Abstract
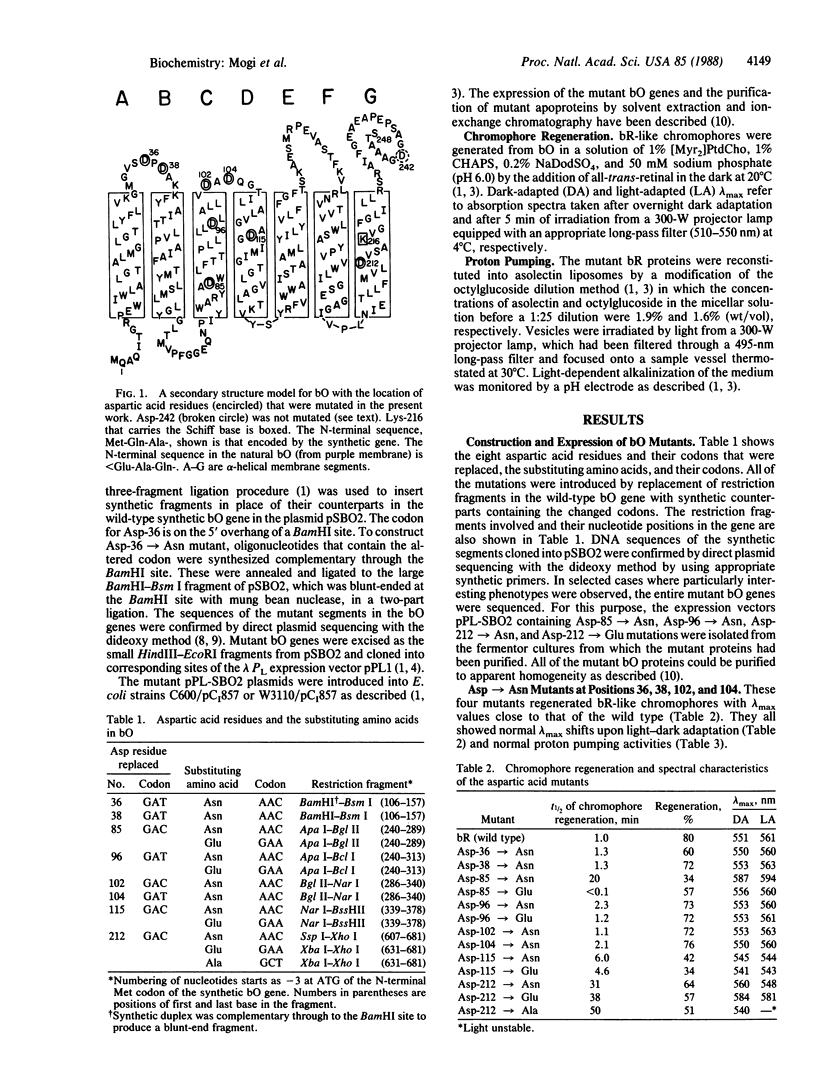
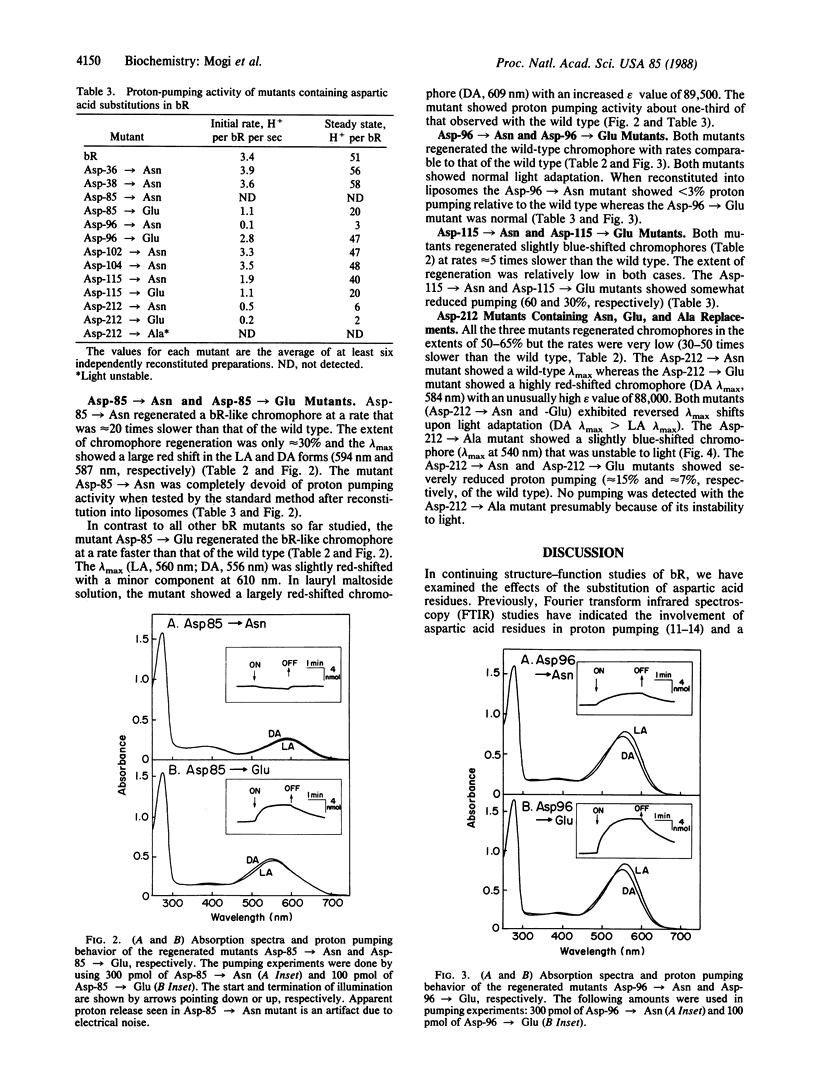
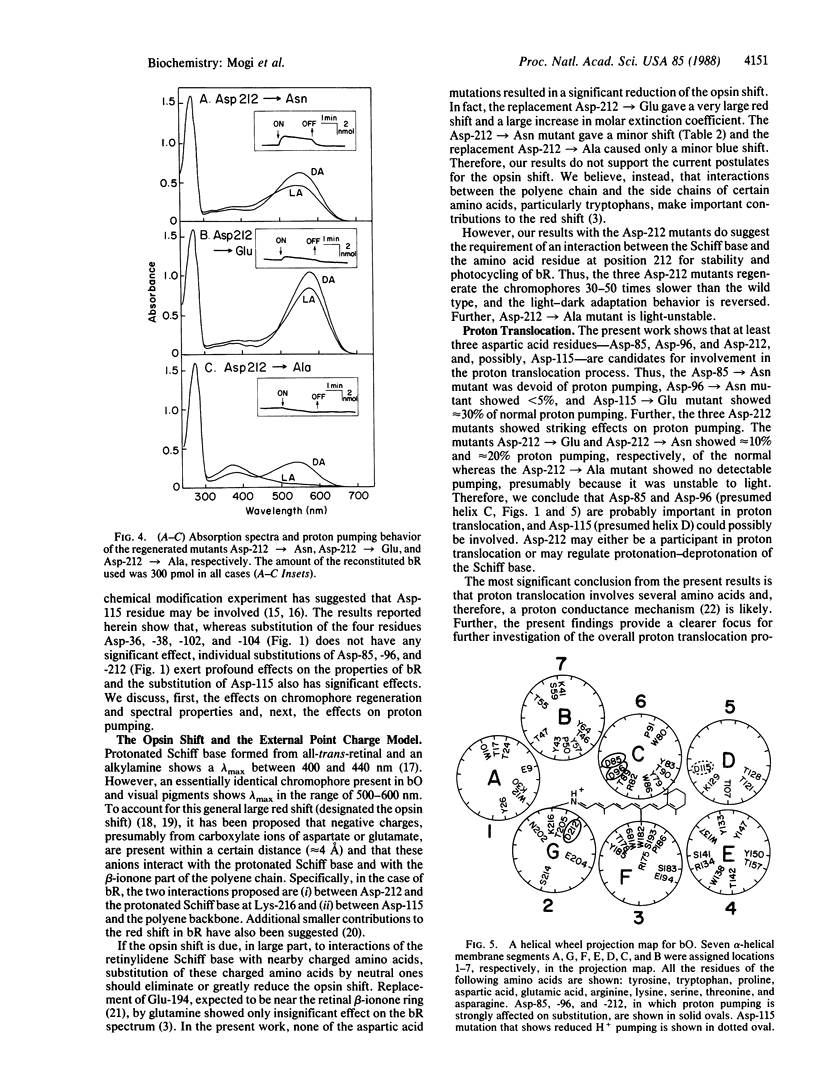
We have substituted each of the aspartic acid residues in bacteriorhodopsin to determine their possible role in proton translocation by this protein. The aspartic acid residues were replaced by asparagines; in addition, Asp-85, -96, -115, and -112 were changed to glutamic acid and Asp-212 was also replaced by alanine. The mutant bacteriorhodopsin genes were expressed in Escherichia coli and the proteins were purified. The mutant proteins all regenerated bacteriorhodopsin-like chromophores when treated with a detergent-phospholipid mixture and retinal. However, the rates of regeneration of the chromophores and their lambda max varied widely. No support was obtained for the external point charge model for the opsin shift. The Asp-85----Asn mutant showed not detectable proton pumping, the Asp-96----Asn and Asp-212----Glu mutants showed less than 10% and the Asp-115----Glu mutant showed approximately equal to 30% of the normal proton pumping. The implications of these findings for possible mechanisms of proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin are discussed.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agard D. A., Stroud R. M. Linking regions between helices in bacteriorhodopsin revealed. Biophys J. 1982 Mar;37(3):589–602. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Stern L. J., Chao B. H., Khorana H. G. Structure-function studies on bacteriorhodopsin. IV. Purification and renaturation of bacterio-opsin polypeptide expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9271–9276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doukas A. G., Pande A., Suzuki T., Callender R. H., Honig B., Ottolenghi M. On the mechanism of hydrogen-deuterium exchange in bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1981 Feb;33(2):275–279. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(81)84889-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg B., Lewis A., Porta T. K., Nagle J. F., Stoeckenius W. Exchange kinetics of the Schiff base proton in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6571–6573. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard M., Gerwert K., Hess B., Kreutz W., Siebert F. Light-driven protonation changes of internal aspartic acids of bacteriorhodopsin: an investigation by static and time-resolved infrared difference spectroscopy using [4-13C]aspartic acid labeled purple membrane. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):400–407. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Zaccai G. Bacteriorhodopsin is an inside-out protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garger S. J., Griffith O. M., Grill L. K. Rapid purification of plasmid DNA by a single centrifugation in a two-step cesium chloride-ethidium bromide gradient. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 28;117(3):835–842. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91672-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett N. R., Stern L. J., Chao B. H., Kronis K. A., Khorana H. G. Structure-function studies on bacteriorhodopsin. V. Effects of amino acid substitutions in the putative helix F. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9277–9284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Unwin P. N. Three-dimensional model of purple membrane obtained by electron microscopy. Nature. 1975 Sep 4;257(5521):28–32. doi: 10.1038/257028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Radhakrishnan R., Bayley H., Khorana H. G. Orientation of retinal in bacteriorhodopsin as studied by cross-linking using a photosensitive analog of retinal. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13616–13623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jubb J. S., Worcester D. L., Crespi H. L., Zaccaï G. Retinal location in purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium: a neutron diffraction study of membranes labelled in vivo with deuterated retinal. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1455–1461. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01996.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Kimura Y., Kinosita K., Jr, Ikegami A. Location and orientation of the chromophore in bacteriorhodopsin. Analysis by fluorescence energy transfer. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):337–359. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90282-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao M. J., Khorana H. G. Removal of the carboxyl-terminal peptide does not affect refolding or function of bacteriorhodopsin as a light-dependent proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4194–4199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lo K. M., Jones S. S., Hackett N. R., Khorana H. G. Specific amino acid substitutions in bacterioopsin: Replacement of a restriction fragment in the structural gene by synthetic DNA fragments containing altered codons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2285–2289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogi T., Stern L. J., Hackett N. R., Khorana H. G. Bacteriorhodopsin mutants containing single tyrosine to phenylalanine substitutions are all active in proton translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5595–5599. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Morowitz H. J. Molecular mechanisms for proton transport in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):298–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassal M., Mogi T., Karnik S. S., Khorana H. G. Structure-function studies on bacteriorhodopsin. III. Total synthesis of a gene for bacterio-opsin and its expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9264–9270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renthal R., Cothran M., Espinoza B., Wall K. A., Bernard M. Light activates the reaction of bacteriorhodopsin aspartic acid-115 with dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 30;24(16):4275–4279. doi: 10.1021/bi00337a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renthal R., Harris G. J., Parrish R. Reaction of the purple membrane with a carbodiimide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 14;547(2):258–269. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., Zagaeski M., Cantore W. A. Conformational changes of bacteriorhodopsin detected by Fourier transform infrared difference spectroscopy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):483–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90478-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiff F., Wallat I., Ermann P., Heyn M. P. A neutron diffraction study on the location of the polyene chain of retinal in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3227–3231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiff F., Westerhausen J., Wallat I., Heyn M. P. Location of the cyclohexene ring of the chromophore of bacteriorhodopsin by neutron diffraction with selectively deuterated retinal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7746–7750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M., Leung D. W., Gillam S., Astell C. R., Montgomery D. L., Hall B. D. Sequence of the gene for iso-1-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. L., McCain D. A., Nakanishi K., Okabe M., Shimizu N., Rodman H., Honig B., Bogomolni R. A. Chromophore/protein interaction in bacterial sensory rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):479–483. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83657-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trewhella J., Anderson S., Fox R., Gogol E., Khan S., Engelman D., Zaccai G. Assignment of segments of the bacteriorhodopsin sequence to positions in the structural map. Biophys J. 1983 Jun;42(3):233–241. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84391-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



