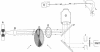
Abstract
The role of Ca2+ in regulating smooth muscle contraction was investigated by measuring isometric force and [Ca2+] simultaneously in individual single smooth-muscle cells. [Ca2+] was measured with fura-2 and a high time-resolution dual-wavelength digital microfluorimeter, and force was measured with an ultrasensitive force transducer attached to a probe around which was tied one end of the cell. Both [Ca2+] and force increase after maximal electrical stimulus, with [Ca2+] increasing considerably before the first detectable increase in force. Force development exhibited maximal sensitivity to [Ca2+] between 150 and 500 nM Ca2+. This Ca2+ sensitivity can account for the fact that many physiological stimuli produce full contraction even though such stimuli only increase Ca2+ to 600-800 nM. When Ca2+ was induced to increase rapidly, the relation between [Ca2+] and force exhibited hysteresis. During the onset of contraction, force at a given [Ca2+] was lower than during the muscle's return to rest, thus suggesting the existence of a slow step(s) linking Ca2+ and force development in smooth muscle. The direction of this hysteresis reversed during contractions in which Ca2+ increased slowly, suggesting that the contractile process becomes desensitized to [Ca2+] with time. These relations between calcium and force in intact single smooth-muscle cells differ in many respects from the relation found previously in chemically permeabilized multicellular preparations of smooth muscle.
Full text
PDF
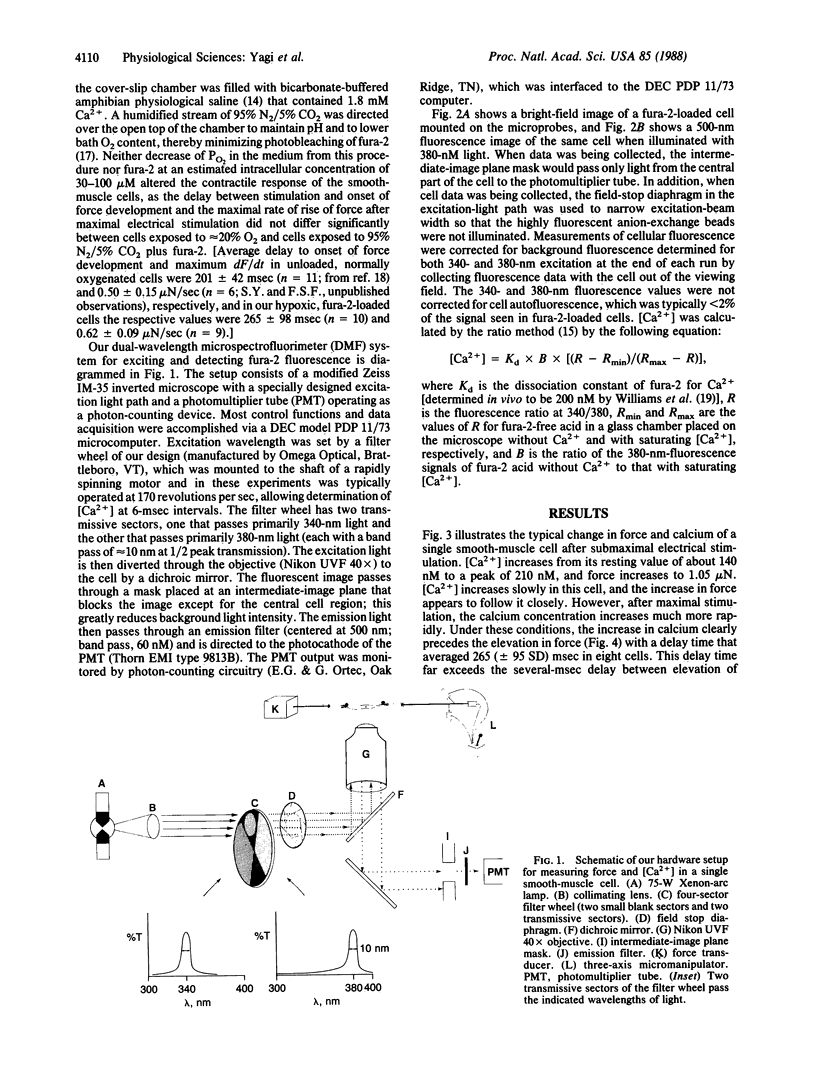
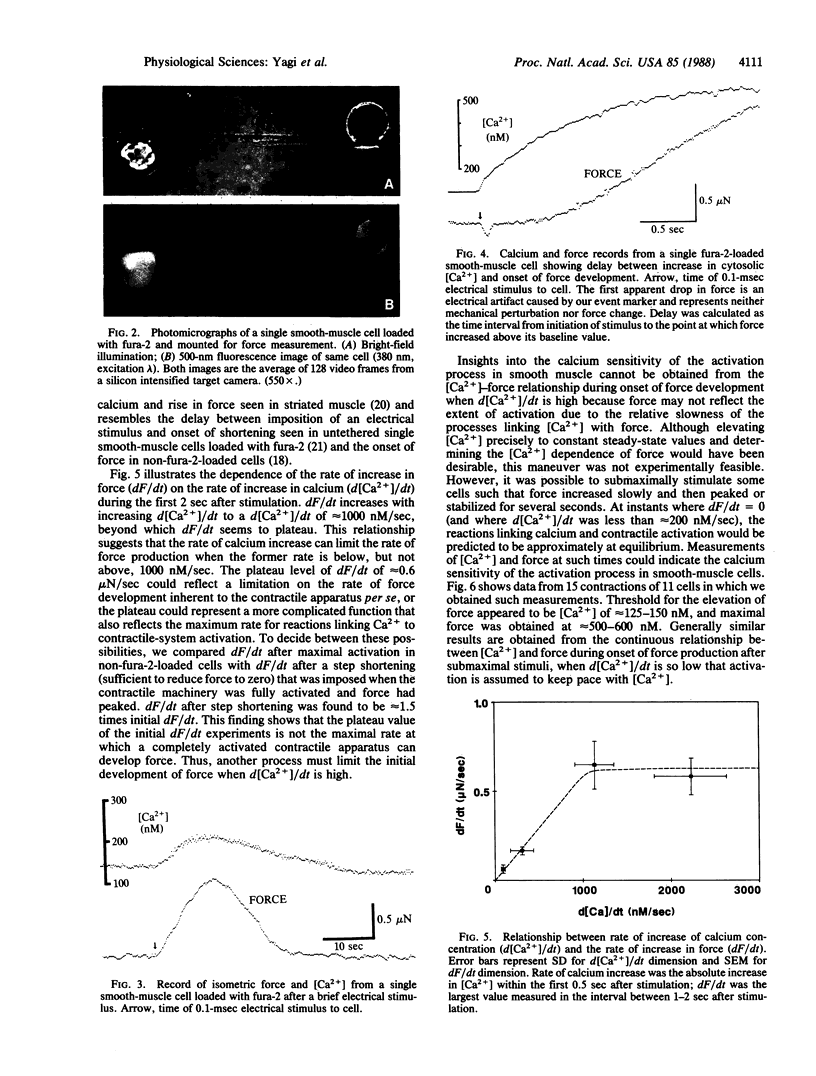
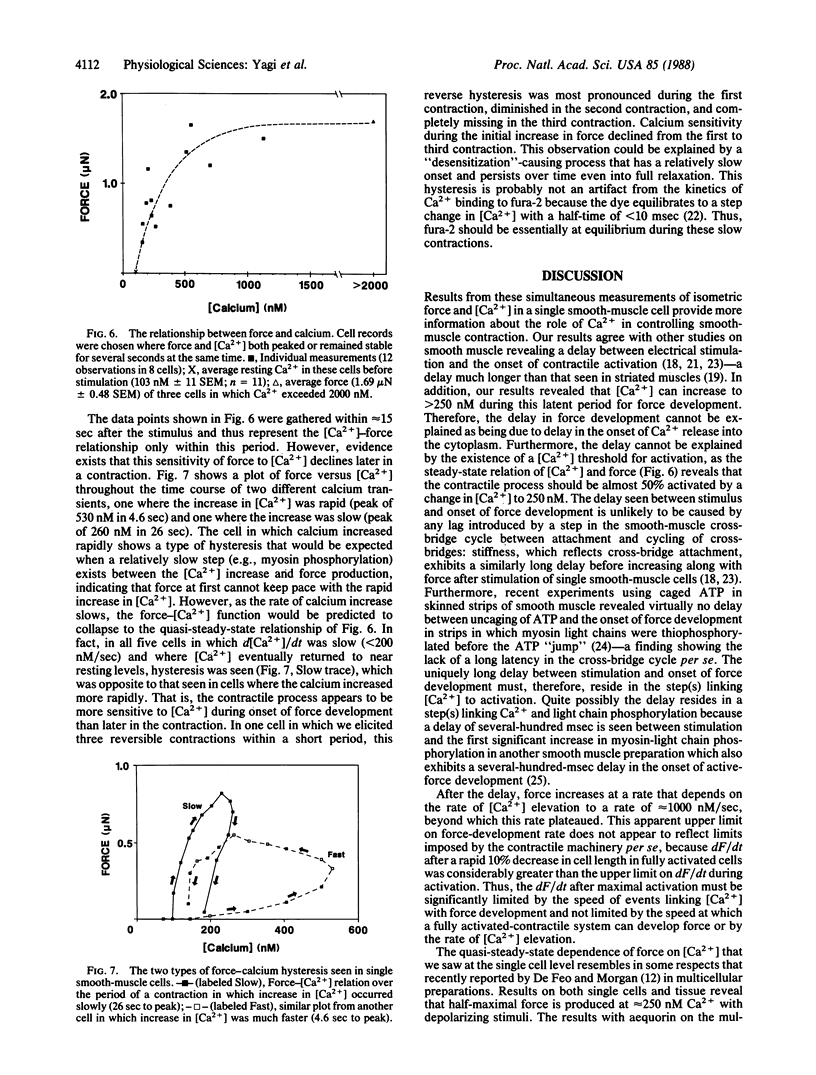

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arner A. Mechanical characteristics of chemically skinned guinea-pig taenia coli. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Dec;395(4):277–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00580790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsotti R. J., Ikebe M., Hartshorne D. J. Effects of Ca2+, Mg2+, and myosin phosphorylation on skinned smooth muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1987 May;252(5 Pt 1):C543–C554. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.5.C543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. L., Fay F. S. Photobleaching of fura-2 and its effect on determination of calcium concentrations. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):C613–C618. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.4.C613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blinks J. R., Rüdel R., Taylor S. R. Calcium transients in isolated amphibian skeletal muscle fibres: detection with aequorin. J Physiol. 1978 Apr;277:291–323. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee M., Murphy R. A. Calcium-dependent stress maintenance without myosin phosphorylation in skinned smooth muscle. Science. 1983 Jul 29;221(4609):464–466. doi: 10.1126/science.6867722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo T. T., Morgan K. G. Calcium-force relationships as detected with aequorin in two different vascular smooth muscles of the ferret. J Physiol. 1985 Dec;369:269–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dillon P. F., Aksoy M. O., Driska S. P., Murphy R. A. Myosin phosphorylation and the cross-bridge cycle in arterial smooth muscle. Science. 1981 Jan 30;211(4481):495–497. doi: 10.1126/science.6893872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay F. S., Hoffmann R., Leclair S., Merriam P. Preparation of individual smooth muscle cells from the stomach of Bufo marinus. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):284–292. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85027-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay F. S. Isometric contractile properties of single isolated smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1977 Feb 10;265(5594):553–556. doi: 10.1038/265553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay F. S., Shlevin H. H., Granger W. C., Jr, Taylor S. R. Aequorin luminescence during activation of single isolated smooth muscle cells. Nature. 1979 Aug 9;280(5722):506–508. doi: 10.1038/280506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagelmann M., Güth K. Effect of inorganic phosphate on the Ca2+ sensitivity in skinned Taenia coli smooth muscle fibers. Comparison of tension, ATPase activity, and phosphorylation of the regulatory myosin light chains. Biophys J. 1987 Mar;51(3):457–463. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83367-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iino M. Tension responses of chemically skinned fibre bundles of the guinea-pig taenia caeci under varied ionic environments. J Physiol. 1981 Nov;320:449–467. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. P., Timmerman M. P., Bagshaw C. R., Ashley C. C. The kinetics of calcium binding to fura-2 and indo-1. FEBS Lett. 1987 May 25;216(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80752-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. Activation of smooth muscle contraction: relation between myosin phosphorylation and stiffness. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.3754063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. Myosin phosphorylation, force, and maximal shortening velocity in neurally stimulated tracheal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985 Sep;249(3 Pt 1):C238–C247. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.249.3.C238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. The function of myosin and myosin light chain kinase phosphorylation in smooth muscle. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:593–620. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kargacin G. J., Fay F. S. Physiological and structural properties of saponin-skinned single smooth muscle cells. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jul;90(1):49–73. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Goldbeter A., Stock J. B. Amplification and adaptation in regulatory and sensory systems. Science. 1982 Jul 16;217(4556):220–225. doi: 10.1126/science.7089556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Y., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Autophosphorylation reversibly regulates the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependence of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4253–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nayler R. A., Sparrow M. P. Inhibition of cycling and noncycling cross bridges in skinned smooth muscle by vanadate. Am J Physiol. 1986 Feb;250(2 Pt 1):C325–C332. