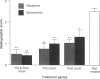
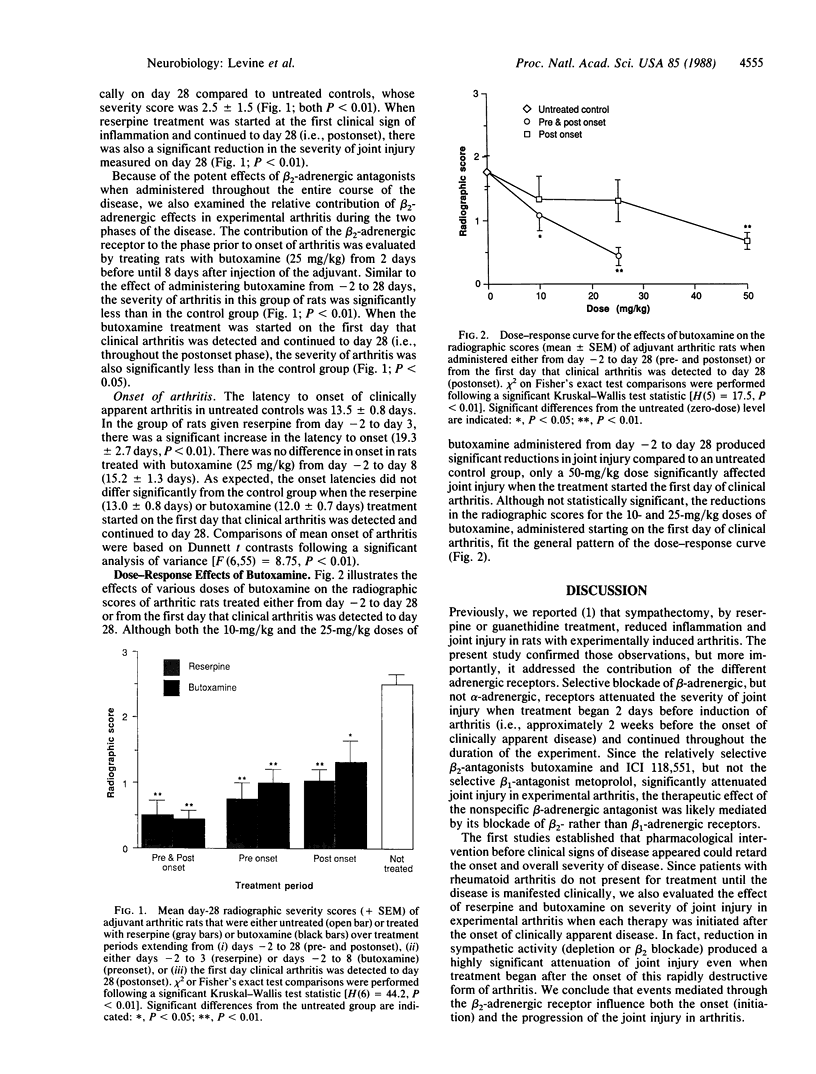
Abstract
We have studied (i) the contribution of specific adrenergic receptors to the proinflammatory effects of the sympathetic nervous system in experimental arthritis and (ii) the phases of the disease during which the sympathetic nervous system influences joint injury. Severity of joint injury was measured radiographically 28 days after induction of adjuvant arthritis in control rats and in rats treated with a variety of sympatholytic agents at various times during the course of the disease. Rats treated with a nonspecific catecholamine depletor (reserpine) or a beta-adrenergic receptor antagonist (propranolol) had a delayed onset and significantly less severe joint injury than saline-treated controls when treatment began prior to injection of the adjuvant and continued to day 28 after the injection. When administered over the same treatment period, neither nonselective (phenoxybenzamine) nor selective [prazosin (alpha 1) and yohimbine (alpha 2)] alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonists affected the onset or severity of joint injury. Metoprolol, a beta 1 antagonist, was also without effect. In contrast, two beta 2 antagonists (butoxamine and ICI 118,551) significantly retarded disease onset and reduced the severity of joint injury. When reserpine or butoxamine treatment was initiated after the onset of clinically apparent arthritis, it was still possible to favorably influence the course of the disease. These data indicate an important contribution of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor to joint injury in experimental arthritis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman N. R., Rooks W. H., 2nd, Shott L., Genant H., Maloney P., West E. Effects of naproxen on connective tissue changes in the adjuvant arthritic rat. Arthritis Rheum. 1979 Dec;22(12):1365–1374. doi: 10.1002/art.1780221208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amir S. Anti-anaphylactic action in the mouse of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is mediated through beta 1-adrenoceptive effectors. Neurosci Lett. 1984 May 4;46(2):127–130. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90429-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. A., Lal H. Discriminative stimulus properties of the vasodilator, hydralazine: differential generalization with alpha 1 and alpha 2 adrenoreceptor drugs. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1982;6(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/s0364-7722(82)80103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borg K. O., Fellenius E., Johansson R., Wallborg M. Pharmacokinetic studies of metoprolol-(3-h) in the rat and the dog. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1975;36(Suppl 5):104–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1975.tb03327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkowski K. R., Quinn P. Adrenaline and the development of spontaneous hypertension in rats. J Auton Pharmacol. 1985 Jun;5(2):89–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1985.tb00109.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Lichtenstein L. M., Melmon K. L., Henney C. S., Weinstein Y., Shearer G. M. Modulation of inflammation and immunity by cyclic AMP. Science. 1974 Apr 5;184(4132):19–28. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4132.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavero I., Roach A. G. The pharmacology of prazosin, a novel antihypertensive agent. Life Sci. 1980 Oct 27;27(17):1525–1540. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90561-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church M. K., Hughes P. J. Adenosine potentiates immunological histamine release from rat mast cells by a novel cyclic AMP-independent cell-surface action. Br J Pharmacol. 1985 May;85(1):3–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1985.tb08823.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper A. J., Kendall H. E., Redfern P. H. The chronic effects of beta-adrenoreceptor antagonists on the efflux of tritiated noradrenaline from sympathetic nerves of the pithed rat. J Auton Pharmacol. 