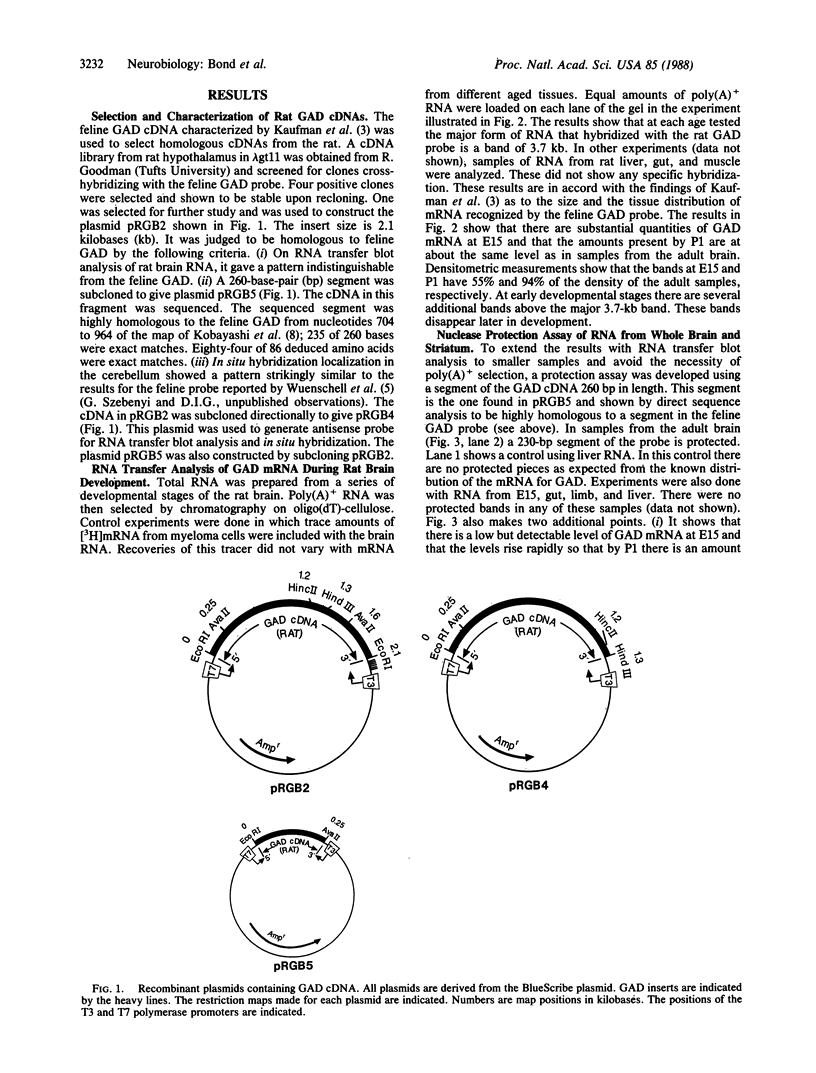
Abstract
The time and pattern of appearance of glutamic acid decarboxylase (glutamate decarboxylase; EC 4.1.1.15) (GAD) mRNA during the development of the rat brain were analyzed. RNA transfer blot analysis of poly(A)+ RNA from whole brain shows that a 3.7-kilobase transcript is the most abundant form of the message from embryonic day 15 (E15) through adulthood. By E15 this form is present at about 50% of its adult abundance relative to other poly(A)+ mRNA species. At birth the abundance is approximately the same as in the adult. In contrast, the enzyme activity level is only 8% of the adult level at birth and takes 3 weeks to reach adult levels. There are qualitative changes in GAD mRNA during development. Several large (7-9 kilobases) transcripts with strong homology to GAD are enriched in early developmental stages but are barely detectable in the adult. A nuclease protection assay shows a developmentally regulated heterogeneity in a coding portion of the mRNA.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Enna S. J. Neurochemical aspects of the ontogenesis of GABAnergic neurons in the rat brain. Brain Res. 1976 Jul 23;111(1):119–133. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(76)91053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb D. I., Chang Y. C., Schwob J. E. Monoclonal antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8808–8812. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. F., Legay F., Dumas S., Tappaz M., Mallet J. Molecular cloning, expression and in situ hybridization of rat brain glutamic acid decarboxylase messenger RNA. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jan 14;73(2):173–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90013-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman D. L., McGinnis J. F., Krieger N. R., Tobin A. J. Brain glutamate decarboxylase cloned in lambda gt-11: fusion protein produces gamma-aminobutyric acid. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1138–1140. doi: 10.1126/science.3518061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Kaufman D. L., Tobin A. J. Glutamic acid decarboxylase cDNA: nucleotide sequence encoding an enzymatically active fusion protein. J Neurosci. 1987 Sep;7(9):2768–2772. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-09-02768.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penny G. R., Afsharpour S., Kitai S. T. The glutamate decarboxylase-, leucine enkephalin-, methionine enkephalin- and substance P-immunoreactive neurons in the neostriatum of the rat and cat: evidence for partial population overlap. Neuroscience. 1986 Apr;17(4):1011–1045. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuenschell C. W., Fisher R. S., Kaufman D. L., Tobin A. J. In situ hybridization to localize mRNA encoding the neurotransmitter synthetic enzyme glutamate decarboxylase in mouse cerebellum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6193–6197. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]