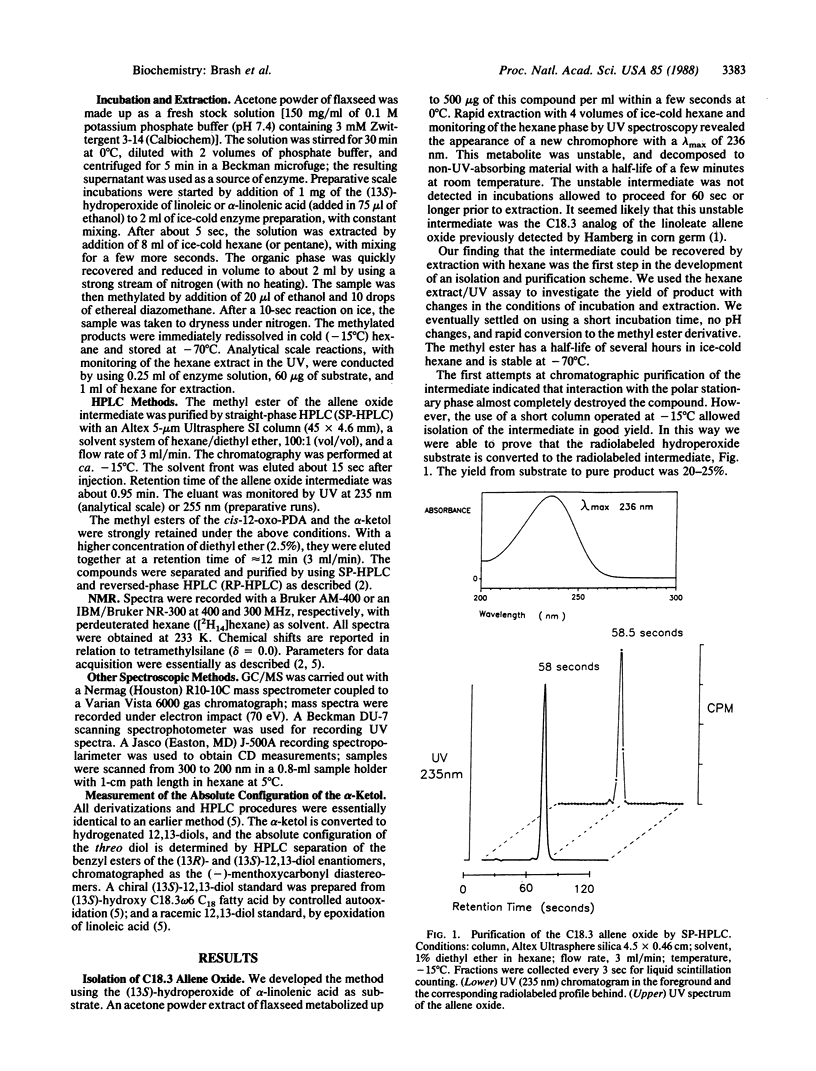
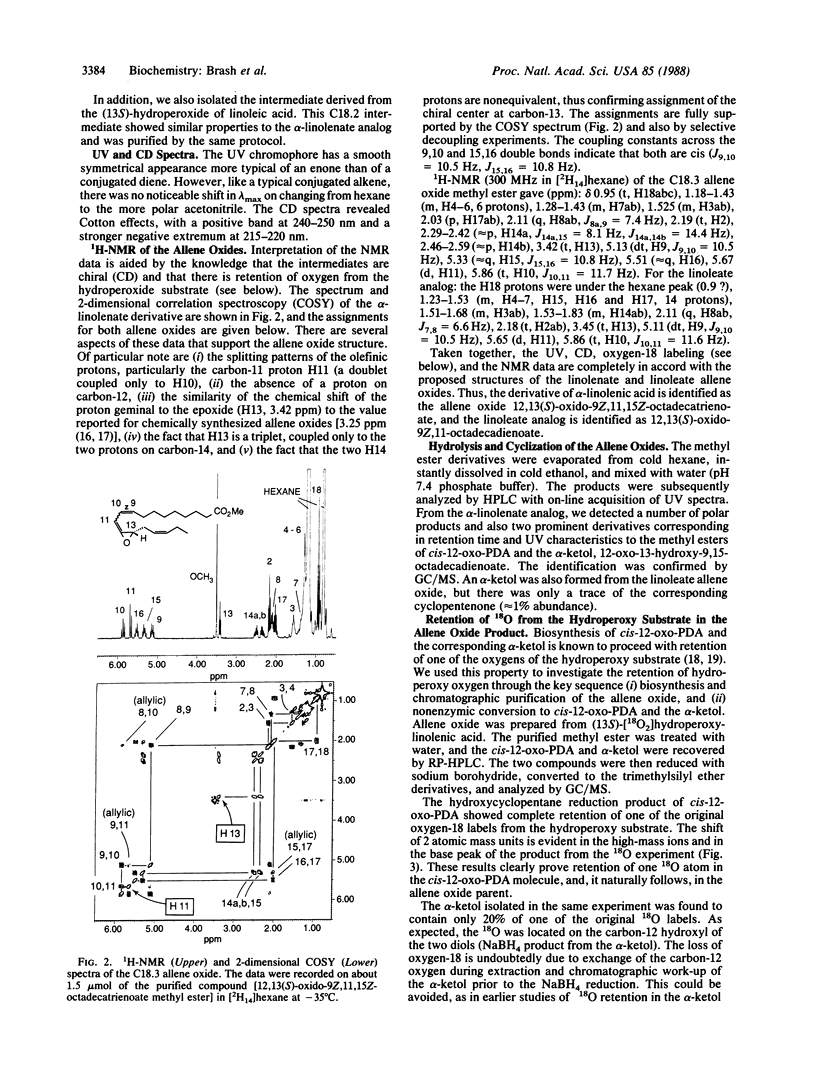
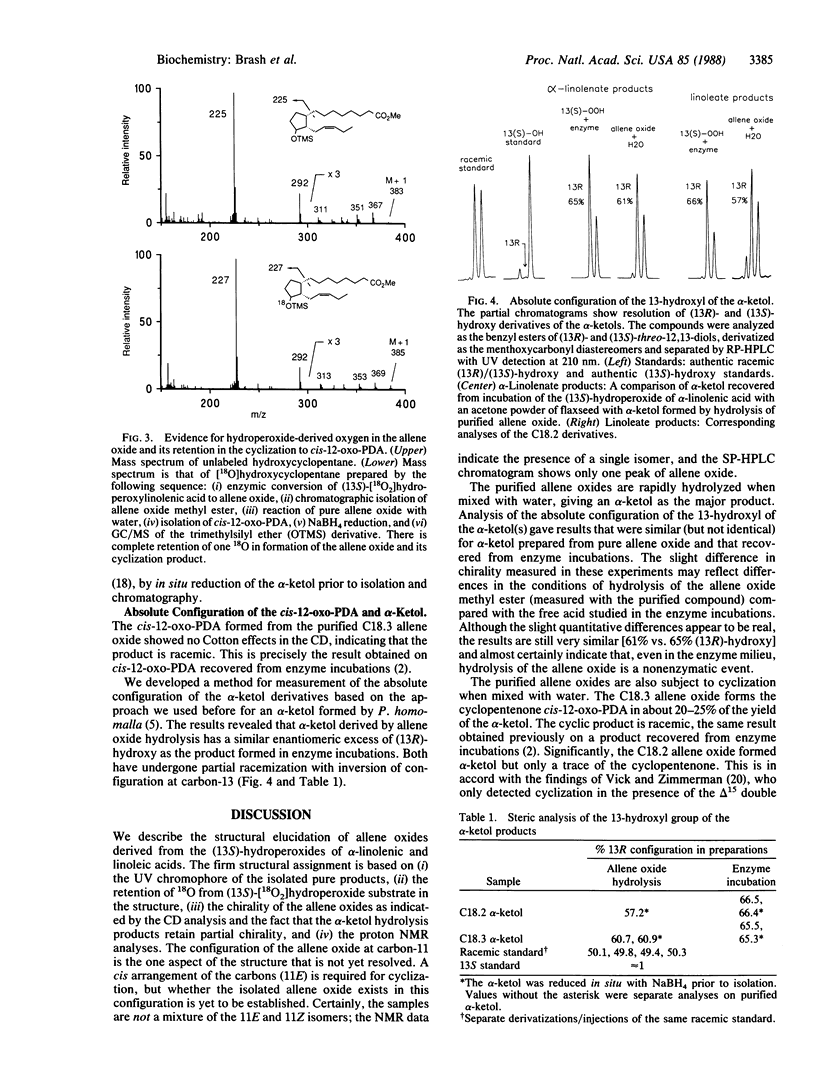
Abstract
Allene oxides are unstable epoxides that have been implicated as intermediates in the biotransformation of hydroperoxyicosatetraenoic acids and related hydroperoxides to ketols and cyclopentenones. Direct proof of the structure of the putative allene oxide intermediates has been hampered by their extreme instability under the conditions of their biosynthesis (t1/2 approximately 15-30 sec at 0 degree C and pH 7.4). We now report the isolation and structural elucidation of allene oxides prepared from the (13S)-hydroperoxides of linoleic and linolenic acids. The compounds were biosynthesized by using a very active enzyme preparation from flaxseed. After a 5-sec incubation at 0 degrees C, the allene oxide metabolites were extracted and purified as the methyl ester derivatives at -15 degrees C. The structures were established by UV, CD, NMR, and oxygen-18 labeling experiments. 12,13(S)-Oxido-9Z,11-octadecadienoic acid is derived from linoleic acid, and 12,13(S)-oxido-9Z,11,15Z-octadecatrienoic acid is from linolenic acid. Analysis of the breakdown products formed on exposure to water led to identification of hydrolysis and