Abstract
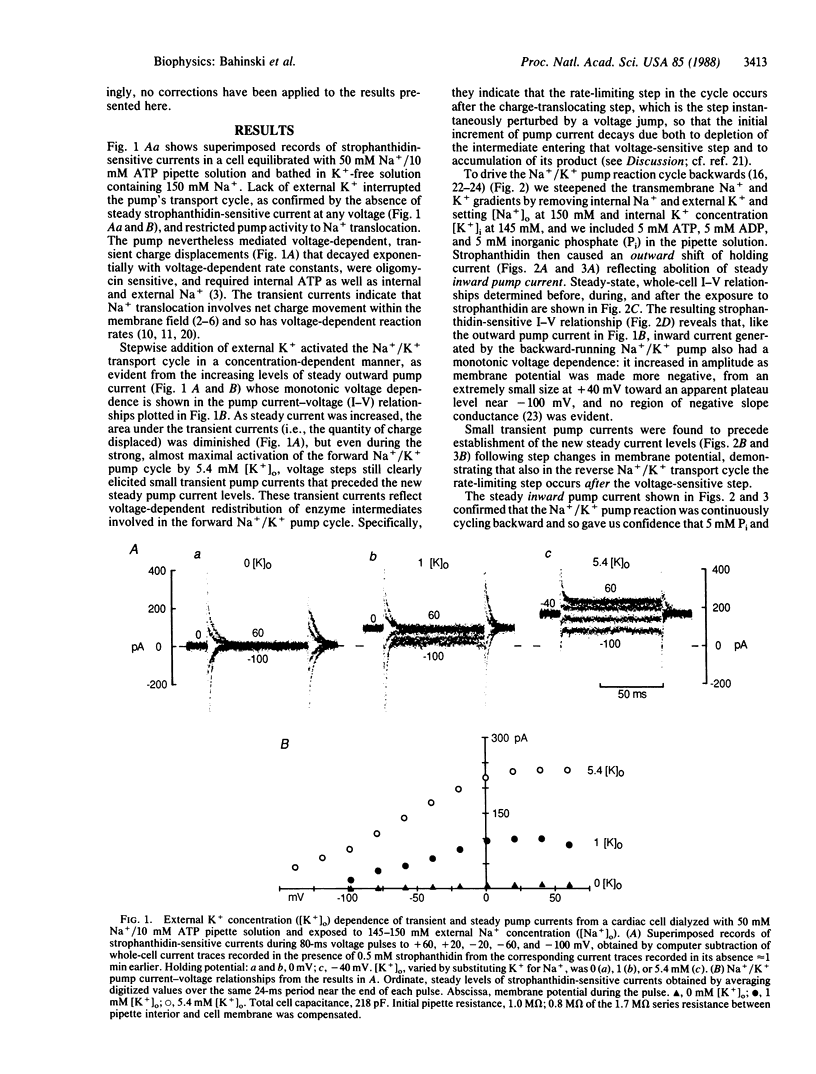
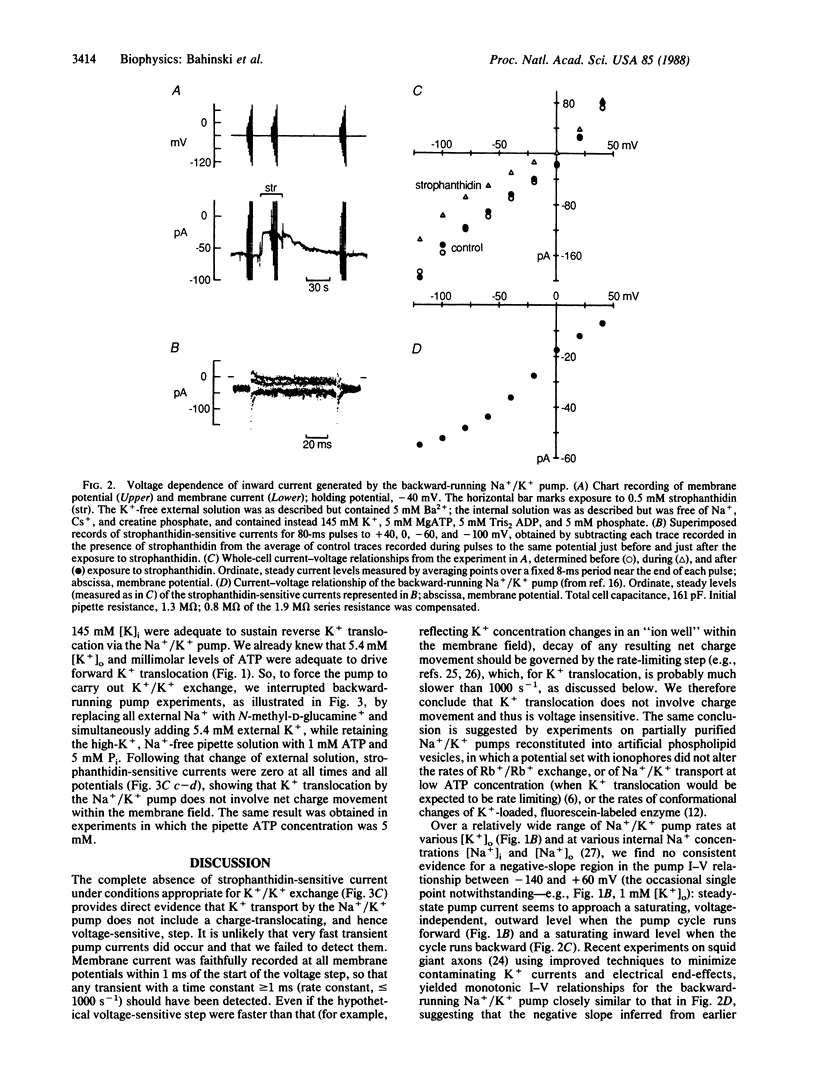
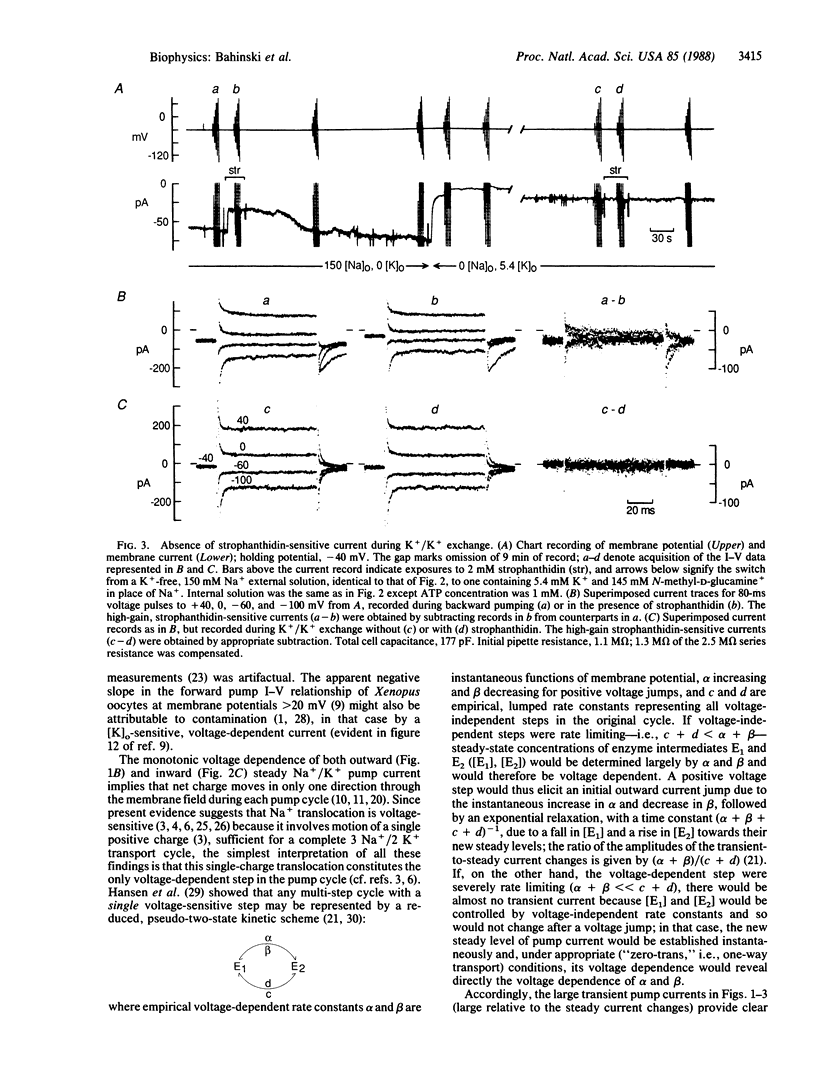
The voltage dependence of steady and transient changes in Na+/K+ pump current, in response to step changes in membrane potential, was investigated in guinea pig ventricular myocytes voltage clamped and internally dialyzed under experimental conditions designed to support four separate modes of Na+/K+ pump activity. Voltage jumps elicited transient pump currents when the pump cycle was running forward or backward, or when pumps were limited to Na+ translocation, but not when they were made to carry out K+/K+ exchange. This result indicates that K+ translocation involves no net charge movement across the membrane field and is therefore voltage insensitive. The transient pump currents seen during Na+/K+ transport demonstrate that both forward and reverse pump cycles are rate limited not by the voltage-dependent step but by a voltage-independent step, probably K+ translocation. These findings severely constrain kinetic models of Na+/K+ pump activity.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apell H. J., Borlinghaus R., Läuger P. Fast charge translocations associated with partial reactions of the Na,K-pump: II. Microscopic analysis of transient currents. J Membr Biol. 1987;97(3):179–191. doi: 10.1007/BF01869221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borlinghaus R., Apell H. J., Läuger P. Fast charge translocations associated with partial reactions of the Na,K-pump: I. Current and voltage transients after photochemical release of ATP. J Membr Biol. 1987;97(3):161–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01869220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman J. B., Johnson E. A., Kootsey J. M. Electrical and biochemical properties of an enzyme model of the sodium pump. J Membr Biol. 1983;74(2):139–153. doi: 10.1007/BF01870503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Weer P., Gadsby D. C., Rakowski R. F. Voltage dependence of the Na-K pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1988;50:225–241. