Abstract
To understand the immune response to infection by tuberculosis and leprosy bacilli and to develop improved vaccines, the nature of antigens that are involved in humoral and cell-mediated immunity was investigated. We have determined that five immunodominant protein antigens under study are homologues of stress proteins. This finding and observations with other pathogens suggest that infectious agents may respond to the host environment by producing stress proteins and that these proteins can be important immune targets. We postulate that abundant and highly conserved stress proteins may have "immunoprophylactic" potential for a broad spectrum of human pathogens.
Full text
PDF

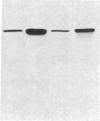
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Eukaryotic Mr 83,000 heat shock protein has a homologue in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5177–5181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco A. E., Favaloro J. M., Burkot T. R., Culvenor J. G., Crewther P. E., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Coppel R. L., Kemp D. J. A repetitive antigen of Plasmodium falciparum that is homologous to heat shock protein 70 of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8713–8717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom B. R., Godal T. Selective primary health care: strategies for control of disease in the developing world. V. Leprosy. Rev Infect Dis. 1983 Jul-Aug;5(4):765–780. doi: 10.1093/clinids/5.4.765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boom W. H., Husson R. N., Young R. A., David J. R., Piessens W. F. In vivo and in vitro characterization of murine T-cell clones reactive to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1987 Sep;55(9):2223–2229. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.9.2223-2229.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton W. J., Garsia R. J., Hellqvist L., Watson J. D., Basten A. The characterization and immunoreactivity of a 70 kD protein common to Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium bovis (BCG). Lepr Rev. 1986 Dec;57 (Suppl 2):67–75. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton W. J., Hellqvist L., Basten A., Inglis A. S. Immunoreactivity of a 70 kD protein purified from Mycobacterium bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guerin by monoclonal antibody affinity chromatography. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):695–708. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman M. F., Morgan R. W., Jacobson F. S., Ames B. N. Positive control of a regulon for defenses against oxidative stress and some heat-shock proteins in Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Bruyn J., Bosmans R., Turneer M., Weckx M., Nyabenda J., Van Vooren J. P., Falmagne P., Wiker H. G., Harboe M. Purification, partial characterization, and identification of a skin-reactive protein antigen of Mycobacterium bovis BCG. Infect Immun. 1987 Jan;55(1):245–252. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.1.245-252.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmrich F., Thole J., van Embden J., Kaufmann S. H. A recombinant 64 kilodalton protein of Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin specifically stimulates human T4 clones reactive to mycobacterial antigens. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):1024–1029. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C. P., Hendrix R. W., Kaiser A. D., Wood W. B. Role of the host cell in bacteriophage morphogenesis: effects of a bacterial mutation on T4 head assembly. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 13;239(89):38–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio239038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn H., Kaufmann S. H. The role of cell-mediated immunity in bacterial infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1981 Nov-Dec;3(6):1221–1250. doi: 10.1093/clinids/3.6.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrom R., Culpepper J., Harrison R. A., Agabian N., Newport G. A major immunogen in Schistosoma mansoni infections is homologous to the heat-shock protein Hsp70. J Exp Med. 1987 May 1;165(5):1430–1435. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.5.1430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husson R. N., Young R. A. Genes for the major protein antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: the etiologic agents of tuberculosis and leprosy share an immunodominant antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1679–1683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins A. J., March J. B., Oliver I. R., Masters M. A DNA fragment containing the groE genes can suppress mutations in the Escherichia coli dnaA gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Mar;202(3):446–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00333275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Väth U., Thole J. E., Van Embden J. D., Emmrich F. Enumeration of T cells reactive with Mycobacterium tuberculosis organisms and specific for the recombinant mycobacterial 64-kDa protein. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Mar;17(3):351–357. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Ivanyi J., Rees A. D., Rothbard J. B., Howland K., Young R. A., Young D. B. Mapping of T cell epitopes using recombinant antigens and synthetic peptides. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1245–1249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02360.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Ivanyi J., Rees A., Young R. A., Young D. B. The identification of T cell epitopes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis using human T lymphocyte clones. Lepr Rev. 1986 Dec;57 (Suppl 2):131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb J. R., Young D. B. A novel approach to the identification of T-cell epitopes in Mycobacterium tuberculosis using human T-lymphocyte clones. Immunology. 1987 Jan;60(1):1–5. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehra V., Sweetser D., Young R. A. Efficient mapping of protein antigenic determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7013–7017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. W., Christman M. F., Jacobson F. S., Storz G., Ames B. N. Hydrogen peroxide-inducible proteins in Salmonella typhimurium overlap with heat shock and other stress proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8059–8063. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustafa A. S., Gill H. K., Nerland A., Britton W. J., Mehra V., Bloom B. R., Young R. A., Godal T. Human T-cell clones recognize a major M. leprae protein antigen expressed in E. coli. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):63–66. doi: 10.1038/319063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oftung F., Mustafa A. S., Husson R., Young R. A., Godal T. Human T cell clones recognize two abundant Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein antigens expressed in Escherichia coli. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):927–931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottenhoff T. H., Klatser P. R., Ivanyi J., Elferink D. G., de Wit M. Y., de Vries R. R. Mycobacterium leprae-specific protein antigens defined by cloned human helper T cells. Nature. 1986 Jan 2;319(6048):66–68. doi: 10.1038/319066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Speculations on the functions of the major heat shock and glucose-regulated proteins. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):959–961. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90693-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Results of a World Health Organization-sponsored workshop on monoclonal antibodies to Mycobacterium leprae. Infect Immun. 1985 May;48(2):603–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.48.2.603-605.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Results of a World Health Organization-sponsored workshop to characterize antigens recognized by mycobacterium-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1986 Feb;51(2):718–720. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.2.718-720.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöffl F., Raschke E., Nagao R. T. The DNA sequence analysis of soybean heat-shock genes and identification of possible regulatory promoter elements. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2491–2497. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02161.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M. The 65-kilodalton antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1080–1088. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1080-1088.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Kakefuda T. Involvement of a bacterial factor in morphogenesis of bacteriophage capsid. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 13;239(89):34–37. doi: 10.1038/newbio239034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D. B., Kent L., Young R. A. Screening of a recombinant mycobacterial DNA library with polyclonal antiserum and molecular weight analysis of expressed antigens. Infect Immun. 1987 Jun;55(6):1421–1425. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.6.1421-1425.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., Kent L., Rees A., Lamb J., Ivanyi J. Immunological activity of a 38-kilodalton protein purified from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):177–183. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.177-183.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Mehra V., Sweetser D., Buchanan T., Clark-Curtiss J., Davis R. W., Bloom B. R. Genes for the major protein antigens of the leprosy parasite Mycobacterium leprae. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):450–452. doi: 10.1038/316450a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]