Abstract
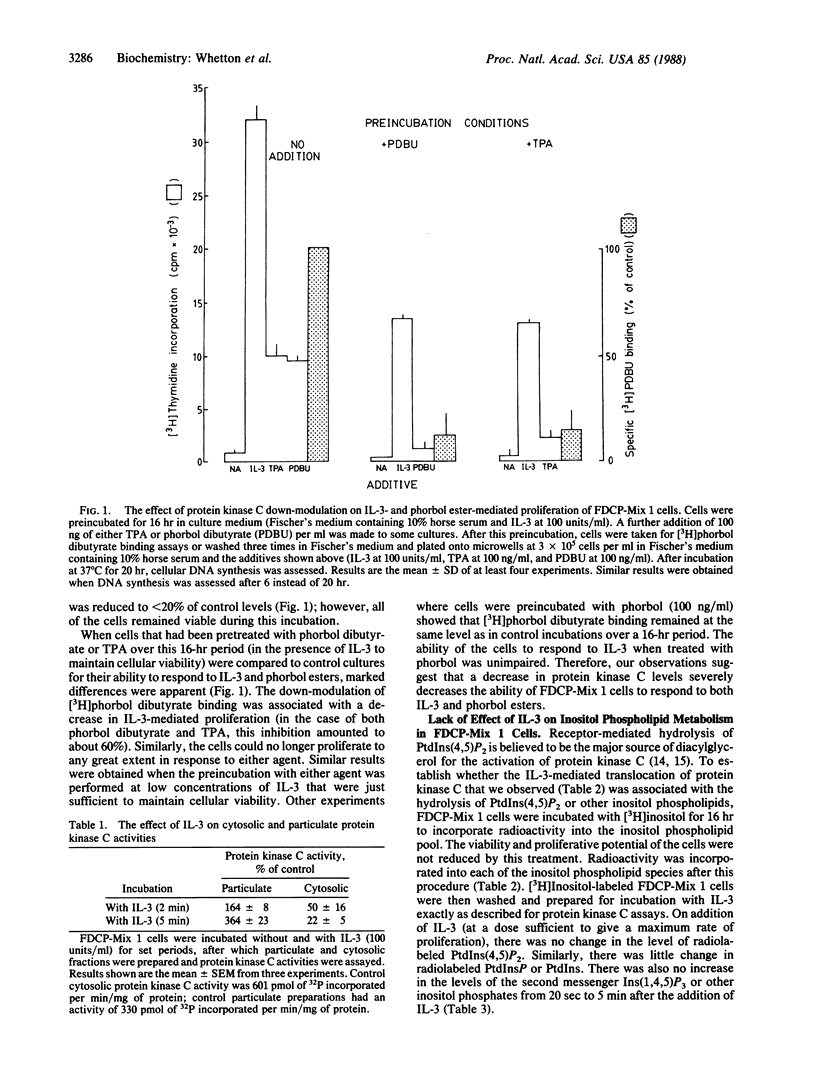
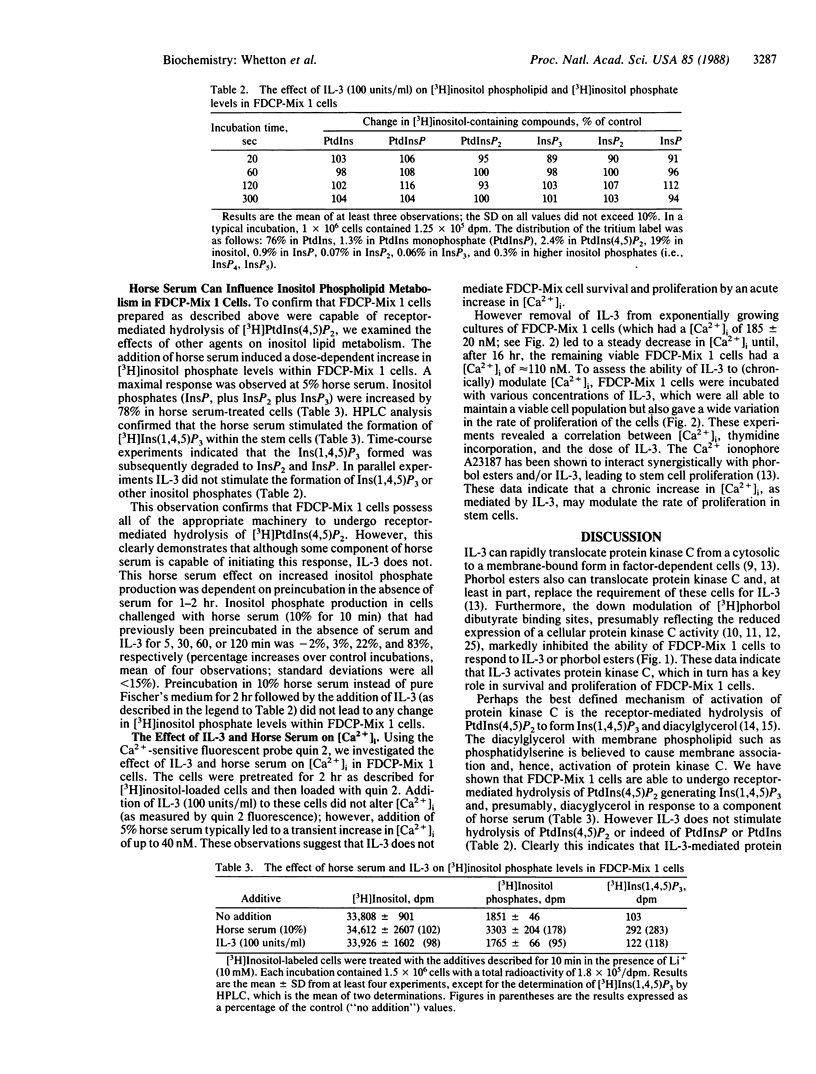
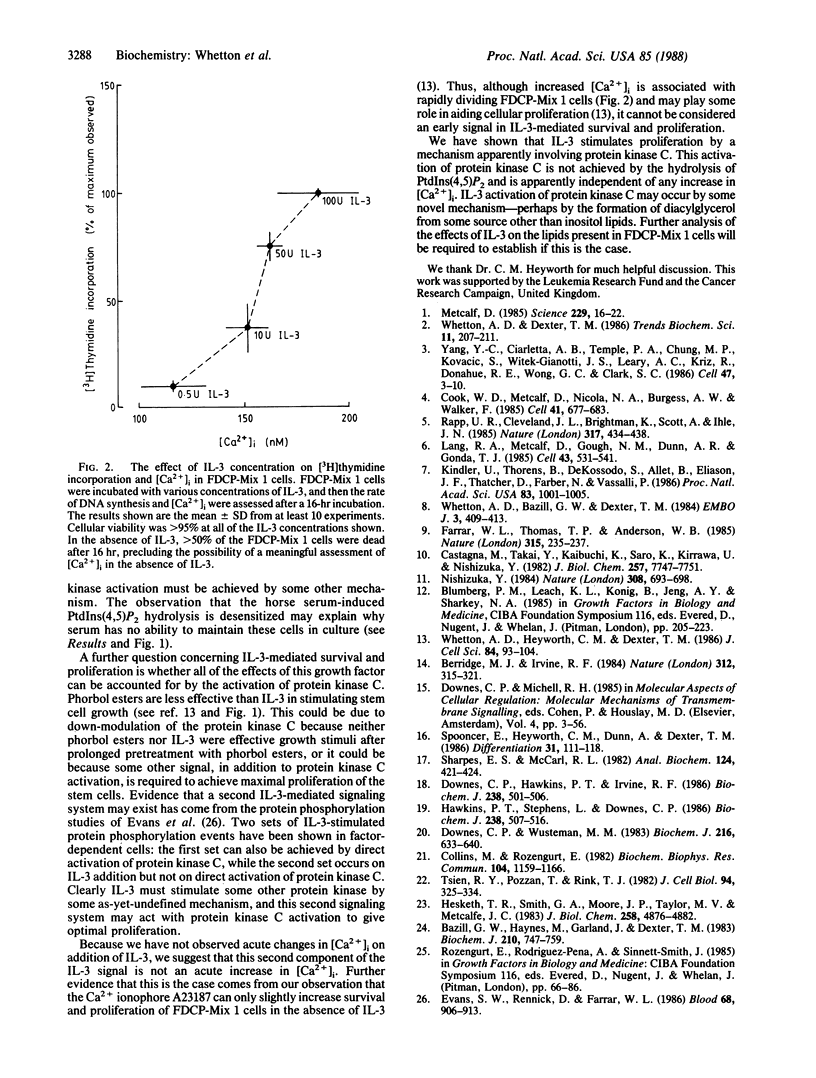
Interleukin 3 (IL-3) is required for the survival and proliferation of the FDCP-Mix 1 multipotent stem cell line. IL-3 or phorbol esters can rapidly translocate protein kinase C from a cytosolic to a membrane-bound form in these cells. Phorbol esters were able to partially replace the requirement of FDCP-Mix 1 cells for IL-3. Down-modulation of protein kinase C levels by chronic treatment with phorbol ester markedly reduced the ability of the cells to proliferate in response to either IL-3 or phorbol esters. These data indicate that IL-3 can activate protein kinase C, leading to the survival and proliferation of stem cells. Protein kinase C is activated conventionally by complexing with diacylglycerol which accumulates in the cell membrane after agonist-stimulated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate [PtdIns(4,5)P2]. However, there was no detectable breakdown of PtdIns(4,5)P2 when IL-3 was added to FDCP-Mix 1 cells, nor was there detectable accumulation of inositol phosphates in response to IL-3. In contrast, rapid hydrolysis of PtdIns(4,5)P2 and accumulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate was elicited by readdition of horse serum to serum-starved cells, thus indicating that these cells possess the necessary machinery to undergo agonist-mediated inositol phospholipid breakdown. We conclude that the mechanism whereby IL-3 can activate protein kinase C leading to proliferation is not associated with inositol phospholipid hydrolysis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bazill G. W., Haynes M., Garland J., Dexter T. M. Characterization and partial purification of a haemopoietic cell growth factor in WEHI-3 cell conditioned medium. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 15;210(3):747–759. doi: 10.1042/bj2100747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Leach K. L., König B., Jeng A. Y., Sharkey N. A. Receptors for the phorbol ester tumour promoters. Ciba Found Symp. 1985;116:205–223. doi: 10.1002/9780470720974.ch13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M., Rozengurt E. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in murine fibroblasts by the tumour promoter teleocidin: relationship to phorbol esters and vasopressin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Feb 26;104(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91372-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. D., Metcalf D., Nicola N. A., Burgess A. W., Walker F. Malignant transformation of a growth factor-dependent myeloid cell line by Abelson virus without evidence of an autocrine mechanism. