosphatase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10599–10599. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L., Stigbrand T. Antigenic determinants of human placental and testicular placental-like alkaline phosphatases as mapped by monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 17;136(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L., Stigbrand T., Jörnvall H. Structural comparisons of two allelic variants of human placental alkaline phosphatase. Int J Biochem. 1985;17(10):1033–1039. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(85)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama T., Yoshida M., Kitamura M. L-leucine sensitive, heat-stable alkaline-phosphatase isoenzyme detected in a patient with pleuritis carcinomatosa. Clin Chim Acta. 1970 Nov;30(2):546–548. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(70)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled simian virus 40 DNA contains Z-DNA segments within transcriptional enhancer sequences. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):674–679. doi: 10.1038/303674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouwen E. J., Hendrix P. G., Dauwe S., Eerdekens M. W., De Broe M. E. Tumor markers in the human ovary and its neoplasms. A comparative immunohistochemical study. Am J Pathol. 1987 Feb;126(2):230–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter C. A., Coseo M. C., Cancro M. P., Harris H. Detection of enzyme polymorphism by using monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):1124–1128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.1124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stigbrand T., Millán J. L., Fishman W. H. The genetic basis of alkaline phosphatase isozyme expression. Isozymes Curr Top Biol Med Res. 1982;6:93–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsavaler L., Penhallow R. C., Kam W., Sussman H. H. Pst I restriction fragment length polymorphism of the human placental alkaline phosphatase gene in normal placentae and tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4529–4532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahren B., Holmgren P. A., Stigbrand T. Placental alkaline phosphatase, alphafetoprotein and carcinoembryonic antigen in testicular tumors. Tissue typing by means of cytologic smears. Int J Cancer. 1979 Dec 15;24(6):749–753. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910240608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei S. C., Doellgast G. J. Immunochemical studies of human placental-type variants of alkaline phosphatase. Structural differences between the "Nagao isoenzyme" and the placental "D-variant". Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(1):39–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05483.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Henthorn P. S., Lafferty M. A., Slaughter C., Raducha M., Harris H. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a human liver/bone/kidney-type alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7182–7186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]