Abstract
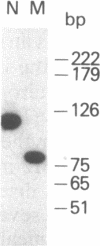
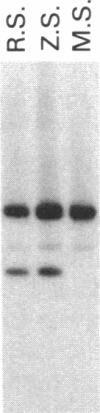
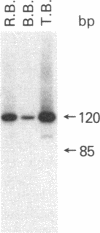
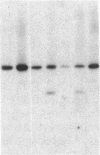
Tay-Sachs disease is an inherited disorder in which the alpha chain of the lysosomal enzyme beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase A bears the mutation. Ashkenazi Jews are found to be carriers for a severe type of Tay-Sachs disease, the classic form, 10 times more frequently than the general population. Ashkenazi Jewish patients with classic Tay-Sachs disease have appeared to be clinically and biochemically identical, and the usual assumption has been that they harbor the same alpha-chain mutation. In this study I have isolated the alpha-chain gene from an Ashkenazi Jewish patient, GM2968, with classic Tay-Sachs disease and compared its nucleotide sequences with that of the normal alpha-chain gene in the promoter region, exon and splice junction regions, and polyadenylylation signal area. Only one difference was observed between these sequences: at the 5' boundary of intron 12, a guanosine in the conserved splice junction dinucleotide sequence G-T had been altered to a cytidine. The alteration is presumed to be functionally significant and to result in aberrant mRNA splicing. Utilizing the polymerase chain reaction to amplify the region encompassing the mutation, I developed an assay to screen patients and heterozygote carriers for this mutation. Surprisingly, in each of two Ashkenazi patients, only one alpha-chain allele harbored the splice junction mutation. Only one parent of each of these patients was positive for the defect. Another Ashkenazi patient did not bear this mutation at all nor did either of the subject's parents. In addition, 30% of obligate heterozygotes tested carried the splice junction mutation, whereas 20 Ashkenazi Jews designated noncarriers by enzymatic assay were negative for this alteration. The data are consistent with the presence of more than one mutation underlying the classic form of Tay-Sachs disease in the Ashkenazi Jewish population.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahearn J. M., Jr, Bartolomei M. S., West M. L., Cisek L. J., Corden J. L. Cloning and sequence analysis of the mouse genomic locus encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10695–10705. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Karam J. H., Rutter W. J. Polymorphic DNA region adjacent to the 5' end of the human insulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5759–5763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broderick T. P., Schaff D. A., Bertino A. M., Dush M. K., Tischfield J. A., Stambrook P. J. Comparative anatomy of the human APRT gene and enzyme: nucleotide sequence divergence and conservation of a nonrandom CpG dinucleotide arrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3349–3353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conzelmann E., Kytzia H. J., Navon R., Sandhoff K. Ganglioside GM2 N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminidase activity in cultured fibroblasts of late-infantile and adult GM2 gangliosidosis patients and of healthy probands with low hexosaminidase level. Am J Hum Genet. 1983 Sep;35(5):900–913. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen S. J., Davie E. W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human prothrombin. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6165–6177. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garger S. J., Griffith O. M., Grill L. K. Rapid purification of plasmid DNA by a single centrifugation in a two-step cesium chloride-ethidium bromide gradient. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91672-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasilik A., Neufeld E. F. Biosynthesis of lysosomal enzymes in fibroblasts. Synthesis as precursors of higher molecular weight. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4937–4945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaslow D. C. A rapid biochemical method for purifying lambda DNA from phage lysates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6767–6767. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korneluk R. G., Mahuran D. J., Neote K., Klavins M. H., O'Dowd B. F., Tropak M., Willard H. F., Anderson M. J., Lowden J. A., Gravel R. A. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for the alpha-subunit of human beta-hexosaminidase. Extensive homology between the alpha- and beta-subunits and studies on Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8407–8413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Hogikyan N. D. A deletion involving Alu sequences in the beta-hexosaminidase alpha-chain gene of French Canadians with Tay-Sachs disease. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15396–15399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Hogikyan N. D. Different mutations in Ashkenazi Jewish and non-Jewish French Canadians with Tay-Sachs disease. Science. 1986 Jun 27;232(4758):1646–1648. doi: 10.1126/science.3754980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Piekarz R., Neufeld E. F., Shows T. B., Suzuki K. Human beta-hexosaminidase alpha chain: coding sequence and homology with the beta chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7830–7834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerowitz R., Proia R. L. cDNA clone for the alpha-chain of human beta-hexosaminidase: deficiency of alpha-chain mRNA in Ashkenazi Tay-Sachs fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5394–5398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno K., Suzuki K. Mutation in GM2-gangliosidosis B1 variant. J Neurochem. 1988 Jan;50(1):316–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb13266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Antonarakis S. E., Goff S. C., Boehm C. D., Sexton J. P., Waber P. G., Giardina P. J. Linkage of beta-thalassaemia mutations and beta-globin gene polymorphisms with DNA polymorphisms in human beta-globin gene cluster. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):627–631. doi: 10.1038/296627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orkin S. H., Kazazian H. H., Jr The mutation and polymorphism of the human beta-globin gene and its surrounding DNA. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:131–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proia R. L., Soravia E. Organization of the gene encoding the human beta-hexosaminidase alpha-chain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5677–5681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhoff K., Conzelmann E. The biochemical basis of gangliosidoses. Neuropediatrics. 1984 Sep;15 (Suppl):85–92. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sando G. N., Neufeld E. F. Recognition and receptor-mediated uptake of a lysosomal enzyme, alpha-l-iduronidase, by cultured human fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):619–627. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Proudfoot N. J., Shander M., Maniatis T. A single-base change at a splice site in a beta 0-thalassemic gene causes abnormal RNA splicing. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):903–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90452-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Meyer F., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Unusual splice sites revealed by mutagenic inactivation of an authentic splice site of the rabbit beta-globin gene. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):38–43. doi: 10.1038/301038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]