Abstract
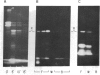
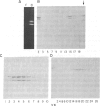
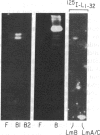
Using purified components in affinity chromatography and blot binding assays, we have found that rat liver lamins A, B, and C can associate in homotypic and heterotypic fashions. Heterotypic A-B and C-B complexes are unusually stable and involve the common amino-terminal domain of lamins A and C, but not their helical "rod" domain. A synthetic peptide, comprising the first 32 amino acid residues of lamins A and C, is able to fully compete with the intact molecules for binding to lamin B. Conversely, heterotypic A-C associations and homotypic A-A and C-C interactions appear significantly weaker than A/C-B binding and do not involve the lamin A and C amino-terminal domain. Homotypic B-B complexes are not formed to any considerable extent unless isolated lamin B subunits are "superphosphorylated" in vitro with protein kinase A. However, when lamins A and C are similarly modified, no changes in their binding specificity can be detected. These data suggest that the nuclear lamina, unlike other multicomponent intermediate filaments, constitutes a nonobligatory heteropolymer. They also indicate that cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of interphase lamin B could cause remodeling of the lamina and establishment of homopolymeric domains.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson R. P., Blobel G. Isolation of nuclear pore complexes in association with a lamina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1007–1011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aebi U., Cohn J., Buhle L., Gerace L. The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate-type filaments. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):560–564. doi: 10.1038/323560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benavente R., Krohne G., Franke W. W. Cell type-specific expression of nuclear lamina proteins during development of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):177–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B., Gerace L. A cell free system to study reassembly of the nuclear envelope at the end of mitosis. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):639–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. Z., Chaudhary N., Blobel G. cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Scheer U., Krohne G., Jarasch E. D. The nuclear envelope and the architecture of the nuclear periphery. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):39s–50s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.39s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Hatzfeld M., Winter S. Protein complexes of intermediate-sized filaments: melting of cytokeratin complexes in urea reveals different polypeptide separation characteristics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7113–7117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Phosphorylation of desmin in vitro inhibits formation of intermediate filaments; identification of three kinase A sites in the aminoterminal head domain. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):15–20. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02778.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Blobel G. Lamin B constitutes an intermediate filament attachment site at the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):117–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Weber K., Geisler N., Blobel G. Binding of two desmin derivatives to the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope of avian erythrocytes: evidence for a conserved site-specificity in intermediate filament-membrane interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6780–6784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. Nuclear lamina and the structural organization of the nuclear envelope. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):967–978. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inagaki M., Nishi Y., Nishizawa K., Matsuyama M., Sato C. Site-specific phosphorylation induces disassembly of vimentin filaments in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):649–652. doi: 10.1038/328649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Dabauvalle M. C., Franke W. W. Cell type-specific differences in protein composition of nuclear pore complex-lamina structures in oocytes and erythrocytes of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):121–141. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Wolin S. L., McKeon F. D., Franke W. W., Kirschner M. W. Nuclear lamin LI of Xenopus laevis: cDNA cloning, amino acid sequence and binding specificity of a member of the lamin B subfamily. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3801–3808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):463–468. doi: 10.1038/319463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. Nuclear reconstitution in vitro: stages of assembly around protein-free DNA. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):205–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. M., Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins by cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C., Burke B. Teratocarcinoma stem cells and early mouse embryos contain only a single major lamin polypeptide closely resembling lamin B. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):383–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90634-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]