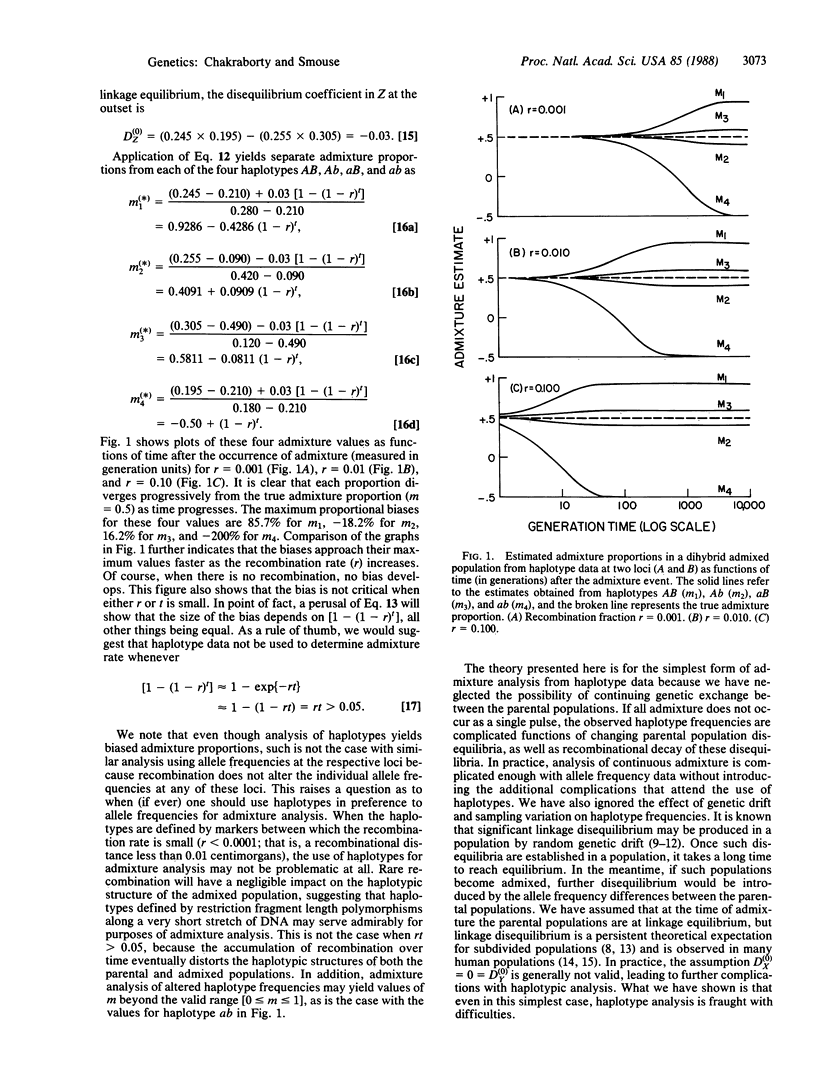
Abstract
A population formed by genetic admixture of two or more source populations may exhibit considerable linkage disequilibrium between genetic loci. In the presence of recombination, this linkage disequilibrium declines with time, a fact that is often ignored when considering haplotypes of closely linked systems [e.g., Gm serum group (gamma globulins), HLA, and, more recently, restriction fragment length polymorphisms]. Recombination alters haplotype frequencies over time, and the haplotype-derived measures of admixture proportions from haplotype frequencies in generations following the admixture event become progressively more biased. The direction and extent of this bias can be predicted only when the history of admixture is known. Numerical illustration suggests that this bias is problematic whenever rt greater than 0.05, where r is the recombination rate between linked loci and t is the time (in generations) that has elapsed since the admixture event. In general, even the haplotype frequencies defined by multiple restriction fragment length polymorphism should be used with caution for admixture analysis. When recombination rates or the time since admixture are not precisely known, it is advantageous to consider each restriction fragment length polymorphism site separately for admixture analysis.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J., Ward R. H. Admixture studies and the detection of selection. Science. 1973 Jun 15;180(4091):1137–1143. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4091.1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. H. Sample sizes required to detect linkage disequilibrium between two or three loci. Theor Popul Biol. 1975 Oct;8(2):184–201. doi: 10.1016/0040-5809(75)90031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty R. Estimation of race admixture--a new method. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1975 May;42(3):507–511. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330420319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elston R. C. The estimation of admixture in racial hybrids. Ann Hum Genet. 1971 Jul;35(1):9–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1956.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhard D. S., Kidd K. K., Kidd J. R., Egeland J. A., Housman D. E. Identification of a recent recombination event within the human beta-globin gene cluster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7875–7879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long J. C., Smouse P. E. Intertribal gene flow between the Ye'cuana and Yanomama: genetic analysis of an admixed village. Am J Phys Anthropol. 1983 Aug;61(4):411–422. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.1330610403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Linkage disequilibrium in subdivided populations. Genetics. 1973 Sep;75(1):213–219. doi: 10.1093/genetics/75.1.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Kimura M. Linkage disequilibrium at steady state determined by random genetic drift and recurrent mutation. Genetics. 1969 Sep;63(1):229–238. doi: 10.1093/genetics/63.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smouse P. E., Neel J. V., Liu W. Multiple-locus departures from panmictic equilibrium within and between village gene pools of Amerindian tribes at different stages of agglomeration. Genetics. 1983 May;104(1):133–153. doi: 10.1093/genetics/104.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smouse P. E., Neel J. V. Multivariate analysis of gametic disequilibrium in the Yanomama. Genetics. 1977 Apr;85(4):733–752. doi: 10.1093/genetics/85.4.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sved J. A. The stability of linked systems of loci with a small population size. Genetics. 1968 Aug;59(4):543–563. doi: 10.1093/genetics/59.4.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treco D., Thomas B., Arnheim N. Recombination hot spot in the human beta-globin gene cluster: meiotic recombination of human DNA fragments in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2029–2038. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



