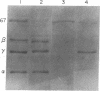
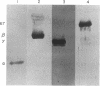
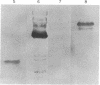
Abstract
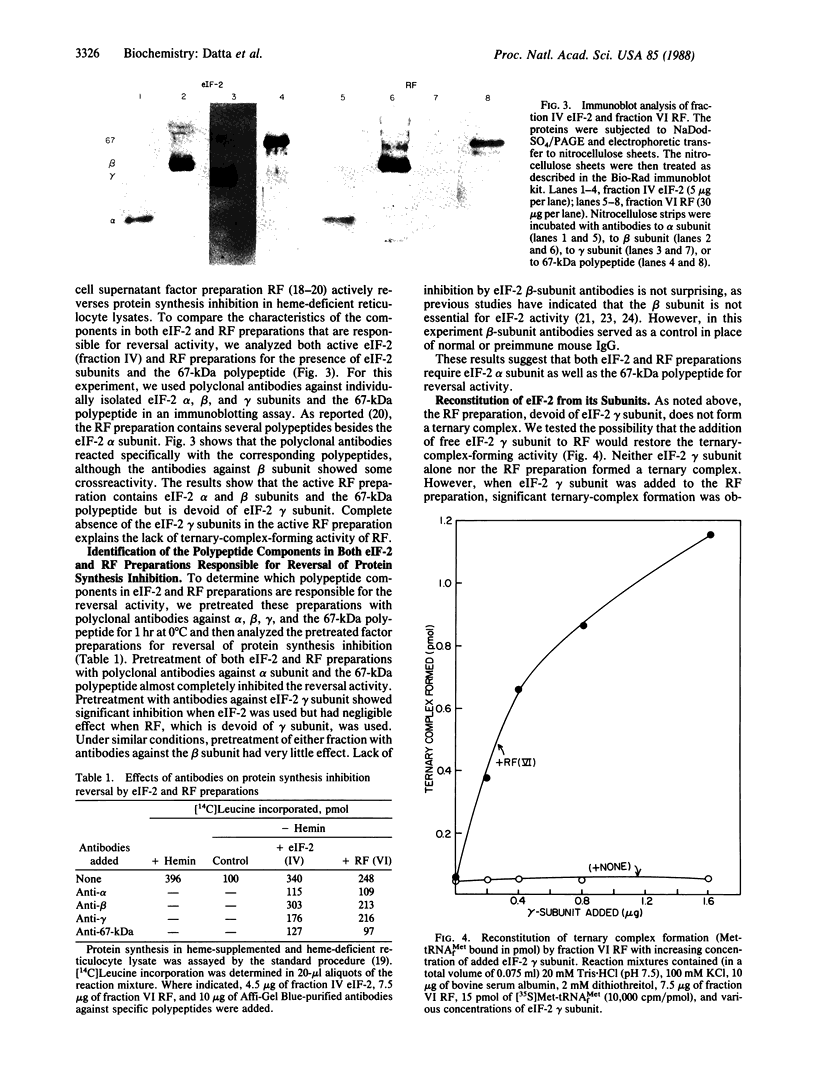
During heme deficiency in reticulocyte lysates, the heme-regulated protein synthesis inhibitor, HRI, phosphorylates the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2) and thus inhibits protein synthesis. Two factors, eIF-2 and a reticulocyte-lysate supernatant factor that we term RF, reverse this inhibition. We now report the following. (i) An active eIF-2 preparation contained, in addition to the three subunits (alpha, beta, and gamma), a 67-kDa polypeptide. Pretreatment of eIF-2 with polyclonal antibodies against either isolated alpha subunit or 67-kDa polypeptide almost completely inhibited the reversal activity. Upon further fractionation, three-subunit eIF-2 and the 67-kDa polypeptide were resolved. Neither the three-subunit eIF-2 nor the 67-kDa polypeptide alone was active in protein synthesis inhibition reversal. The activity was, however, restored by combining both the three-subunit eIF-2 and the 67-kDa polypeptide. (ii) Active RF preparations contained eIF-2 alpha (unphosphorylated) and beta subunits and the 67-kDa polypeptide. As with eIF-2, prior treatment of the RF preparation with antibodies to either the alpha subunit or the 67-kDa polypeptide almost completely inhibited the reversal activity. The RF preparation devoid of eIF-2 gamma subunit did not form ternary complex (Met-tRNA(fMet).eIF-2.GTP). The eIF-2 gamma subunit in the free form was isolated, and addition of this isolated gamma subunit to RF promoted significant ternary-complex formation. (iii) Purified HRI efficiently phosphorylated the alpha subunit in the three subunit eIF-2. However, the extent of such phosphorylation was significantly reduced when eIF-2 containing the 67-kDa polypeptide was used. The 67-kDa polypeptide apparently protected eIF-2 alpha subunit from HRI-catalyzed phosphorylation but did not inhibit HRI activity. Based on these results, we suggest that the protein synthesis inhibition reversal activity in both eIF-2 and RF is due to the same components--namely, eIF-2 alpha subunit and the 67-kDa polypeptide. The 67-kDa polypeptide protects eIF-2 alpha subunit from HRI-catalyzed phosphorylation and may also be a necessary component of the functioning eIF-2 molecule.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amesz H., Goumans H., Haubrich-Morree T., Voorma H. O., Benne R. Purification and characterization of a protein factor that reverses the inhibition of protein synthesis by the heme-regulated translational inhibitor in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):513–520. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhuri A., Stringer E. A., Valenzuela D., Maitra U. Characterization of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 containing two polypeptide chains of Mr = 48,000 and 38,000. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3988–3994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J. Functional relationships between a reticulocyte polypeptide-chain-initiation factor (IF-MP) and the translational inhibitor involved in regulation of protein synthesis by haemin. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):413–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10531.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens M. J., Henshaw E. C., Rahamimoff H., London I. M. Met-tRNAfMet binding to 40S ribosomal subunits: a site for the regulation of initiation of protein synthesis by hemin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):2946–2950. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.2946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das A., Bagchi M. K., Ghosh-Dastidar P., Gupta N. K. Protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes. A study of peptide chain initiation using native and beta-subunit-depleted eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1282–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace M., Bagchi M., Ahmad F., Yeager T., Olson C., Chakravarty I., Nasrin N., Banerjee A., Gupta N. K. Protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes: a study of the mechanism of action of the protein factor RF that reverses protein synthesis inhibition in heme-deficient reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5379–5383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace M., Ralston R. O., Banerjee A. C., Gupta N. K. Protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes: characteristics of the protein factor RF that reverses inhibition of protein synthesis in heme-deficient reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6517–6521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross M. Control of protein synthesis by hemin. Isolation and characterization of a supernatant factor from rabbit reticulocyte lysate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 1;447(4):445–459. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90082-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny A., Safer B. Purification of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2-eukaryotic initiation factor 2B complex and characterization of its guanine nucleotide exchange activity during protein synthesis initiation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3402–3408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matts R. L., Levin D. H., London I. M. Effect of phosphorylation of the alpha-subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 on the function of reversing factor in the initiation of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsui K., Datta A., Ochoa S. Removal of beta subunit of the eukaryotic polypeptide chain initiation factor 2 by limited proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4128–4132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldave K. Eukaryotic protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1109–1149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa S. Regulation of protein synthesis initiation in eucaryotes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jun;223(2):325–349. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston R. O., Das A., Dasgupta A., Roy R., Palmieri S., Gupta N. K. Protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes: characteristics of a ribosomal factor that reverses inhibition of protein synthesis in heme-deficient lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4858–4862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston R. O., Das A., Grace M., Das H., Gupta N. K. Protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocytes: characteristics of a postribosomal supernatant factor that reverses inhibition of protein synthesis in heme-deficient lysates and inhibition of ternary complex (Met-tRNAfMet.eIF-2.GTP) formation by heme-regulated inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5490–5494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranu R. S., Levin D. H., Delaunay J., Ernst V., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates: characteristics of inhibition of protein synthesis by a translational inhibitor from heme-deficient lysates and its relationship to the initiation factor which binds Met-tRNAf. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2720–2724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel P. A., Merrick W. C., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. Regulation of a protein synthesis initiation factor by adenovirus virus-associated RNA. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):196–200. doi: 10.1038/313196a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Kerr I. M. Interferon-mediated, double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase is inhibited in extracts from vaccinia virus-infected cells. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):229–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.229-236.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. C., Ranu R. S. Regulation of protein synthesis in rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Requirement of initiation factor eIF-2 holoprotein for substrate specificity of heme-regulated protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):162–164. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81103-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B. 2B or not 2B: regulation of the catalytic utilization of eIF-2. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA prevents phosphorylation of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha subunit subsequent to infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4321–4325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Manne V., Mauser L., Ochoa S. Polypeptide chain initiation in eukaryotes: reversibility of the ternary complex-forming reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1232–1235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekierka J., Mariano T. M., Reichel P. A., Mathews M. B. Translational control by adenovirus: lack of virus-associated RNAI during adenovirus infection results in phosphorylation of initiation factor eIF-2 and inhibition of protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1959–1963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahba A. J., Woodley C. L. Molecular aspects of development in the brine shrimp Artemia. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1984;31:221–265. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60379-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]