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):677–683. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Irvine R. F. Inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and not phosphatidylinositol 3,4-bisphosphate is the probable precursor of inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in agonist-stimulated parotid gland. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):501–506. doi: 10.1042/bj2380501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. P., Wusteman M. M. Breakdown of polyphosphoinositides and not phosphatidylinositol accounts for muscarinic agonist-stimulated inositol phospholipid metabolism in rat parotid glands. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 15;216(3):633–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2160633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. W., Rennick D., Farrar W. L. Multilineage hematopoietic growth factor interleukin 3 and direct activators of protein kinase C stimulate phosphorylation of common substrates. Blood. 1986 Oct;68(4):906–913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar W. L., Thomas T. P., Anderson W. B. Altered cytosol/membrane enzyme redistribution on interleukin-3 activation of protein kinase C. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):235–237. doi: 10.1038/315235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins P. T., Stephens L., Downes C. P. Rapid formation of inositol 1,3,4,5-tetrakisphosphate and inositol 1,3,4-trisphosphate in rat parotid glands may both result indirectly from receptor-stimulated release of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate from phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 1;238(2):507–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2380507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesketh T. R., Smith G. A., Moore J. P., Taylor M. V., Metcalfe J. C. Free cytoplasmic calcium concentration and the mitogenic stimulation of lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4876–4882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Thorens B., de Kossodo S., Allet B., Eliason J. F., Thatcher D., Farber N., Vassalli P. Stimulation of hematopoiesis in vivo by recombinant bacterial murine interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1001–1005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang R. A., Metcalf D., Gough N. M., Dunn A. R., Gonda T. J. Expression of a hemopoietic growth factor cDNA in a factor-dependent cell line results in autonomous growth and tumorigenicity. