Abstract
Glucose is a well-known stimulus of proinsulin biosynthesis. In purified beta cells, the sugar induces a 25-fold increase in the synthesis of insulin immunoreactive material over 60-min incubation. Autoradiographic analysis of the individual cells shows that this effect is achieved via dose-dependent recruitment of pancreatic beta cells to biosynthetic activity. Recruitment of beta cells is also seen in isolated islets exposed to glucose. The sigmoidal dose-response curve for glucose-induced proinsulin biosynthesis thus reflects a heterogeneous responsiveness of pancreatic beta cells rather than a progressively increasing activity of functionally homogeneous cells. Dose-dependent recruitment of functionally diverse cells may be a ubiquitous mechanism in tissue function.
Full text
PDF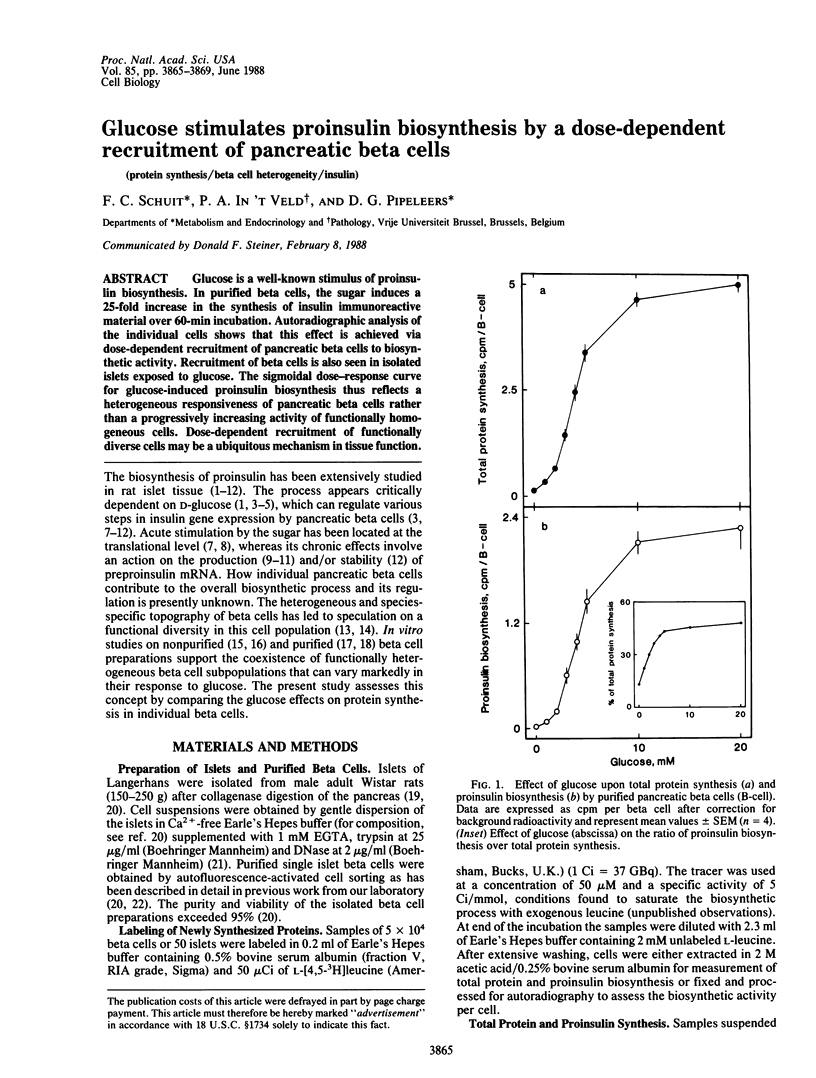



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berne C. Anti-insulin serum coupled to Sepharose 4B as a tool for the investigation of insulin biosynthesis in the B-cells of obese hyperglycemic mice. Endocrinology. 1975 Nov;97(5):1241–1247. doi: 10.1210/endo-97-5-1241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black S. Reversible interconversion of two forms of a valyl-tRNA synthetase-containing protein complex. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1111–1114. doi: 10.1126/science.3535073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone A. J., Taylor K. W. Mitabolic adaptation to pregnancy shown by increased biosynthesis of insulin in islets of Langerhans isolated from pregnant rat. Nature. 1976 Aug 5;262(5568):501–502. doi: 10.1038/262501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunstedt J., Chan S. J. Direct effect of glucose on the preproinsulin mRNA level in isolated pancreatic islets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jun 30;106(4):1383–1389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. M., Matthews E. K. Glucose-induced electrical activity in pancreatic islet cells. J Physiol. 1970 Sep;210(2):255–264. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmedt J. E., Godaux E. Fast motor units are not preferentially activated in rapid voluntary contractions in man. Nature. 1977 Jun 23;267(5613):717–719. doi: 10.1038/267717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber H., Peter H. J., Bachmeier C., Kaempf J., Studer H. Progressive recruitment of follicular cells with graded secretory responsiveness during stimulation of the thyroid gland by thyrotropin. Endocrinology. 1987 Jan;120(1):91–96. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giddings S. J., Chirgwin J., Permutt M. A. The effects of fasting and feeding on preproinsulin messenger RNA in rats. J Clin Invest. 1981 Apr;67(4):952–960. doi: 10.1172/JCI110145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodsky G. M. A threshold distribution hypothesis for packet storage of insulin and its mathematical modeling. J Clin Invest. 1972 Aug;51(8):2047–2059. doi: 10.1172/JCI107011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN E. Relation between size of neurons and their susceptibility to discharge. Science. 1957 Dec 27;126(3287):1345–1347. doi: 10.1126/science.126.3287.1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENNEMAN E., SOMJEN G., CARPENTER D. O. FUNCTIONAL SIGNIFICANCE OF CELL SIZE IN SPINAL MOTONEURONS. J Neurophysiol. 1965 May;28:560–580. doi: 10.1152/jn.1965.28.3.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halban P. A., Wollheim C. B. Intracellular degradation of insulin stores by rat pancreatic islets in vitro. An alternative pathway for homeostasis of pancreatic insulin content. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6003–6006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellman B., Sehlin J., Täljedal I. Uptake of alanine, arginine and leucine by mammalian pancreatic beta-cells. Endocrinology. 1971 Dec;89(6):1432–1439. doi: 10.1210/endo-89-6-1432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell S. L., Taylor K. W. Effects of glucose concentration on incorporation of [3H]leucine into insulin using isolated mammalian islets of Langerhans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 28;130(2):519–521. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Okamoto H. Translational control of proinsulin synthesis by glucose. Nature. 1980 Jan 3;283(5742):100–102. doi: 10.1038/283100a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACY P. E. Electron microscopy of the normal islets of Langerhans; studies in the dog, rabbit, guinea pig and rat. Diabetes. 1957 Nov-Dec;6(6):498–507. doi: 10.2337/diab.6.6.498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin B. J., Nagy B. R., Haist R. E. Effect of various concentrations of glucose on insulin biosynthesis. Endocrinology. 1972 Jul;91(1):309–311. doi: 10.1210/endo-91-1-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. T., Palmer W., Wu J. Y., Chan L. Estrogen induction of very low density apolipoprotein II synthesis, a major avian liver yolk protein, involves the recruitment of hepatocytes. Endocrinology. 