Abstract
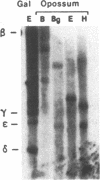
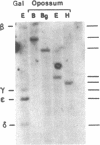
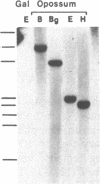
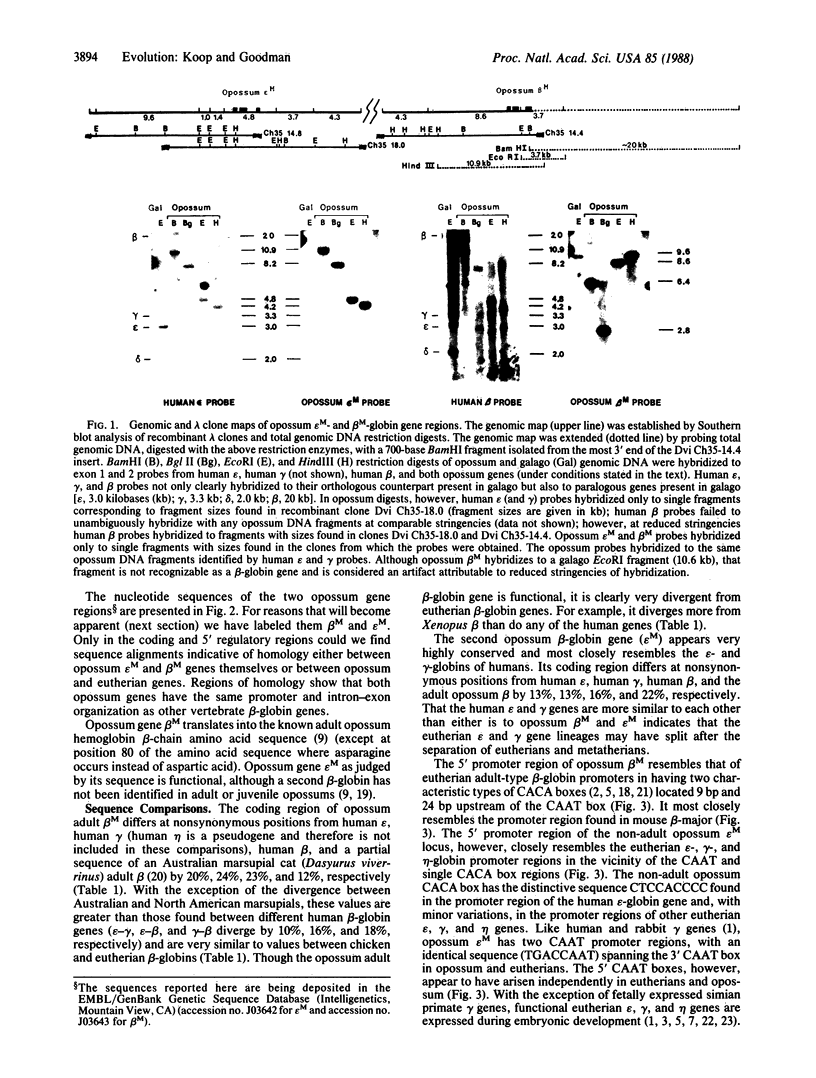
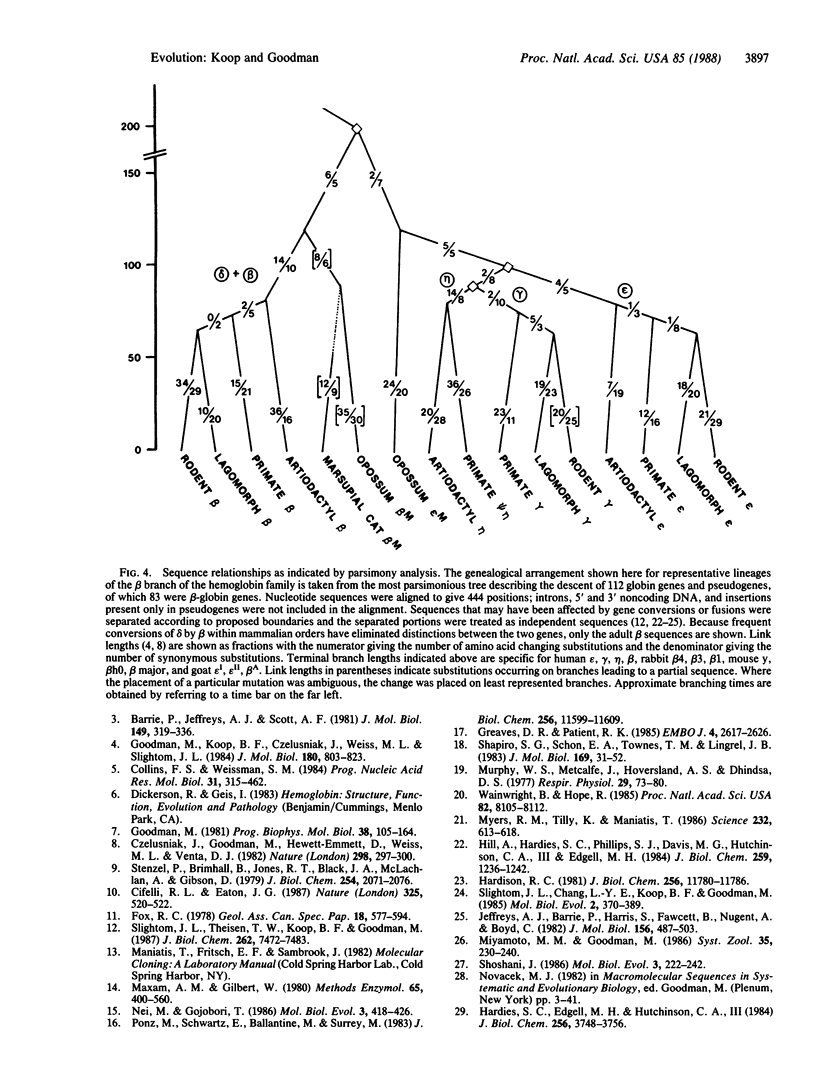
A series of gene duplications that began in a stem species of Mammalia and led to five developmentally regulated hemoglobin beta-chain loci (epsilon, gamma, eta, delta, and beta) in a common ancestor of eutherian orders Artiodactyla, Rodentia, Lagomorpha, and Primates had important consequences in mammalian evolution. Findings reported here indicate that two progenitors of the five linked genes existed by the time of the eutherian (placental mammal)-metatherian (marsupial mammal) split and that these two genes were already differentiated with respect to their promoter regions and developmental expression. Southern blot and sequence analyses of the hemoglobin beta-chain genes of the opossum (Didelphis virginiana) revealed only two genes, one with coding and promoter sequences similar to eutherian prenatally expressed epsilon, gamma, and eta genes and the other coding for adult opossum hemoglobin beta-chains and having eutherian adult beta-type promoters. The most parsimonious arrangement of greater than 80 beta-globin exon sequences depicts the opossum embryonic-type gene as orthologously related to eutherian epsilon, gamma, and eta genes and the opossum adult-type gene as orthologously related to delta and beta genes. These data further indicate that after the initial beta duplication in the stem of Mammalia, the locus that became developmentally delayed in its expression evolved at a faster rate than the locus that became embryonically expressed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrie P. A., Jeffreys A. J., Scott A. F. Evolution of the beta-globin gene cluster in man and the primates. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 5;149(3):319–336. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90476-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Weissman S. M. The molecular genetics of human hemoglobin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1984;31:315–462. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czelusniak J., Goodman M., Hewett-Emmett D., Weiss M. L., Venta P. J., Tashian R. E. Phylogenetic origins and adaptive evolution of avian and mammalian haemoglobin genes. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):297–300. doi: 10.1038/298297a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. Decoding the pattern of protein evolution. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1981;38(2):105–164. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(81)90012-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M., Koop B. F., Czelusniak J., Weiss M. L. The eta-globin gene. Its long evolutionary history in the beta-globin gene family of mammals. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):803–823. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90258-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves D. R., Patient R. K. (AT)n is an interspersed repeat in the Xenopus genome. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2617–2626. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03979.