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.2.C325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul R. J., Doerman G., Zeugner C., Rüegg J. C. The dependence of unloaded shortening velocity on Ca++, calmodulin, and duration of contraction in "chemically skinned" smooth muscle. Circ Res. 1983 Sep;53(3):342–351. doi: 10.1161/01.res.53.3.342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg J. C., Paul R. J. Vascular smooth muscle. Calmodulin and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase after calcium sensitivity in porcine carotid skinned fibers. Circ Res. 1982 Mar;50(3):394–399. doi: 10.1161/01.res.50.3.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somlyo A. V., Goldman Y. E., Fujimori T., Bond M., Trentham D. R., Somlyo A. P. Cross-bridge kinetics, cooperativity, and negatively strained cross-bridges in vertebrate smooth muscle. A laser-flash photolysis study. J Gen Physiol. 1988 Feb;91(2):165–192. doi: 10.1085/jgp.91.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparrow M. P., Pfitzer G., Gagelmann M., Rüegg J. C. Effect of calmodulin, Ca2+, and cAMP protein kinase on skinned tracheal smooth muscle. Am J Physiol. 1984 Mar;246(3 Pt 1):C308–C314. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1984.246.3.C308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshaw D. M., Fay F. S. Cross-bridge elasticity in single smooth muscle cells. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Aug;82(2):157–199. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.2.157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshaw D. M., McBride W. J., Hubbard M. S. Ca2+ and MgATP2- dependence of shortening in skinned single smooth muscle cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 1):C418–C427. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.252.4.C418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Becker P. L., Fay F. S. Regional changes in calcium underlying contraction of single smooth muscle cells. Science. 1987 Mar 27;235(4796):1644–1648. doi: 10.1126/science.3103219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. A., Fogarty K. E., Tsien R. Y., Fay F. S. Calcium gradients in single smooth muscle cells revealed by the digital imaging microscope using Fura-2. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):558–561. doi: 10.1038/318558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]