1986 Feb;118(2):538–544. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-2-538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malaisse W. J., Sener A., Herchuelz A., Hutton J. C. Insulin release: the fuel hypothesis. Metabolism. 1979 Apr;28(4):373–386. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(79)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-Brown H. S., Stein R. B., Yemm R. The orderly recruitment of human motor units during voluntary isometric contractions. J Physiol. 1973 Apr;230(2):359–370. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen D. A., Welsh M., Casadaban M. J., Steiner D. F. Control of insulin gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells and in an insulin-producing cell line, RIN-5F cells. I. Effects of glucose and cyclic AMP on the transcription of insulin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13585–13589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Unger R. H. Functional subdivision of islets of Langerhans and possible role of D cells. Lancet. 1975 Dec 20;2(7947):1243–1244. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Permutt M. A., Kipnis D. M. Insulin biosynthesis. I. On the mechanism of glucose stimulation. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1194–1199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Marichal M., Malaisse W. J. The stimulus-secretion coupling of glucose-induced insulin release. XIV. Glucose regulation of insular biosynthetic activity. Endocrinology. 1973 Nov;93(5):1001–1011. doi: 10.1210/endo-93-5-1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Pipeleers-Marichal M. A. A method for the purification of single A, B and D cells and for the isolation of coupled cells from isolated rat islets. Diabetologia. 1981 Jun;20(6):654–663. doi: 10.1007/BF00257436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Pipeleers-Marichal M. A., Karl I. E., Kipnis D. M. Secretory capability of islets transplanted intraportally in the diabetic rat. Diabetes. 1978 Aug;27(8):817–824. doi: 10.2337/diab.27.8.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., Schuit F. C., in't Veld P. A., Maes E., Hooghe-Peters E. L., Van de Winkel M., Gepts W. Interplay of nutrients and hormones in the regulation of insulin release. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):824–833. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. G., in't Veld P. A., Van de Winkel M., Maes E., Schuit F. C., Gepts W. A new in vitro model for the study of pancreatic A and B cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):806–816. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. Islet cell interactions with pancreatic B-cells. Experientia. 1984 Oct 15;40(10):1114–1126. doi: 10.1007/BF01971459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipeleers D. The biosociology of pancreatic B cells. Diabetologia. 1987 May;30(5):277–291. doi: 10.1007/BF00299019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon D., Meda P. Heterogeneity and contact-dependent regulation of hormone secretion by individual B cells. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Feb;162(2):507–520. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90354-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Cunningham D., Spigelman L., Aten B. Insulin biosynthesis: evidence for a precursor. Science. 1967 Aug 11;157(3789):697–700. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3789.697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van De Winkel M., Pipeleers D. Autofluorescence-activated cell sorting of pancreatic islet cells: purification of insulin-containing B-cells according to glucose-induced changes in cellular redox state. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 29;114(2):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90857-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schravendijk C. F., Foriers A., Hooghe-Peters E. L., Rogiers V., De Meyts P., Sodoyez J. C., Pipeleers D. G. Pancreatic hormone receptors on islet cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):841–848. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Winkle M., Maes E., Pipeleers D. Islet cell analysis and purification by light scatter and autofluorescence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jul 30;107(2):525–532. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91523-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M., Nielsen D. A., MacKrell A. J., Steiner D. F. Control of insulin gene expression in pancreatic beta-cells and in an insulin-producing cell line, RIN-5F cells. II. Regulation of insulin mRNA stability. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13590–13594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh M., Scherberg N., Gilmore R., Steiner D. F. Translational control of insulin biosynthesis. Evidence for regulation of elongation, initiation and signal-recognition-particle-mediated translational arrest by glucose. Biochem J. 1986 Apr 15;235(2):459–467. doi: 10.1042/bj2350459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]