Abstract
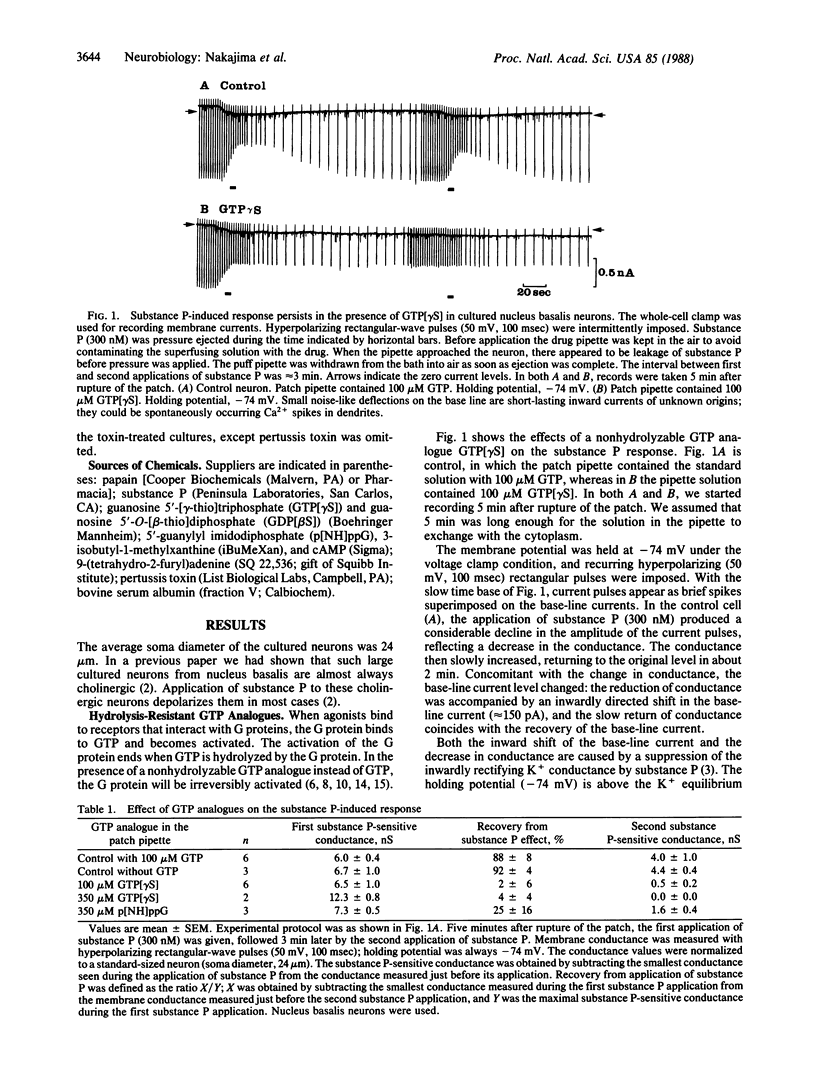
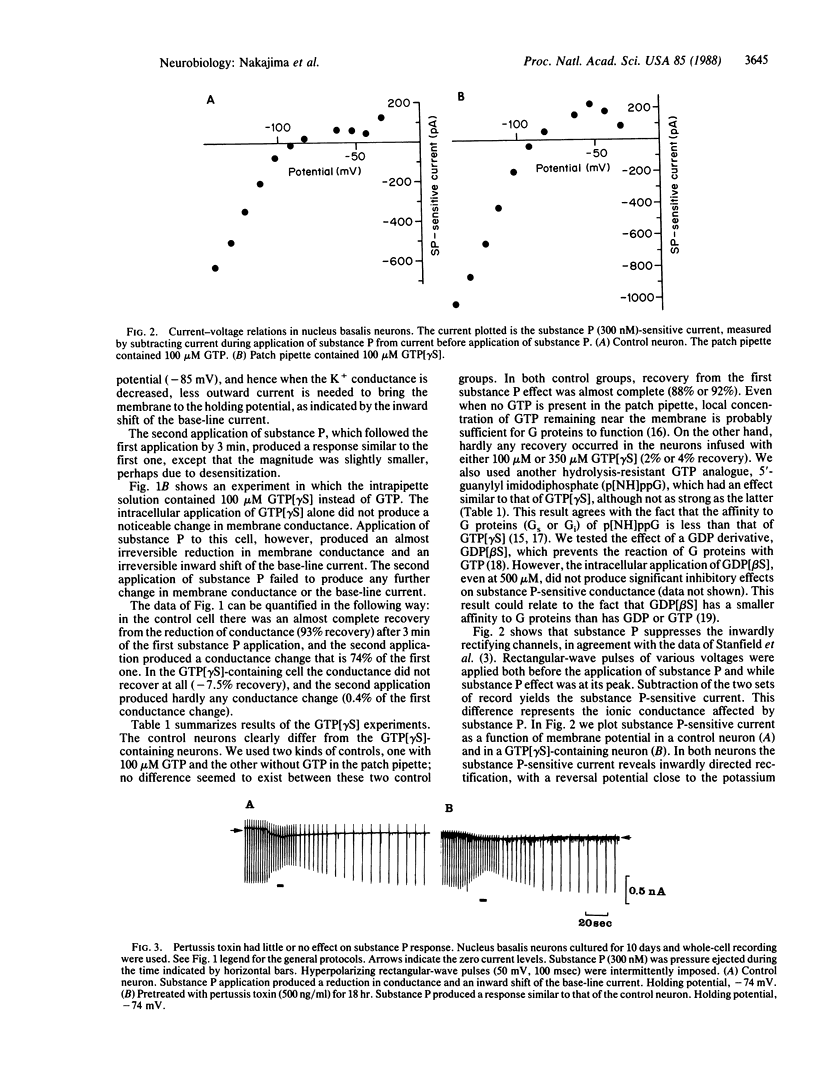
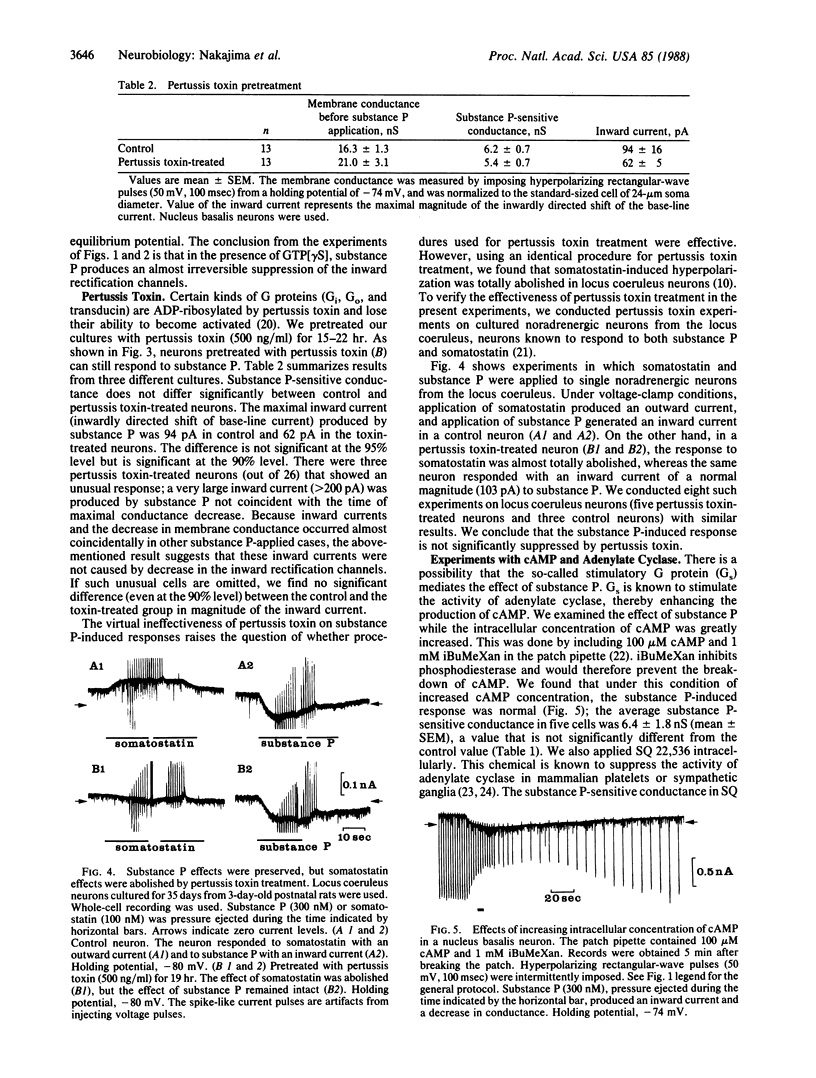
Substance P excites neurons by suppressing inward rectification channels. We have investigated whether the substance P receptor interacts with the inward rectification channels through a guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein) by using dissociated cultured neurons from the nucleus basalis of newborn rats. During intracellular application of guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate and 5'-guanylyl imidodiphosphate, hydrolysis-resistant GTP analogues that irreversibly stimulate G proteins, substance P application almost irreversibly suppressed the inward rectification channels. Pretreatment with pertussis toxin did not significantly influence substance P action. Intracellular application of cAMP and 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine or of 9-(tetrahydro-2-furyl)adenine (SQ 22,536), an inhibitor of adenylate cyclase, did not alter the substance P-induced response. We conclude that the inhibition of inward rectification channels by substance P is mediated through a G protein. However, the effect is not mediated through adenylate cyclase or the cAMP system. This G protein, which is insensitive to pertussis toxin, could be an unidentified G protein.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrade R., Malenka R. C., Nicoll R. A. A G protein couples serotonin and GABAB receptors to the same channels in hippocampus. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1261–1265. doi: 10.1126/science.2430334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aub D. L., Frey E. A., Sekura R. D., Cote T. E. Coupling of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor to phospholipase C by a GTP-binding protein distinct from the inhibitory or stimulatory GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9333–9340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beach T. G., Tago H., McGeer E. G. Light microscopic evidence for a substance P-containing innervation of the human nucleus basalis of Meynert. Brain Res. 1987 Apr 7;408(1-2):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)90382-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3560–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolam J. P., Ingham C. A., Izzo P. N., Levey A. I., Rye D. B., Smith A. D., Wainer B. H. Substance P-containing terminals in synaptic contact with cholinergic neurons in the neostriatum and basal forebrain: a double immunocytochemical study in the rat. Brain Res. 1986 Nov 12;397(2):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90629-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and beta-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):538–540. doi: 10.1038/317538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Dunn P. M. Cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate and beta-effects in rat isolated superior cervical ganglia. Br J Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;79(2):441–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1983.tb11017.