Abstract
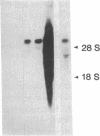
The complete nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the human platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor is presented. The cDNA contains an open reading frame that codes for a protein of 1106 amino acids. Comparison to the mouse PDGF receptor reveals an overall amino acid sequence identity of 86%. This sequence identity rises to 98% in the cytoplasmic split tyrosine kinase domain. RNA blot hybridization analysis of poly(A)+ RNA from human dermal fibroblasts detects a major (approximately 5.7 kb) and a minor (approximately 4.8 kb) transcript using the cDNA as a probe. Baby hamster kidney cells, transfected with an expression vector containing the receptor cDNA, express an approximately equal to 190-kDa cell surface protein that is recognized by an anti-human PDGF receptor antibody. The recombinant PDGF receptor is functional in the transfected baby hamster kidney cells as demonstrated by ligand-induced phosphorylation of the receptor. Binding properties of the recombinant PDGF receptor were also assessed with pure preparations of BB and AB isoforms of PDGF (i.e., PDGF dimers composed of two B chains or an A and a B chain). Unlike human dermal fibroblasts, which bind both isoforms with high affinity, the transfected baby hamster kidney cells bind only the BB isoform of PDGF with high affinity. This observation is consistent with the existence of more than one PDGF receptor class.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amasino R. M. Acceleration of nucleic acid hybridization rate by polyethylene glycol. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):304–307. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90413-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D., Stiles C. D. Purification of human platelet-derived growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1809–1813. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkner K., Busby S., Davie E., Hart C., Insley M., Kisiel W., Kumar A., Murray M., O'Hara P., Woodbury R. Isolation and expression of cDNAs encoding human factor VII. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):531–541. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishayee S., Ross A. H., Womer R., Scher C. D. Purified human platelet-derived growth factor receptor has ligand-stimulated tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6756–6760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Methods for studying the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Methods Enzymol. 1985;109:69–100. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)09078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busby S., Kumar A., Joseph M., Halfpap L., Insley M., Berkner K., Kurachi K., Woodbury R. Expression of active human factor IX in transfected cells. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):271–273. doi: 10.1038/316271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Williams L. T. Purification of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor by using an anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2684–2687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Proffitt R. T., Baenziger J. U., Chang D., Kennedy B. B. Human platelet-derived growth factor. Purification and resolution into two active protein fractions. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 10;256(17):8896–8899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frackelton A. R., Jr, Tremble P. M., Williams L. T. Evidence for the platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor in vivo. Immunopurification using a monoclonal antibody to phosphotyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7909–7915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischer L. E., Hagen F. S., Garber R. L. An inversion that disrupts the Antennapedia gene causes abnormal structure and localization of RNAs. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1017–1023. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90816-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn K., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. III. Identification of a platelet-derived growth factor receptor by affinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5172–5176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen F. S., Gray C. L., O'Hara P., Grant F. J., Saari G. C., Woodbury R. G., Hart C. E., Insley M., Kisiel W., Kurachi K. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart C. E., Seifert R. A., Ross R., Bowen-Pope D. F. Synthesis, phosphorylation, and degradation of multiple forms of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor studied using a monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10780–10785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Ek B., Rönnstrand L. Characterization of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor on human fibroblasts. Demonstration of an intimate relationship with a 185,000-Dalton substrate for the platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated kinase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10054–10061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Johnsson A., Wennergren S., Wernstedt C., Betsholtz C., Westermark B. A human osteosarcoma cell line secretes a growth factor structurally related to a homodimer of PDGF A-chains. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):511–514. doi: 10.1038/319511a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Platelet-derived growth factor: purification and partial characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3722–3726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Wasteson A., Westermark B., Deuel T. F., Huang J. S., Seeburg P. H., Gray A., Ullrich A., Scrace G. The c-sis gene encodes a precursor of the B chain of platelet-derived growth factor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):921–928. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01908.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnsson A., Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Wasteson A. Platelet-derived growth factor: identification of constituent polypeptide chains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):66–74. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91941-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly J. D., Raines E. W., Ross R., Murray M. J. The B chain of PDGF alone is sufficient for mitogenesis. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3399–3405. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04096.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler N., Lipton A. Platelets as a source of fibroblast growth-promoting activity. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Aug;87(2):297–301. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90484-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura J., Huang J. S., Deuel T. F. Platelet-derived growth factor stimulates tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity in Swiss mouse 3T3 cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4303–4307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike L. J., Bowen-Pope D. F., Ross R., Krebs E. G. Characterization of platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation in cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9383–9390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines E. W., Ross R. Platelet-derived growth factor. I. High yield purification and evidence for multiple forms. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5154–5160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J. Conversion of low-affinity interleukin 2 receptors to a high-affinity state following fusion of cell membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3992–3996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Glomset J., Kariya B., Harker L. A platelet-dependent serum factor that stimulates the proliferation of arterial smooth muscle cells in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1207–1210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Raines E. W., Bowen-Pope D. F. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Isolation and expression of an altered mouse dihydrofolate reductase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroobant P., Waterfield M. D. Purification and properties of porcine platelet-derived growth factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2963–2967. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02241.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waechter D. E., Baserga R. Effect of methylation on expression of microinjected genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Tremble P. M., Lavin M. F., Sunday M. E. Platelet-derived growth factor receptors form a high affinity state in membrane preparations. Kinetics and affinity cross-linking studies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5287–5294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]