Abstract
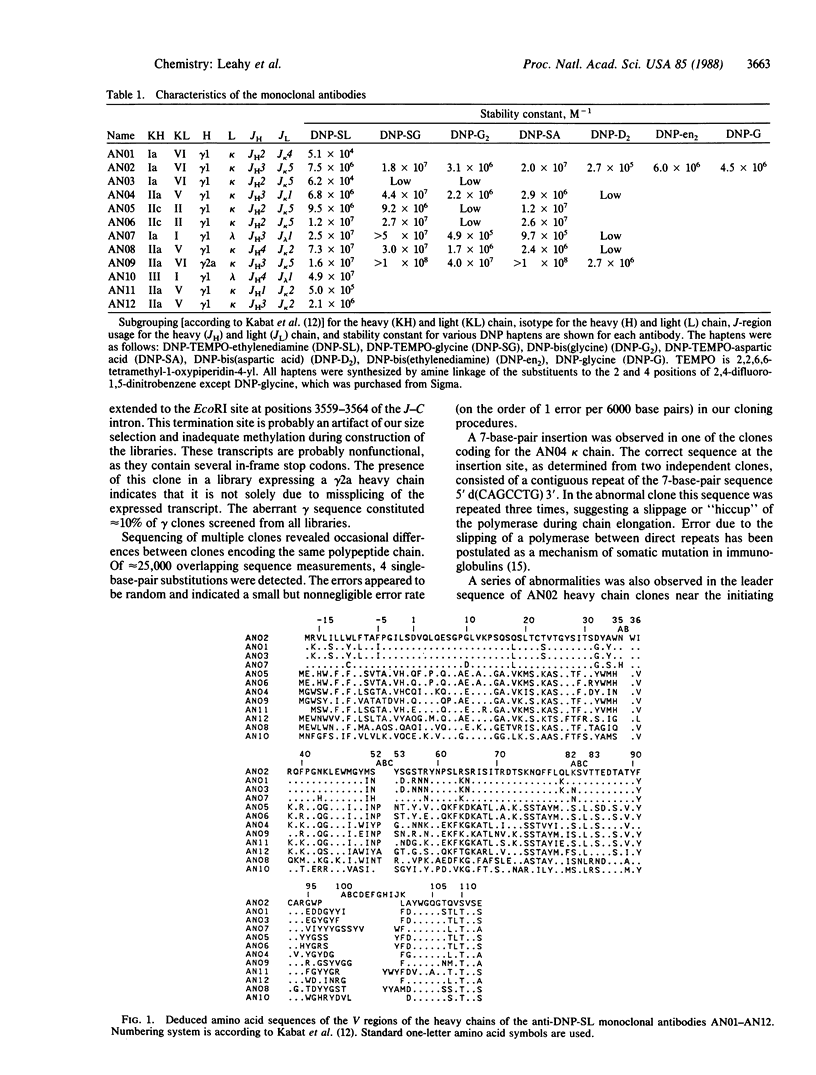
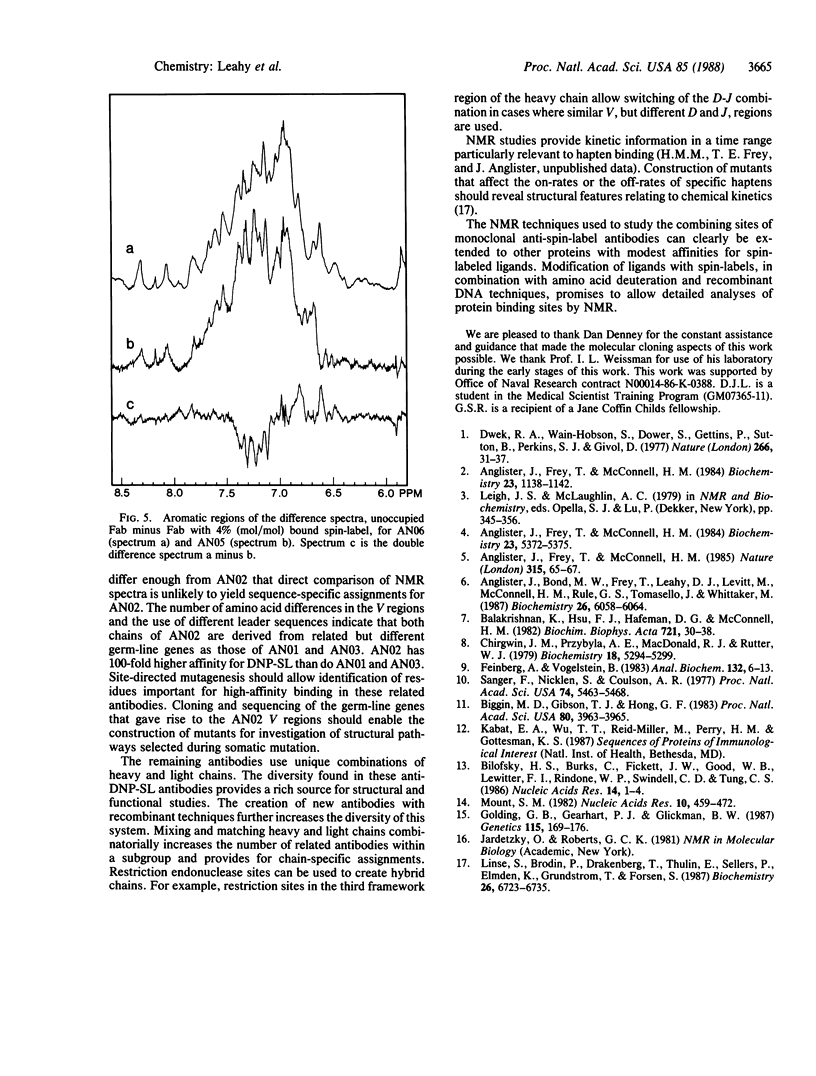
Eleven monoclonal antibodies specific for a spin-labeled dinitrophenyl hapten (DNP-SL) have been produced for use in NMR studies. They have been named AN01 and AN03-AN12. The stability constants for the association of these antibodies with DNP-SL and related haptens were measured by fluorescence quenching and ranged from 5.0 X 10(4) M-1 to greater than 1.0 X 10(8) M-1. cDNA clones coding for the heavy and light chains of each antibody and of an additional anti-DNP-SL monoclonal antibody, AN02, have been isolated. The nucleic acid sequence of the 5' end of each clone has been determined, and the amino acid sequence of the variable regions of each antibody has been deduced from the cDNA sequence. The sequences are relatively heterogeneous, but both the heavy and the light chains of AN01 and AN03 are derived from the same variable-region gene families as those of the AN02 antibody. AN07 has a heavy chain that is related to that of AN02, and AN09 has a related light chain. AN05 and AN06 are unrelated to AN02 but share virtually identical heavy and light chains. Preliminary NMR difference spectra comparing related antibodies show that sequence-specific assignment of resonances is possible. Such spectra also provide a measure of structural relatedness.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anglister J., Bond M. W., Frey T., Leahy D., Levitt M., McConnell H. M., Rule G. S., Tomasello J., Whittaker M. Contribution of tryptophan residues to the combining site of a monoclonal anti dinitrophenyl spin-label antibody. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6058–6064. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anglister J., Frey T., McConnell H. M. Distances of tyrosine residues from a spin-label hapten in the combining site of a specific monoclonal antibody. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 23;23(22):5372–5375. doi: 10.1021/bi00317a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anglister J., Frey T., McConnell H. M. NMR technique for assessing contributions of heavy and light chains to an antibody combining site. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):65–67. doi: 10.1038/315065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balakrishnan K., Hsu F. J., Hafeman D. G., McConnell H. M. Monoclonal antibodies to a nitroxide lipid hapten. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 13;721(1):30–38. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(82)90020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilofsky H. S., Burks C., Fickett J. W., Goad W. B., Lewitter F. I., Rindone W. P., Swindell C. D., Tung C. S. The GenBank genetic sequence databank. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):1–4. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwek R. A., Wain-Hobson S., Dower S., Gettins P., Sutton B., Perkins S. J., Givol D. Structure of an antibody combining site by magnetic resonance. Nature. 1977 Mar 3;266(5597):31–37. doi: 10.1038/266031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding G. B., Gearhart P. J., Glickman B. W. Patterns of somatic mutations in immunoglobulin variable genes. Genetics. 1987 Jan;115(1):169–176. doi: 10.1093/genetics/115.1.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linse S., Brodin P., Drakenberg T., Thulin E., Sellers P., Elmdén K., Grundström T., Forsén S. Structure-function relationships in EF-hand Ca2+-binding proteins. Protein engineering and biophysical studies of calbindin D9k. Biochemistry. 1987 Oct 20;26(21):6723–6735. doi: 10.1021/bi00395a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