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.50.030188.001301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Weer P., Rakowski R. F. Current generated by backward-running electrogenic Na pump in squid giant axons. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):450–452. doi: 10.1038/309450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendler K., Grell E., Bamberg E. Kinetics of pump currents generated by the Na+,K+-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80427-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendler K., Grell E., Haubs M., Bamberg E. Pump currents generated by the purified Na+K+-ATPase from kidney on black lipid membranes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3079–3085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04048.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbush B., 3rd Na+ movement in a single turnover of the Na pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C., Kimura J., Noma A. Voltage dependence of Na/K pump current in isolated heart cells. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):63–65. doi: 10.1038/315063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The incorporation of inorganic phosphate into adenosine triphosphate by reversal of the sodium pump. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):237–256. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M., Karlish S. J. The sodium pump. Annu Rev Physiol. 1975;37:13–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.37.030175.000305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldshlegger R., Karlish S. J., Rephaeli A., Stein W. D. The effect of membrane potential on the mammalian sodium-potassium pump reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. J Physiol. 1987 Jun;387:331–355. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U. P., Gradmann D., Sanders D., Slayman C. L. Interpretation of current-voltage relationships for "active" ion transport systems: I. Steady-state reaction-kinetic analysis of class-I mechanisms. J Membr Biol. 1981;63(3):165–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01870979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Klockner U. Calcium tolerant ventricular myocytes prepared by preincubation in a "KB medium". Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):6–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00584963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura J., Miyamae S., Noma A. Identification of sodium-calcium exchange current in single ventricular cells of guinea-pig. J Physiol. 1987 Mar;384:199–222. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafaire A. V., Schwarz W. Voltage dependence of the rheogenic Na+/K+ ATPase in the membrane of oocytes of Xenopus laevis. J Membr Biol. 1986;91(1):43–51. doi: 10.1007/BF01870213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Gadsby D. C. Voltage dependence of Na translocation by the Na/K pump. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):628–630. doi: 10.1038/323628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rephaeli A., Richards D. E., Karlish S. J. Electrical potential accelerates the E1P(Na)----E2P conformational transition of (Na,K)-ATPase in reconstituted vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12437–12440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rephaeli A., Richards D., Karlish S. J. Conformational transitions in fluorescein-labeled (Na,K)ATPase reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6248–6254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Johnson E. A., Tanford C. Incorporation of membrane potential into theoretical analysis of electrogenic ion pumps. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6869–6873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima M., Noma A. Mode of regulation of the ACh-sensitive K-channel by the muscarinic receptor in rabbit atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00587544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



