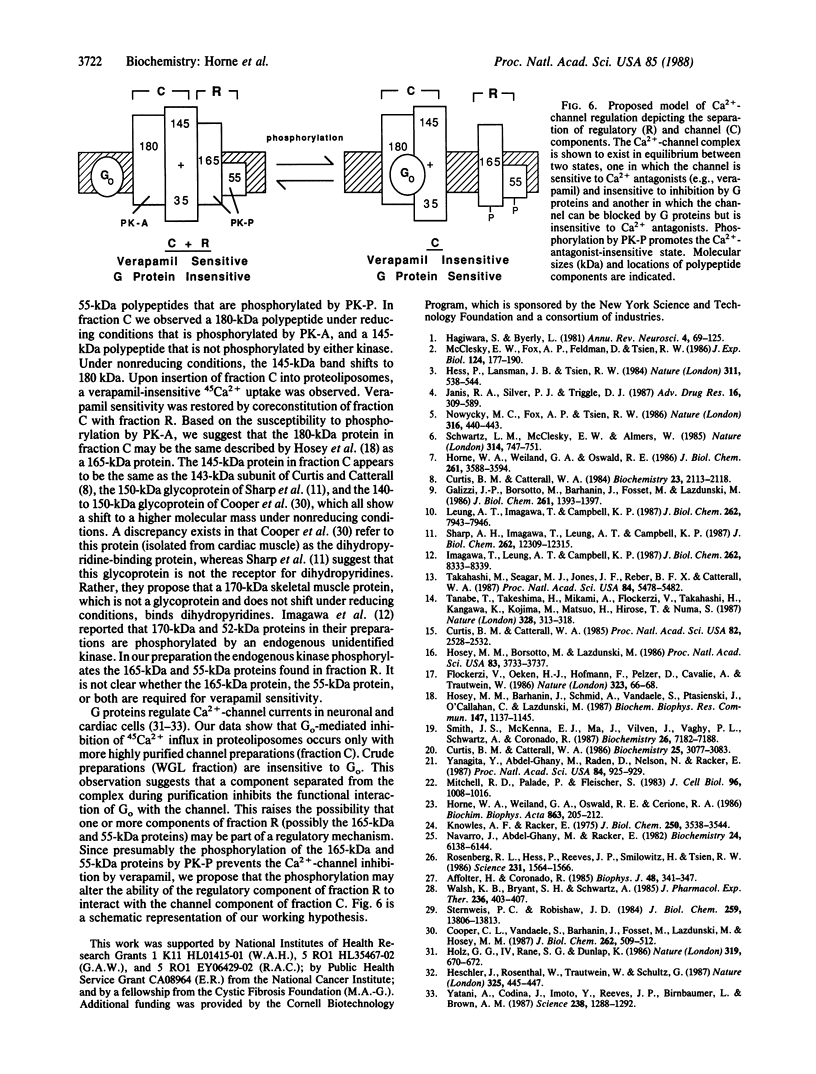
Abstract
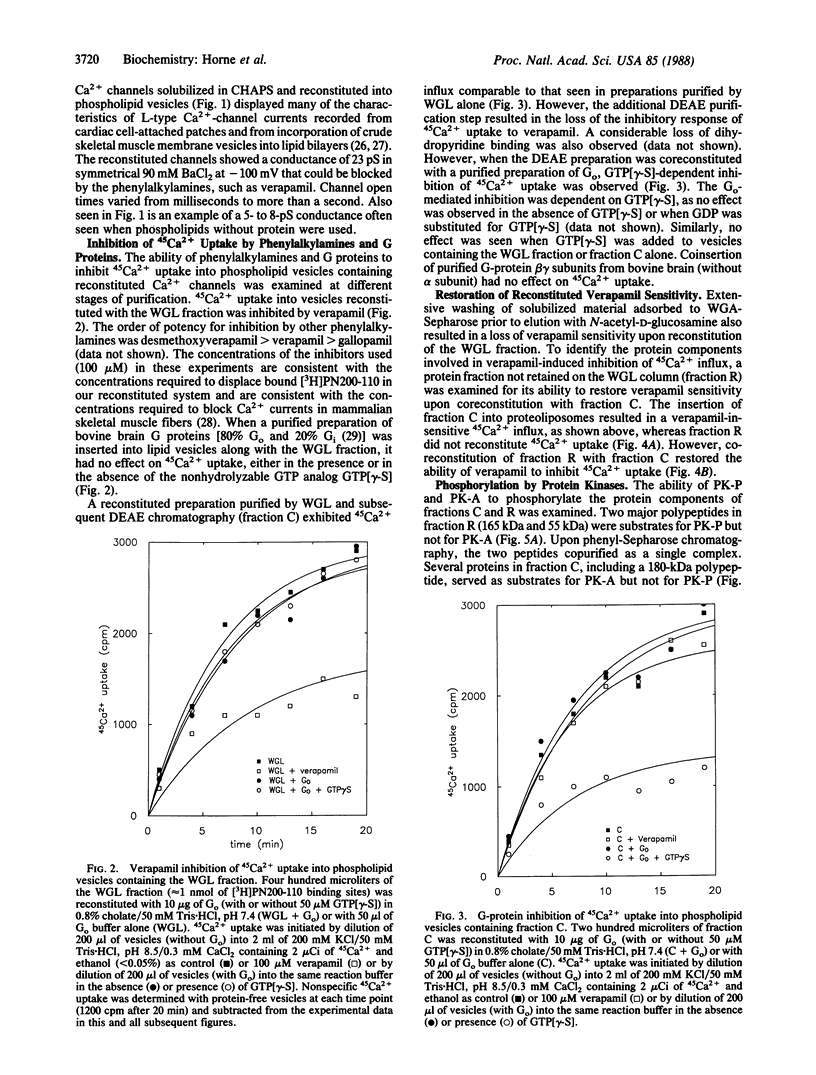
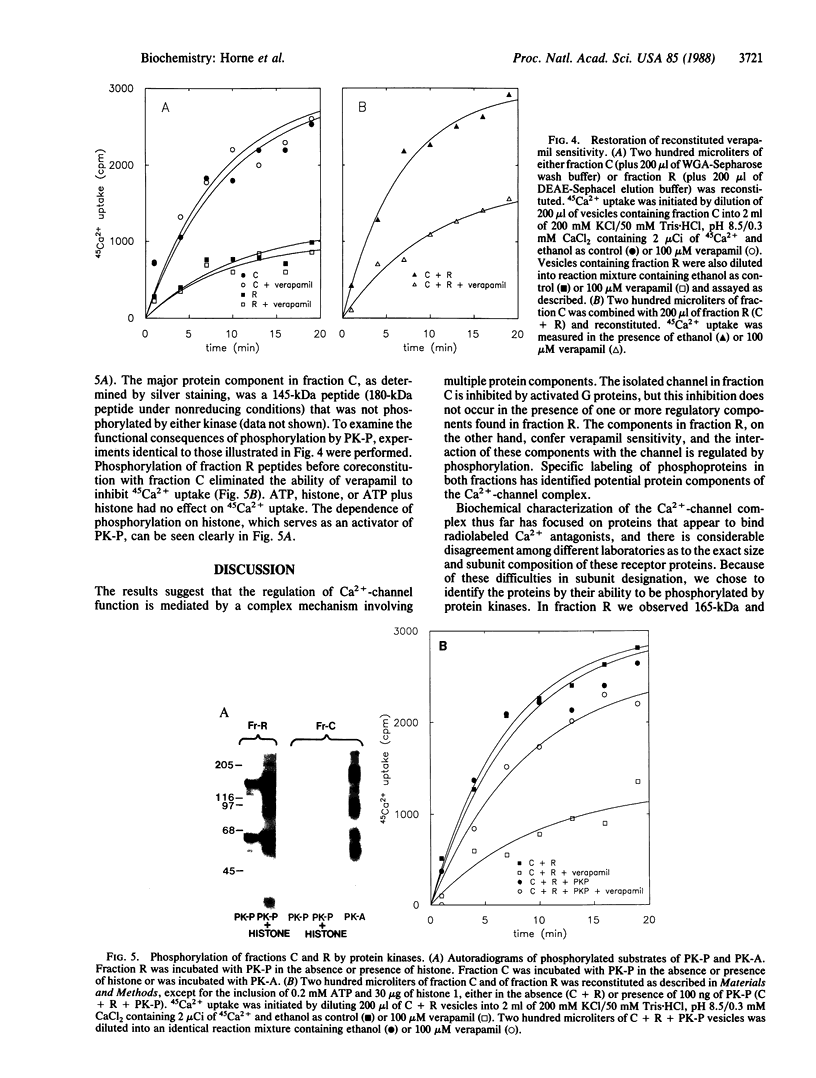
Regulatory properties of a partially purified Ca2+ -channel preparation from isolated rabbit skeletal muscle triads were examined in proteoliposomes. These properties included (i) inhibition by phenylalkylamine antagonists, such as verapamil, (ii) inhibition by the GTP-binding protein Go in the presence of guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate, and (iii) regulation of phenylalkylamine inhibition as a result of phosphorylation by a polypeptide-dependent protein kinase (PK-P). By selective reconstitution of protein fractions obtained by wheat germ lectin and ion-exchange chromatography, a separation of Ca2+-channel activity (fraction C) from regulatory component(s) (fraction R) responsible for verapamil sensitivity was achieved. Reconstitution of fraction C alone yielded vesicles that exhibited channel-mediated 45Ca2+ uptake that could be directly inhibited by coreconstitution of Go in the presence of guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate. However, the 45Ca2+ uptake obtained with fraction C was not inhibited by verapamil. Coreconstitution of fractions C and R yielded vesicles in which the sensitivity of 45Ca2+ uptake to verapamil was restored. The verapamil sensitivity of this preparation could be inhibited by PK-P. Fraction C, obtained by wheat germ agglutinin-Sepharose chromatography followed by DEAE-Sephacel chromatography, included a 180-kDa protein that was phosphorylated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PK-A) but not by PK-P and a 145-kDa protein (180 kDa under nonreducing conditions) that was not phosphorylated by either kinase. Fraction R contained proteins that did not adsorb to wheat germ lectin and included 165-kDa and 55-kDa proteins that were phosphorylated by PK-P but not by PK-A. These results suggest a complex model for Ca2+-channel regulation in skeletal muscle involving a number of distinct, separable protein components.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Affolter H., Coronado R. Agonists Bay-K8644 and CGP-28392 open calcium channels reconstituted from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biophys J. 1985 Aug;48(2):341–347. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83789-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper C. L., Vandaele S., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M., Hosey M. M. Purification and characterization of the dihydropyridine-sensitive voltage-dependent calcium channel from cardiac tissue. