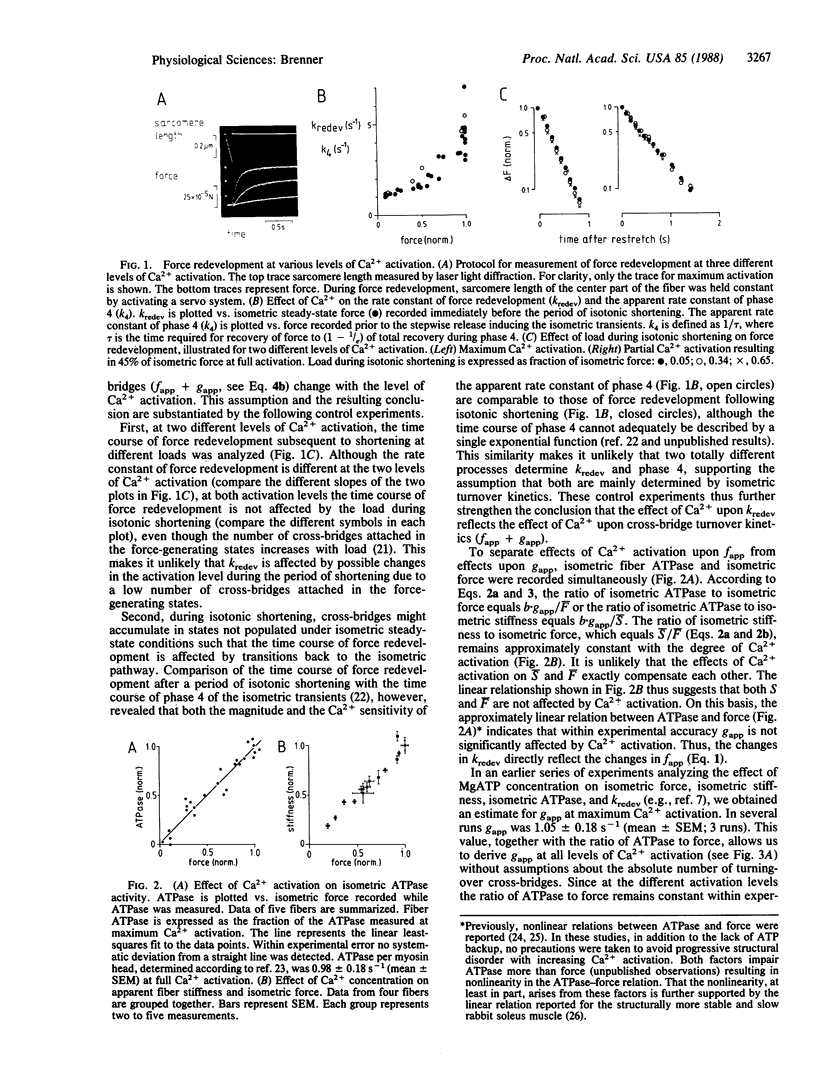
Abstract
The effect of Ca2+ upon the rate constant of force redevelopment following a period of isotonic shortening with immediate restretch to the starting sarcomere length was studied in rabbit psoas fibers at 5 degrees C. Control experiments support the assumption that the rate constant of force redevelopment represents isometric cross-bridge turnover kinetics (fapp + gapp), where fapp and gapp are the rate constants characterizing the transitions from the non-force-generating states to the force-generating states and back to the non-force-generating states, respectively. Parallel measurements of the rate constant of force redevelopment and of force, stiffness, and fiber ATPase during isometric contraction allow the effect of Ca2+ upon fapp and gapp to be determined. Analysis reveals that Ca2+ has a marked effect upon fapp, while gapp remains approximately unchanged. Furthermore, in the range above 25-30% of maximum Ca2+ activation, regulation of force, stiffness, and ATPase is mediated through changes in fapp. Below this range, however, it cannot be ruled out that, in addition, cross-bridges are also switched in and out of the turnover process ("recruitment"). As a consequence of regulation through turnover kinetics, both Ca2+ sensitivity and the slope of force-pCa (-log[Ca2+]) relations are shown to be affected by the ratio fapp/gapp, which may represent an important mechanism of modulation of contractile function in addition to modulation through changes within the regulatory protein system.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner B., Eisenberg E. Rate of force generation in muscle: correlation with actomyosin ATPase activity in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3542–3546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. The cross-bridge cycle in muscle. Mechanical, biochemical, and structural studies on single skinned rabbit psoas fibers to characterize cross-bridge kinetics in muscle for correlation with the actomyosin-ATPase in solution. Basic Res Cardiol. 1986;81 (Suppl 1):1–15. doi: 10.1007/978-3-662-11374-5_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebashi S., Endo M., Otsuki I. Control of muscle contraction. Q Rev Biophys. 1969 Nov;2(4):351–384. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Hill T. L. Muscle contraction and free energy transduction in biological systems. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):999–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.3156404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs F. The binding of calcium to detergent-extracted rabbit psoas muscle fibres during relaxation and force generation. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Aug;6(4):477–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00712584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glyn H., Sleep J. Dependence of adenosine triphosphatase activity of rabbit psoas muscle fibres and myofibrils on substrate concentration. J Physiol. 1985 Aug;365:259–276. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellam D. C., Podolsky R. J. Force measurements in skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1969 Feb;200(3):807–819. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1969.sp008723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R. Relationships between chemical and mechanical events during muscular contraction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:119–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Eisenberg E., Chalovich J. M. Theoretical models for cooperative steady-state ATPase activity of myosin subfragment-1 on regulated actin. Biophys J. 1981 Jul;35(1):99–112. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84777-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J. Activation in a skeletal muscle contraction model with a modification for insect fibrillar muscle. Biophys J. 1969 Apr;9(4):547–570. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(69)86403-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian F. J. The effect of calcium on the force-velocity relation of briefly glycerinated frog muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1971 Oct;218(1):117–145. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Krasner B. Force and ATPase rate in skinned skeletal muscle fibers. Fed Proc. 1982 May;41(7):2232–2237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. M., Umazume Y., Kushmerick M. J. Ca2+ dependence of tension and ADP production in segments of chemically skinned muscle fibers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 May 14;430(2):352–365. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(76)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persechini A., Stull J. T., Cooke R. The effect of myosin phosphorylation on the contractile properties of skinned rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7951–7954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky R. J., Teichholz L. E. The relation between calcium and contraction kinetics in skinned muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1970 Nov;211(1):19–35. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld S. S., Taylor E. W. The ATPase mechanism of skeletal and smooth muscle acto-subfragment 1. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11908–11919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schädler M. Proportional Aktivierung von ATPase-Aktivität und Kontraktionsspannung durch Calciumionen in isolierten contractilen Strukturen verschiedener Muskelarten. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1967;296(1):70–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Huxley H. E., Finch J. T. Regulation of skeletal muscle contraction. II. Structural studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 30;72(3):619–632. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vibert P. J., Haselgrove J. C., Lowy J., Poulsen F. R. Structural changes in actin-containing filaments of muscle. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):757–767. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]