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):531–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. The granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factors. Science. 1985 Jul 5;229(4708):16–22. doi: 10.1126/science.2990035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Cleveland J. L., Brightman K., Scott A., Ihle J. N. Abrogation of IL-3 and IL-2 dependence by recombinant murine retroviruses expressing v-myc oncogenes. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):434–438. doi: 10.1038/317434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharps E. S., McCarl R. L. A high-performance liquid chromatographic method to measure 32P incorporation into phosphorylated metabolites in cultured cells. Anal Biochem. 1982 Aug;124(2):421–424. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooncer E., Heyworth C. M., Dunn A., Dexter T. M. Self-renewal and differentiation of interleukin-3-dependent multipotent stem cells are modulated by stromal cells and serum factors. Differentiation. 1986;31(2):111–118. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetton A. D., Bazill G. W., Dexter T. M. Haemopoietic cell growth factor mediates cell survival via its action on glucose transport. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):409–413. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01821.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whetton A. D., Heyworth C. M., Dexter T. M. Phorbol esters activate protein kinase C and glucose transport and can replace the requirement for growth factor in interleukin-3-dependent multipotent stem cells. J Cell Sci. 1986 Aug;84:93–104. doi: 10.1242/jcs.84.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. C., Ciarletta A. B., Temple P. A., Chung M. P., Kovacic S., Witek-Giannotti J. S., Leary A. C., Kriz R., Donahue R. E., Wong G. G. Human IL-3 (multi-CSF): identification by expression cloning of a novel hematopoietic growth factor related to murine IL-3. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):3–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90360-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