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):509–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Phosphorylation of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2528–2532. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Purification of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2113–2118. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Reconstitution of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel purified from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3077–3083. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flockerzi V., Oeken H. J., Hofmann F., Pelzer D., Cavalié A., Trautwein W. Purified dihydropyridine-binding site from skeletal muscle t-tubules is a functional calcium channel. Nature. 1986 Sep 4;323(6083):66–68. doi: 10.1038/323066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galizzi J. P., Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Fosset M., Lazdunski M. Characterization and photoaffinity labeling of receptor sites for the Ca2+ channel inhibitors d-cis-diltiazem, (+/-)-bepridil, desmethoxyverapamil, and (+)-PN 200-110 in skeletal muscle transverse tubule membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1393–1397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Byerly L. Calcium channel. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1981;4:69–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.04.030181.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hescheler J., Rosenthal W., Trautwein W., Schultz G. The GTP-binding protein, Go, regulates neuronal calcium channels. 1987 Jan 29-Feb 4Nature. 325(6103):445–447. doi: 10.1038/325445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Lansman J. B., Tsien R. W. Different modes of Ca channel gating behaviour favoured by dihydropyridine Ca agonists and antagonists. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):538–544. doi: 10.1038/311538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz G. G., 4th, Rane S. G., Dunlap K. GTP-binding proteins mediate transmitter inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):670–672. doi: 10.1038/319670a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne W. A., Weiland G. A., Oswald R. E., Cerione R. A. Rapid incorporation of the solubilized dihydropyridine receptor into phospholipid vesicles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 16;863(2):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90260-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne W. A., Weiland G. A., Oswald R. E. Solubilization and hydrodynamic characterization of the dihydropyridine receptor from rat ventricular muscle. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3588–3594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosey M. M., Barhanin J., Schmid A., Vandaele S., Ptasienski J., O'Callahan C., Cooper C., Lazdunski M. Photoaffinity labelling and phosphorylation of a 165 kilodalton peptide associated with dihydropyridine and phenylalkylamine-sensitive calcium channels. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Sep 30;147(3):1137–1145. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80188-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosey M. M., Borsotto M., Lazdunski M. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of dihydropyridine-sensitive voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel in skeletal muscle membranes by cAMP- and Ca2+-dependent processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3733–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa T., Leung A. T., Campbell K. P. Phosphorylation of the 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel by an intrinsic protein kinase in isolated triads from rabbit skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8333–8339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles A. F., Racker E. Properties of a reconstituted calcium pump. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3538–3544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung A. T., Imagawa T., Campbell K. P. Structural characterization of the 1,4-dihydropyridine receptor of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel from rabbit skeletal muscle. Evidence for two distinct high molecular weight subunits. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):7943–7946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCleskey E. W., Fox A. P., Feldman D., Tsien R. W. Different types of calcium channels. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:177–190. doi: 10.1242/jeb.124.1.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. D., Palade P., Fleischer S. Purification of morphologically intact triad structures from skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;96(4):1008–1016. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.4.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navarro J., Abdel Ghany M., Racker E. Inhibition of tyrosine protein kinases by halomethyl ketones. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6138–6144. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowycky M. C., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W. Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):440–443. doi: 10.1038/316440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Hess P., Reeves J. P., Smilowitz H., Tsien R. W. Calcium channels in planar lipid bilayers: insights into mechanisms of ion permeation and gating. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1564–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.2420007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. M., McCleskey E. W., Almers W. Dihydropyridine receptors in muscle are voltage-dependent but most are not functional calcium channels. 1985 Apr 25-May 1Nature. 314(6013):747–751. doi: 10.1038/314747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp A. H., Imagawa T., Leung A. T., Campbell K. P. Identification and characterization of the dihydropyridine-binding subunit of the skeletal muscle dihydropyridine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12309–12315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. S., McKenna E. J., Ma J. J., Vilven J., Vaghy P. L., Schwartz A., Coronado R. Calcium channel activity in a purified dihydropyridine-receptor preparation of skeletal muscle. Biochemistry. 1987 Nov 3;26(22):7182–7188. doi: 10.1021/bi00396a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Seagar M. J., Jones J. F., Reber B. F., Catterall W. A. Subunit structure of dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channels from skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5478–5482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Takeshima H., Mikami A., Flockerzi V., Takahashi H., Kangawa K., Kojima M., Matsuo H., Hirose T., Numa S. Primary structure of the receptor for calcium channel blockers from skeletal muscle. Nature. 1987 Jul 23;328(6128):313–318. doi: 10.1038/328313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh K. B., Bryant S. H., Schwartz A. Effect of calcium antagonist drugs on calcium currents in mammalian skeletal muscle fibers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1986 Feb;236(2):403–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagita Y., Abdel-Ghany M., Raden D., Nelson N., Racker E. Polypeptide-dependent protein kinase from bakers' yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):925–929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Codina J., Imoto Y., Reeves J. P., Birnbaumer L., Brown A. M. A G protein directly regulates mammalian cardiac calcium channels. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1288–1292. doi: 10.1126/science.2446390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]