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Axelrod J. Dissociation of bradykinin-induced prostaglandin formation from phosphatidylinositol turnover in Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts: evidence for G protein regulation of phospholipase A2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6374–6378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Activation of turkey erythrocyte adenylate cyclase and blocking of the catecholamine-stimulated GTPase by guanosine 5'-(gamma-thio) triphosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Aug 8;77(3):868–873. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(77)80058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Codina J., Yatani A., Grenet D., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. The alpha subunit of the GTP binding protein Gk opens atrial potassium channels. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):442–445. doi: 10.1126/science.2436299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coyle J. T., Price D. L., DeLong M. R. Alzheimer's disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervation. Science. 1983 Mar 11;219(4589):1184–1190. doi: 10.1126/science.6338589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckstein F., Cassel D., Levkovitz H., Lowe M., Selinger Z. Guanosine 5'-O-(2-thiodiphosphate). An inhibitor of adenylate cyclase stimulation by guanine nucleotides and fluoride ions. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9829–9834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. N., Asaad M. M., Phillips M. B., Goldenberg H. J., Antonaccio M. J. Inhibition of adenylate cyclase in human blood platelets by 9-substituted adenine derivatives. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;5(2):125–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huettner J. E., Baughman R. W. Primary culture of identified neurons from the visual cortex of postnatal rats. J Neurosci. 1986 Oct;6(10):3044–3060. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-10-03044.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyengar R., Rich K. A., Herberg J. T., Grenet D., Mumby S., Codina J. Identification of a new GTP-binding protein. A Mr = 43,000 substrate for pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9239–9245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Kusakabe K., Ui M. A new GTP-binding protein in brain tissues serving as the specific substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 23;213(2):353–358. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81521-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. L., Weight F. F., Luini A. A guanine nucleotide-binding protein mediates the inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium current by somatostatin in a pituitary cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9035–9039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone activates a Ca2+-dependent polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in permeable GH3 cells. GTP gamma S potentiation by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2918–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuko S., Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Yamaguchi K. Noradrenergic neurons from the locus ceruleus in dissociated cell culture: culture methods, morphology, and electrophysiology. J Neurosci. 1986 Nov;6(11):3229–3241. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-11-03229.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Leonard R. J., Yamaguchi K. Acetylcholine raises excitability by inhibiting the fast transient potassium current in cultured hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):3022–3026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.3022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima Y., Nakajima S., Obata K., Carlson C. G., Yamaguchi K. Dissociated cell culture of cholinergic neurons from nucleus basalis of Meynert and other basal forebrain nuclei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6325–6329. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Biochemical properties of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:533–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Camardo J. S., Kandel E. R. Serotonin and cyclic AMP close single K+ channels in Aplysia sensory neurones. Nature. 1982 Sep 30;299(5882):413–417. doi: 10.1038/299413a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R., Nakajima Y., Yamaguchi K. Substance P raises neuronal membrane excitability by reducing inward rectification. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):498–501. doi: 10.1038/315498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor C. W., Merritt J. E., Putney J. W., Jr, Rubin R. P. A guanine nucleotide-dependent regulatory protein couples substance P receptors to phospholipase C in rat parotid gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):362–368. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90919-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toutant M., Aunis D., Bockaert J., Homburger V., Rouot B. Presence of three pertussis toxin substrates and Go alpha immunoreactivity in both plasma and granule membranes of chromaffin cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 11;215(2):339–344. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka G., Eckstein F., Stryer L. Stereochemistry of the guanyl nucleotide binding site of transducin probed by phosphorothioate analogues of GTP and GDP. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):8094–8101. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita N., Kojima I., Shibuya N., Ogata E. Pertussis toxin inhibits somatostatin-induced K+ conductance in human pituitary tumor cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Jul;253(1 Pt 1):E28–E32. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1987.253.1.E28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



