Abstract
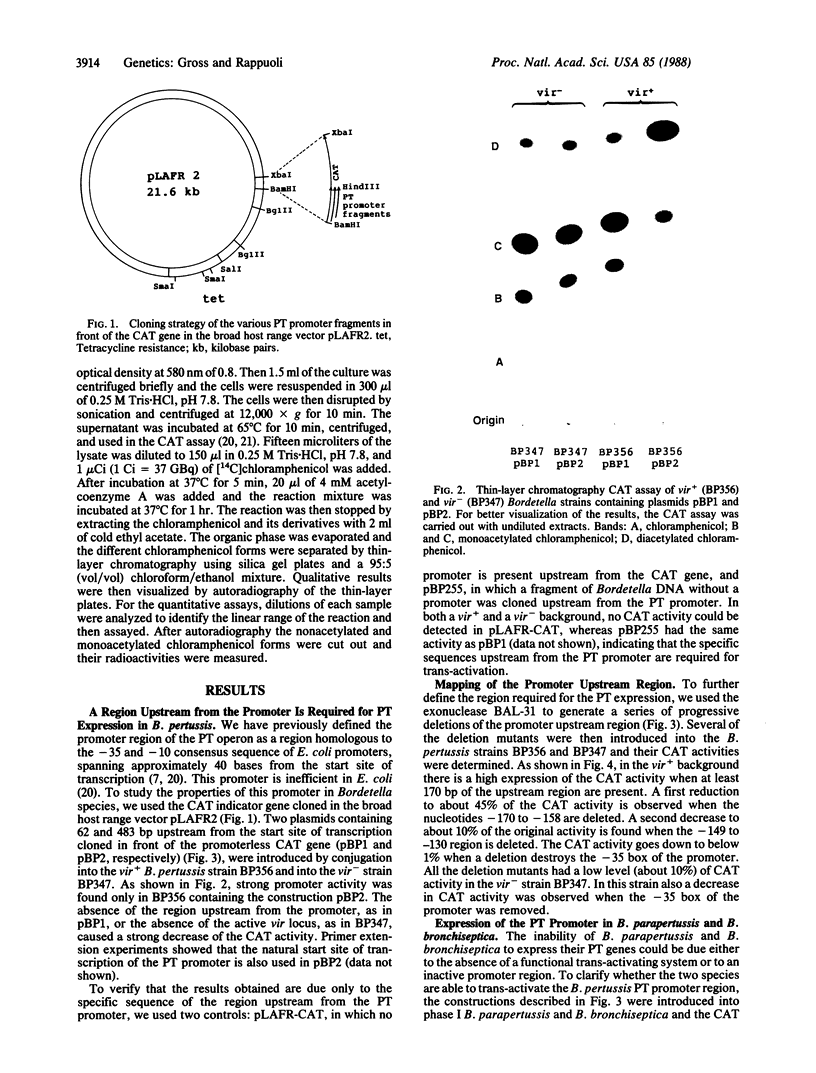
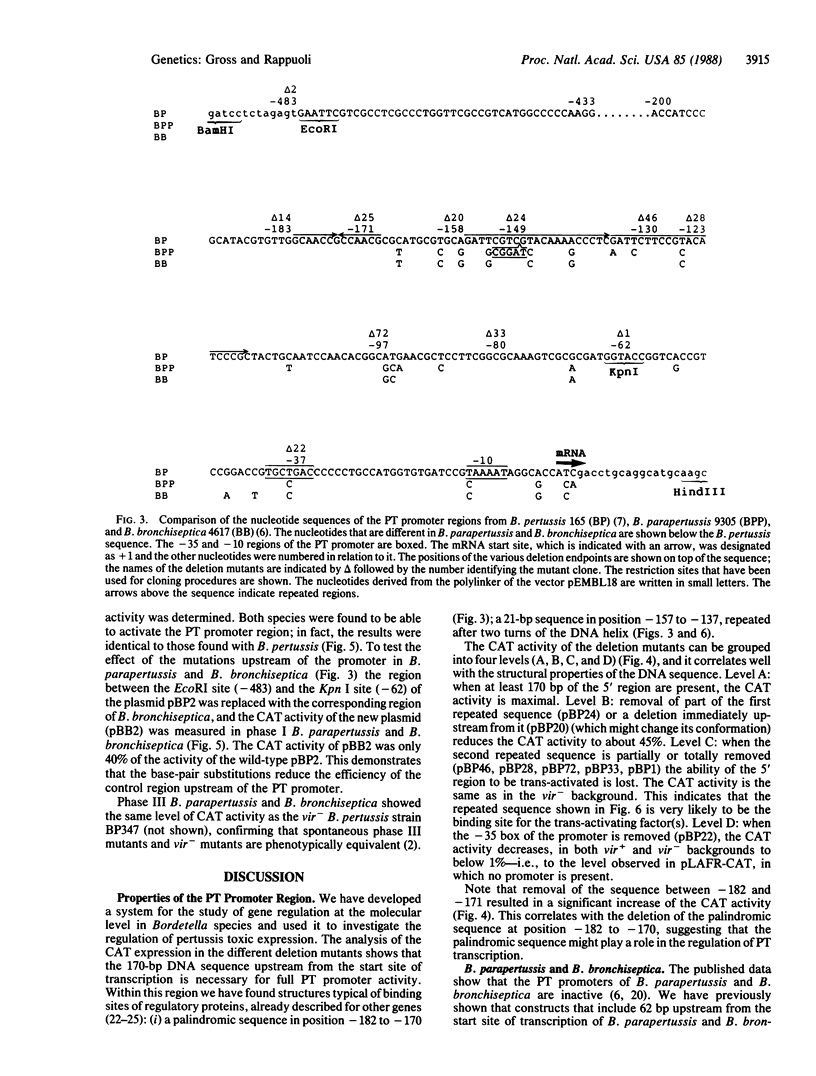
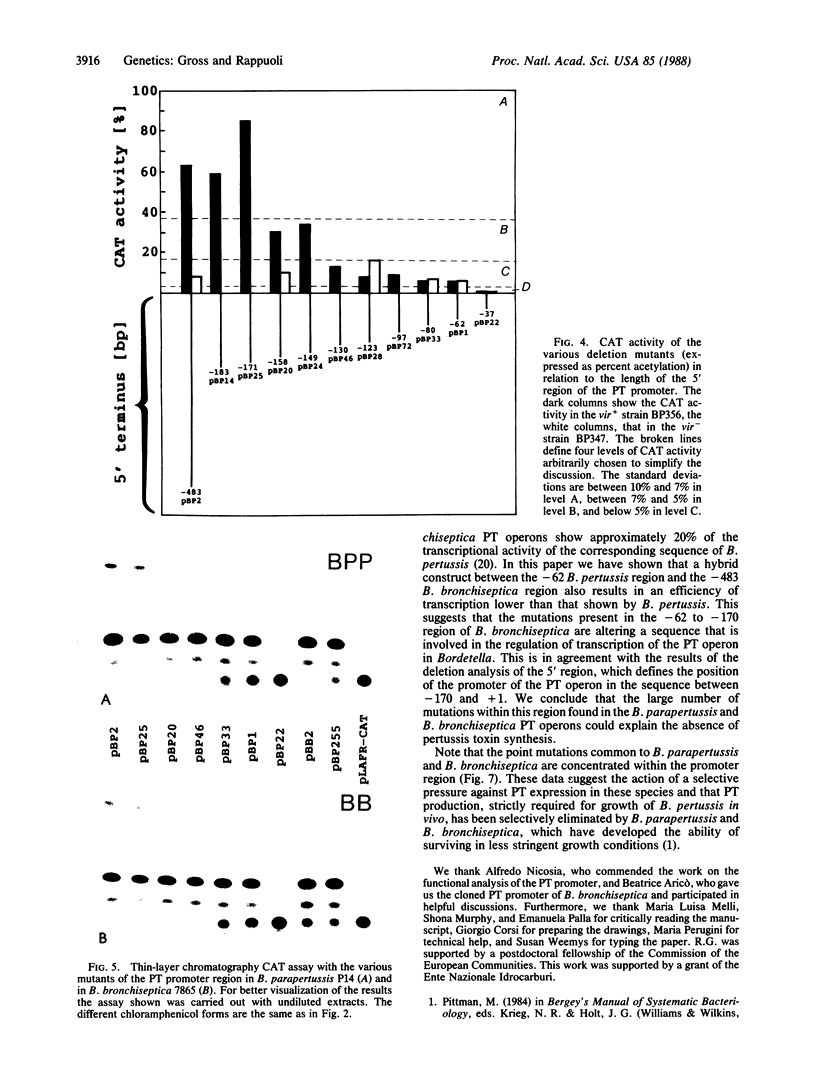
Although the genus Bordetella contains several closely related species, pertussis toxin (PT) is produced only by phase I Bordetella pertussis. In this work we have studied the regulation of expression of the PT operon and investigated why PT is produced by phase I and not by phase III B. pertussis despite the presence of the PT genes. We have constructed a vector for Bordetella species that contains the PT promoter fused to the coding region of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene, and we have used it to identify the regulatory elements involved in the transcription of the PT operon. Efficient transcription of these genes requires at least two features: (i) the 170-base-pair DNA sequence upstream from the start site of transcription and (ii) a trans-activating factor encoded by the vir locus. Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica, although endowed with a functional trans-activating system, do not produce PT because of mutations within their PT promoter regions. In contrast, phase III Bordetella species do not show any trans activity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aricò B., Gross R., Smida J., Rappuoli R. Evolutionary relationships in the genus Bordetella. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):301–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aricò B., Rappuoli R. Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica contain transcriptionally silent pertussis toxin genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2847–2853. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2847-2853.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Onofrio C., Colantuoni V., Cortese R. Structure and cell-specific expression of a cloned human retinol binding protein gene: the 5'-flanking region contains hepatoma specific transcriptional signals. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1981–1989. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03881.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Hodnett J. L., Gray H. B., Jr Extracellular nucleases of pseudomonas BAL 31. III. Use of the double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activity as the basis of a convenient method for the mapping of fragments of DNA produced by cleavage with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1445–1464. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin gene: nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1258–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.3704651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller V. L., Taylor R. K., Mekalanos J. J. Cholera toxin transcriptional activator toxR is a transmembrane DNA binding protein. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):271–279. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Schwartz M. Positive control of transcription initiation in bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:173–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Genetic analysis of phase change in Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):263–269. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.263-269.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Tn5-induced mutations affecting virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):33–41. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.33-41.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






