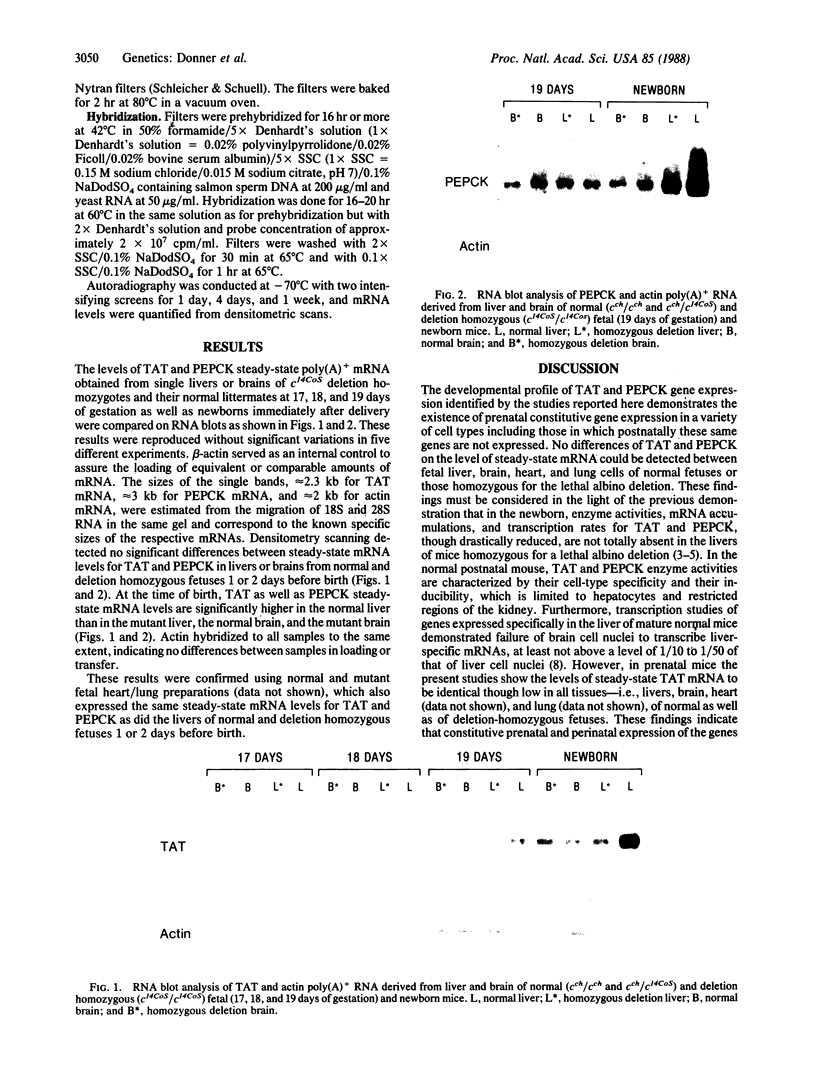
Abstract
Deletions in chromosome 7 of the mouse have been shown to cause failure of expression of certain liver-specific enzymes in newborn deletion homozygotes. Among these enzymes are L-tyrosine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase (EC 2.6.1.5) and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) [GTP:oxaloacetate carboxy-lase (transphosphorylating); EC 4.1.1.32]. The studies reported here show that in fetal stages constitutive expression of the relevant genes on the level of steady-state mRNA is identical in the livers of homozygous deletion mutants and normal littermates. Furthermore, prenatally these enzymes are expressed also in cell types other than hepatocytes. Thus, the putative trans-acting regulatory factors encoded in the deleted region of chromosome 7 of the mouse appear to be concerned specifically with the regulation of cell type-specific inducible expression of various hepatocyte-specific genes, whereas constitutive expression of the same genes is not affected.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker P., Renkawitz R., Schütz G. Tissue-specific DNaseI hypersensitive sites in the 5'-flanking sequences of the tryptophan oxygenase and the tyrosine aminotransferase genes. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2015–2020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02084.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cori C. F., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S., Shaw P. A., Robinson C. Correction of a genetically caused enzyme defect by somatic cell hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6611–6614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Developmental genetics of hepatic gluconeogenic enzymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1986;478:101–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb15524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Genetic control of morphogenetic and biochemical differentiation: lethal albino deletions in the mouse. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):225–237. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfeld A. E., Firestone G. L., Shaw P. A., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Recessive lethal deletion on mouse chromosome 7 affects glucocorticoid receptor binding activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1431–1434. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killary A. M., Fournier R. E. A genetic analysis of extinction: trans-dominant loci regulate expression of liver-specific traits in hepatoma hybrid cells. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loose D. S., Shaw P. A., Krauter K. S., Robinson C., Englard S., Hanson R. W., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Trans regulation of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) gene, identified by deletions in chromosome 7 of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5184–5188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothrock R., Lee K. L., Isham K. R., Johnson A. C., Kenney F. T. Different mechanisms control developmental activation of transcription of genes subject to identical hormonal regulation in adult liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 14;144(3):1182–1187. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91436-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid W., Müller G., Schütz G., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Deletions near the albino locus on chromosome 7 of the mouse affect the level of tyrosine aminotransferase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2866–2869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorndike J., Trigg M. J., Stockert R., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S., Cori C. F. Multiple biochemical effects of a series of x-ray induced mutations at the albino locus in the mouse. Biochem Genet. 1973 May;9(1):25–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00485588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoo-Warren H., Monahan J. E., Short J., Short H., Bruzel A., Wynshaw-Boris A., Meisner H. M., Samols D., Hanson R. W. Isolation and characterization of the gene coding for cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) from the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3656–3660. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