1986 Dec;6(4):259–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1986.tb00652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farsang C., Ramirez-Gonzalez M. D., Mucci L., Kunos G. Possible role of an endogenous opiate in the cardiovascular effects of central alpha adrenoceptor stimulation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Jul;214(1):203–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galant S. P., Allred S. J. Demonstration of beta-2 adrenergic receptors of high coupling efficiency in human neutrophil sonicates. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Jul;96(1):15–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häggendal J., Dahlström A. The recovery of the capacity for uptake-retention of ( 3 H)noradrenaline in rat adrenergic nerves after reserpine. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1972 Jul;24(7):565–574. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1972.tb09058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan R., Robinson C. A., Scavulli J. F., Vaughan J. H. Propranolol and the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Feb;23(2):253–255. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Dardick S. J., Basbaum A. I., Scipio E. Reflex neurogenic inflammation. I. Contribution of the peripheral nervous system to spatially remote inflammatory responses that follow injury. J Neurosci. 1985 May;5(5):1380–1386. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-05-01380.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Dardick S. J., Roizen M. F., Helms C., Basbaum A. I. Contribution of sensory afferents and sympathetic efferents to joint injury in experimental arthritis. J Neurosci. 1986 Dec;6(12):3423–3429. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-12-03423.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J. D., Fye K., Heller P., Basbaum A. I., Whiting-O'Keefe Q. Clinical response to regional intravenous guanethidine in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1986 Dec;13(6):1040–1043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipe S., Summers R. J. Autoradiographic analysis of the distribution of beta-adrenoceptors in the dog splenic vasculature. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Mar;87(3):603–609. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb10203.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljung B., Ablad B., Dahlöf C., Henning M., Hultberg E. Impaired vasoconstrictor nerve function in spontaneously hypertensive rats after long-term treatment with propranolol and metroprolol. Blood Vessels. 1975;12(5):311–315. doi: 10.1159/000158067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K. Pancreatic polypeptide family (APP, BPP, NPY and PYY) in relation to sympathetic vasoconstriction resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewski H. Modulation of noradrenaline release through activation of presynaptic beta-adrenoreceptors. J Auton Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;3(1):47–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-8673.1983.tb00496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkelaars E. J., Bonta I. L. Beta 2-adrenoceptor agonists reverse the leukotriene C4-induced release response of macrophages. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Dec 15;107(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90092-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulus I. H., Wurtman R. J. Selective response of rat peripheral sympathetic nervous system to various stimuli. J Physiol. 1979 Aug;293:513–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Lundgren Y., Folkow B. Effects of prolonged treatment with adrenergic beta-receptor antagonists on blood pressure, cardiovascular design and reactivity in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). Acta Physiol Scand. 1974 Aug;91(4):447–457. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1974.tb05701.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Lefkowitz R. J. Identification of beta-adrenergic receptors in human lymphocytes by (-) (3H) alprenolol binding. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jan;57(1):149–155. doi: 10.1172/JCI108254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]