Abstract
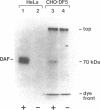
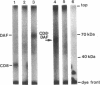
Decay-accelerating factor (DAF) is one of a family of cell-associated proteins that undergo posttranslational modifications in which glycolipid anchoring structures are substituted for membrane-spanning sequences. The signals that direct the covalent substitution reaction in these proteins are unknown. Human DAF was expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells and murine BW lymphocytes. In both cases, the xenogeneic DAF in transfectants incorporated a glycolipid anchor. A chimeric CD8-DAF cDNA, encompassing the extra-cellular region of the T-lymphocyte surface antigen CD8 and the 3' end of DAF mRNA (encoding the C-terminal region of mature DAF as well as the hydrophobic extension peptide), was expressed in human leukemia lines after transfection with an Epstein-Barr virus-based episomal vector. The chimeric protein in transfectants demonstrated glycolipid anchoring, whereas unaltered CD8 in control experiments did not. The signals directing glycolipid anchoring in eukaryotic cells are thus evolutionarily conserved and contained in the 3' end of the DAF sequence.
Full text
PDF

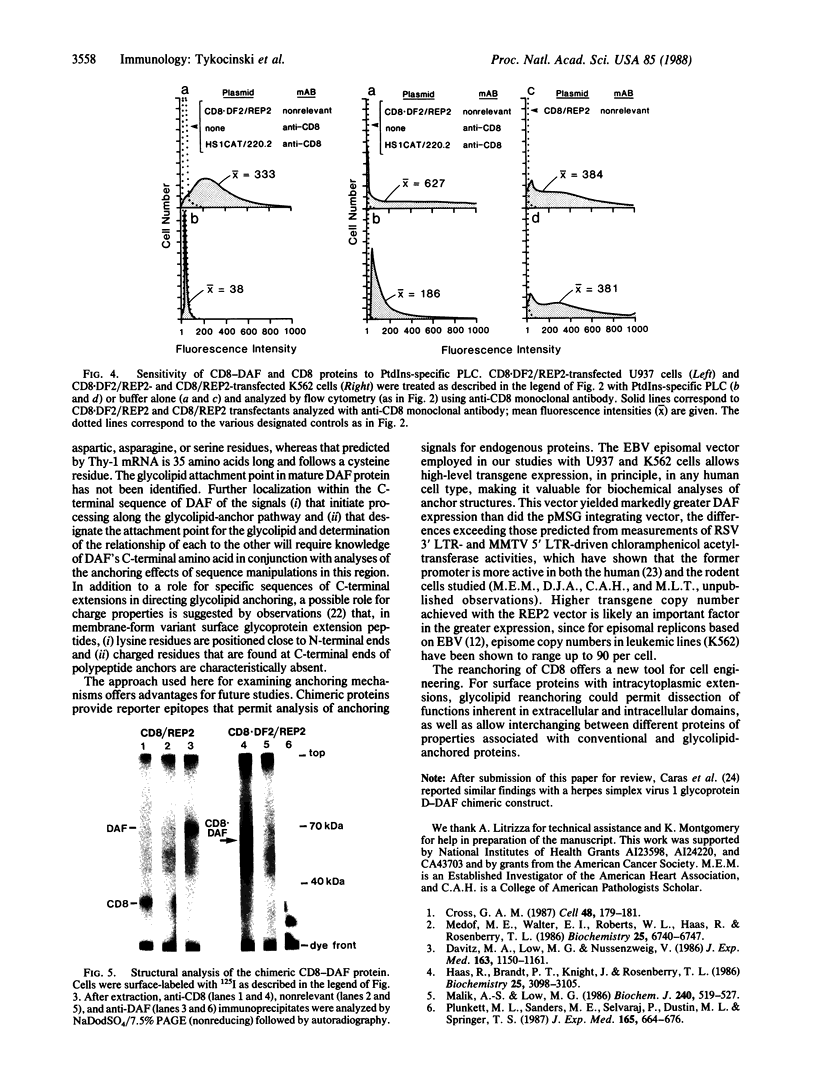

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caras I. W., Davitz M. A., Rhee L., Weddell G., Martin D. W., Jr, Nussenzweig V. Cloning of decay-accelerating factor suggests novel use of splicing to generate two proteins. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):545–549. doi: 10.1038/325545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caras I. W., Weddell G. N., Davitz M. A., Nussenzweig V., Martin D. W., Jr Signal for attachment of a phospholipid membrane anchor in decay accelerating factor. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1280–1283. doi: 10.1126/science.2446389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Eukaryotic protein modification and membrane attachment via phosphatidylinositol. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Low M. G., Nussenzweig V. Release of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) from the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PIPLC). Selective modification of a complement regulatory protein. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1150–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futerman A. H., Low M. G., Silman I. A hydrophobic dimer of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo californica electric organ is solubilized by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Sep 19;40(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas R., Brandt P. T., Knight J., Rosenberry T. L. Identification of amine components in a glycolipid membrane-binding domain at the C-terminus of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3098–3105. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman D. R., Thomas Y., Maddon P. J., Chess L., Axel R. The isolation and sequence of the gene encoding T8: a molecule defining functional classes of T lymphocytes. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90138-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Kincade P. W. Phosphatidylinositol is the membrane-anchoring domain of the Thy-1 glycoprotein. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):62–64. doi: 10.1038/318062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. S., Low M. G. Conversion of human placental alkaline phosphatase from a high Mr form to a low Mr form during butanol extraction. An investigation of the role of endogenous phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):519–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2400519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Kinoshita T., Nussenzweig V. Inhibition of complement activation on the surface of cells after incorporation of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) into their membranes. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1558–1578. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Lublin D. M., Holers V. M., Ayers D. J., Getty R. R., Leykam J. F., Atkinson J. P., Tykocinski M. L. Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding the complete sequence of decay-accelerating factor of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2007–2011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Roberts W. L., Haas R., Rosenberry T. L. Decay accelerating factor of complement is anchored to cells by a C-terminal glycolipid. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6740–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plunkett M. L., Sanders M. E., Selvaraj P., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. Rosetting of activated human T lymphocytes with autologous erythrocytes. Definition of the receptor and ligand molecules as CD2 and lymphocyte function-associated antigen 3 (LFA-3). J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):664–676. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Kim B. H., Rosenberry T. L. Differences in the glycolipid membrane anchors of bovine and human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7817–7821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Rosenberry T. L. Selective radiolabeling and isolation of the hydrophobic membrane-binding domain of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3091–3098. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandri-Goldin R. M., Goldin A. L., Levine M., Glorioso J. High-efficiency transfer of DNA into eukaryotic cells by protoplast fusion. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:402–411. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford H. A., Tykocinski M. L., Lublin D. M., Holers V. M., Rosse W. F., Atkinson J. P., Medof M. E. Normal polymorphic variations and transcription of the decay accelerating factor gene in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):880–884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner M. J., Cardoso de Almeida M. L., Gurnett A. M., Raper J., Ward J. Biosynthesis, attachment and release of variant surface glycoproteins of the African trypanosome. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;117:23–55. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70538-0_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]