cyclization products previously characterized as enzymic derivatives of the (13S)-hydroperoxides in flaxseed. Our results give direct proof of the structure of the allene oxide intermediates and should facilitate further investigation of the metabolism of this class of epoxide to prostaglandins, clavulones, and other stable end products.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baertschi S. W., Ingram C. D., Harris T. M., Brash A. R. Absolute configuration of cis-12-oxophytodienoic acid of flaxseed: implications for the mechanism of biosynthesis from the 13(S)-hydroperoxide of linolenic acid. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):18–24. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhagwat S. S., Hamann P. R., Still W. C., Bunting S., Fitzpatrick F. A. Synthesis and structure of the platelet aggregation factor thromboxane A2. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):511–513. doi: 10.1038/315511a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brash A. R., Baertschi S. W., Ingram C. D., Harris T. M. On non-cyclooxygenase prostaglandin synthesis in the sea whip coral, Plexaura homomalla: an 8(R)-lipoxygenase pathway leads to formation of an alpha-ketol and a Racemic prostanoid. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15829–15839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick F. A., Morton D. R., Wynalda M. A. Albumin stabilizes leukotriene A4. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):4680–4683. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldink G. A., Vliegenthart J. F.G., Boldingh J. Oxygen transfer in the enzymatic conversion of 18O-labelled linoleic acid hydroperoxide into the 12-keto-13-hydroxyoctadec-cis-9-enoic acid. FEBS Lett. 1970 Apr 2;7(2):188–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vick B. A., Feng P., Zimmerman D. C. Formation of 12-[18-O]oxo-cis-10, cis-15-phytodienoic acid from 13[18-O]hydroperoxylinolenic acid by hydroperoxide cyclase. Lipids. 1980 Jun;15(6):468–471. doi: 10.1007/BF02534074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vick B. A., Zimmerman D. C. Substrate specificity for the synthesis of cyclic Fatty acids by a flaxseed extract. Plant Physiol. 1979 Mar;63(3):490–494. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.3.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman D. C., Vick B. A. Hydroperoxide isomerase: a new enzyme of lipid metabolism. Plant Physiol. 1970 Sep;46(3):445–453. doi: 10.1104/pp.46.3.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