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardies S. C., Edgell M. H., Hutchison C. A., 3rd Evolution of the mammalian beta-globin gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3748–3756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison R. C. Comparison of the beta-like globin gene families of rabbits and humans indicates that the gene cluster 5'-epsilon-gamma-delta-beta-3' predates the mammalian radiation. Mol Biol Evol. 1984 Sep;1(5):390–410. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardison R. C. The nucleotide sequence of rabbit embryonic globin gene beta 3. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11780–11786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Barrie P. A., Harris S., Fawcett D. H., Nugent Z. J., Boyd A. C. Isolation and sequence analysis of a hybrid delta-globin pseudogene from the brown lemur. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):487–503. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. S., Metcalfe J., Hoversland A. S., Dhindsa D. S. Postnatal changes in blood respiratory characteristics in an American opossum (Didelphis virginiana). Respir Physiol. 1977 Feb;29(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(77)90118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Tilly K., Maniatis T. Fine structure genetic analysis of a beta-globin promoter. Science. 1986 May 2;232(4750):613–618. doi: 10.1126/science.3457470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Gojobori T. Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 Sep;3(5):418–426. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Schwartz E., Ballantine M., Surrey S. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the delta beta-globin gene region in humans. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11599–11609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro S. G., Schon E. A., Townes T. M., Lingrel J. B. Sequence and linkage of the goat epsilon I and epsilon II beta-globin genes. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):31–52. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoshani J. Mammalian phylogeny: comparison of morphological and molecular results. Mol Biol Evol. 1986 May;3(3):222–242. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Chang L. Y., Koop B. F., Goodman M. Chimpanzee fetal G gamma and A gamma globin gene nucleotide sequences provide further evidence of gene conversions in hominine evolution. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Sep;2(5):370–389. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Theisen T. W., Koop B. F., Goodman M. Orangutan fetal globin genes. Nucleotide sequence reveal multiple gene conversions during hominid phylogeny. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7472–7483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenzel P., Brimhall B., Jones R. T., Black J. A., McLachlan A., Gibson D. Opossum hemoglobin. The amino acid sequences of the alpha and beta chains. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):2071–2076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wainwright B., Hope R. Cloning and chromosomal location of the alpha- and beta-globin genes from a marsupial. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8105–8108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]