Abstract
Mature viral-encoded proteins of tobacco etch virus (TEV) arise by proteolytic processing of a large precursor. The proteinase responsible for most of these cleavages is a viral-encoded 49-kDa protein. All known or predicted cleavage sites in the TEV polyprotein are flanked by the conserved sequence motif Glu-Xaa-Xaa-Tyr-Xaa-Gln-Ser or Gly, with the scissile bond located between the Gln-Ser or Gly dipeptide. By using cell-free systems to manipulate and express cloned cDNA sequences, a 25-amino acid segment containing a putative proteolytic cleavage site of the TEV polyprotein has been introduced into the TEV capsid protein sequence. This recombinant protein is cleaved by the 49-kDa proteinase at the introduced cleavage site, thus demonstrating portability of a functional cleavage site. The role of the conserved amino acid sequence in determining substrate activity was tested by construction of engineered proteins that contained part or all of this motif. A protein that harbored an insertion of the conserved 7-amino acid segment was cleaved by the 49-kDa TEV proteinase. Cleavage of the synthetic precursor was shown to occur accurately between the expected Gln-Ser dipeptide by microsequence analysis. Proteins containing insertions that generated only the Gln-Ser, or only the serine moiety of the conserved sequence, were insensitive to the 49-kDa proteinase.
Full text
PDF


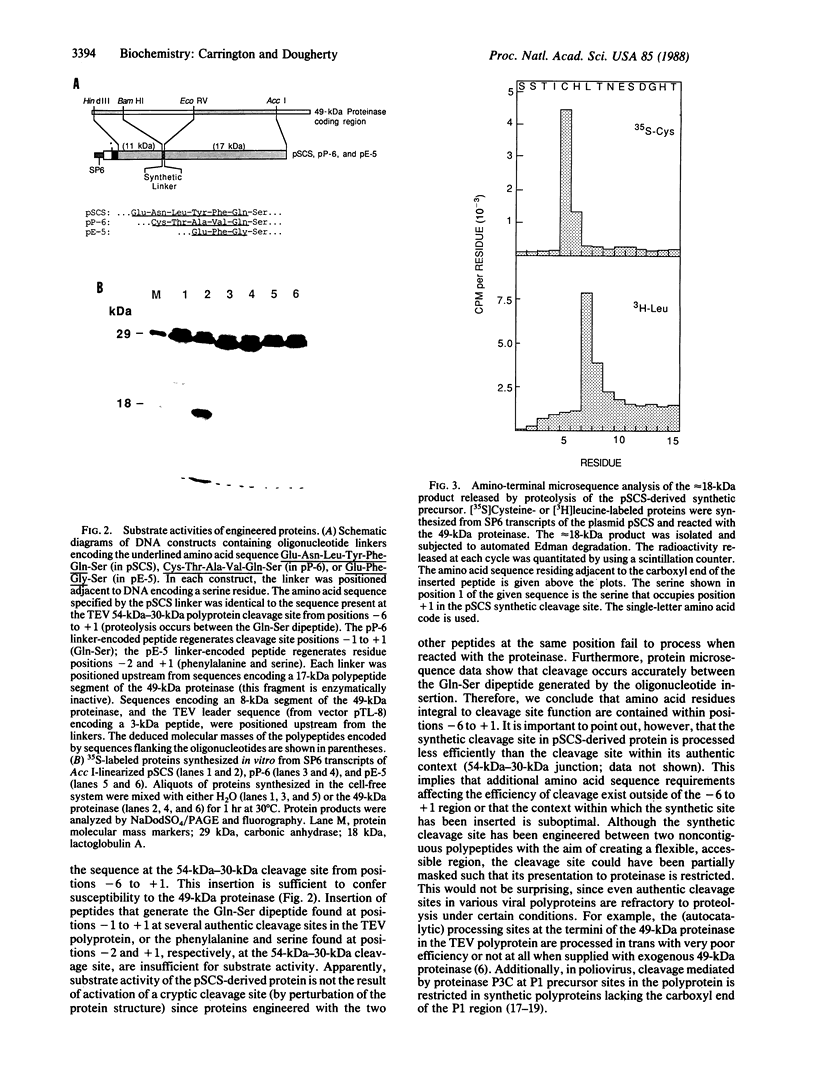

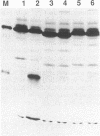
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison R. F., Sorenson J. C., Kelly M. E., Armstrong F. B., Dougherty W. G. Sequence determination of the capsid protein gene and flanking regions of tobacco etch virus: Evidence for synthesis and processing of a polyprotein in potyvirus genome expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):3969–3972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.3969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold E., Luo M., Vriend G., Rossmann M. G., Palmenberg A. C., Parks G. D., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Implications of the picornavirus capsid structure for polyprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):21–25. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger A., Schechter I. Mapping the active site of papain with the aid of peptide substrates and inhibitors. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1970 Feb 12;257(813):249–264. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1970.0024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrington J. C., Dougherty W. G. Small nuclear inclusion protein encoded by a plant potyvirus genome is a protease. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2540–2548. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2540-2548.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domier L. L., Franklin K. M., Shahabuddin M., Hellmann G. M., Overmeyer J. H., Hiremath S. T., Siaw M. F., Lomonossoff G. P., Shaw J. G., Rhoads R. E. The nucleotide sequence of tobacco vein mottling virus RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5417–5430. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenth J., Kalk K. H., Swen H. M. Binding of chloromethyl ketone substrate analogues to crystalline papain. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3731–3738. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knuhtsen H., Hiebert E., Purcifull D. E. Partial purification and some properties of tobacco etch virus induced intranuclear inclusions. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):200–209. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe G., Yuthavong Y. Kinetic specificity in papain-catalysed hydrolyses. Biochem J. 1971 Aug;124(1):107–115. doi: 10.1042/bj1240107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklin M. J., Kräusslich H. G., Toyoda H., Dunn J. J., Wimmer E. Poliovirus polypeptide precursors: expression in vitro and processing by exogenous 3C and 2A proteinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4002–4006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. On the active site of proteases. 3. Mapping the active site of papain; specific peptide inhibitors of papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Sep 6;32(5):898–902. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellink J., Rezelman G., Goldbach R., Beyreuther K. Determination of the proteolytic processing sites in the polyprotein encoded by the bottom-component RNA of cowpea mosaic virus. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.50-58.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Semler B. L. In vitro molecular genetics as a tool for determining the differential cleavage specificities of the poliovirus 3C proteinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2069–2088. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ypma-Wong M. F., Semler B. L. Processing determinants required for in vitro cleavage of the poliovirus P1 precursor to capsid proteins. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3181–3189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3181-3189.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]