Abstract
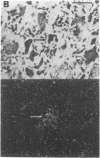
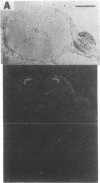
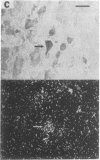
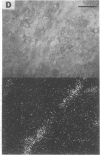
Autoradiographic studies localize [3H]bradykinin receptor binding sites to the substantia gelatinosa, dorsal root, and a subset of small cells in both the dorsal root and trigeminal ganglia of the guinea pig. [3H]Bradykinin labeling is also observed over myocardial/coronary visceral afferent fibers. The localization of [3H]bradykinin receptors to nociceptive pathways supports a role for bradykinin in pain mediation. Several bradykinin antagonists block bradykinin-induced acute vascular pain in the rat. The bradykinin antagonists also relieve bradykinin- and urate-induced hyperalgesia in the rat paw. These results indicate that bradykinin is a physiologic mediator of pain and that bradykinin antagonists have analgesic activity in both acute and chronic pain models.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deffenu G., Pegrassi L., Lumachi B. The use of bradykinin-induced effects in rats as an assay for analgesic drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1966 Feb;18(2):135–135. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1966.tb07838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Innis R. B., Manning D. C., Stewart J. M., Snyder S. H. [3H]Bradykinin receptor binding in mammalian tissue membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2630–2634. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. C., Snyder S. H., Kachur J. F., Miller R. J., Field M. Bradykinin receptor-mediated chloride secretion in intestinal function. Nature. 1982 Sep 16;299(5880):256–259. doi: 10.1038/299256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. C., Vavrek R., Stewart J. M., Snyder S. H. Two bradykinin binding sites with picomolar affinities. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 May;237(2):504–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson G. A. Analysis of radioligand binding experiments. A collection of computer programs for the IBM PC. J Pharmacol Methods. 1985 Nov;14(3):213–228. doi: 10.1016/0160-5402(85)90034-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odya C. E., Goodfriend T. L., Peña C. Bradykinin receptor-like binding studied with iodinated analogues. Biochem Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;29(2):175–185. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(80)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDALL L. O., SELITTO J. J. A method for measurement of analgesic activity on inflamed tissue. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1957 Sep 1;111(4):409–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roscher A. A., Manganiello V. C., Jelsema C. L., Moss J. Receptors for bradykinin in intact cultured human fibroblasts. Identification and characterization by direct binding study. J Clin Invest. 1983 Aug;72(2):626–635. doi: 10.1172/JCI111012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SICUTERI F., FRANCIULLACCI M., FRANCHI G., DELBIANCO P. L. SEROTONIN--BRADYKININ POTENTIATION ON THE PAIN RECEPTORS IN MAN. Life Sci. 1965 Feb;4:309–316. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(65)90147-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staszewka-Barczak J., Ferreira S. H., Vane J. R. An excitatory nociceptive cardiac reflex elicited by bradykinin and potentiated by prostaglandins and myocardial ischaemia. Cardiovasc Res. 1976 May;10(3):314–327. doi: 10.1093/cvr/10.3.314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steranka L. R., DeHaas C. J., Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M., Enna S. J., Snyder S. H. Antinociceptive effects of bradykinin antagonists. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Apr 14;136(2):261–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90723-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida Y., Murao S. Bradykinin-induced excitation of afferent cardiac sympathetic nerve fibers. Jpn Heart J. 1974 Jan;15(1):84–91. doi: 10.1536/ihj.15.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vavrek R. J., Stewart J. M. Competitive antagonists of bradykinin. Peptides. 1985 Mar-Apr;6(2):161–164. doi: 10.1016/0196-9781(85)90033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE J. C. Cardiac pain: anatomic pathways and physiologic mechanisms. Circulation. 1957 Oct;16(4):644–655. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.16.4.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]