Abstract
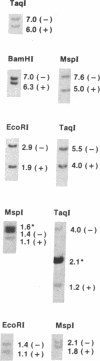
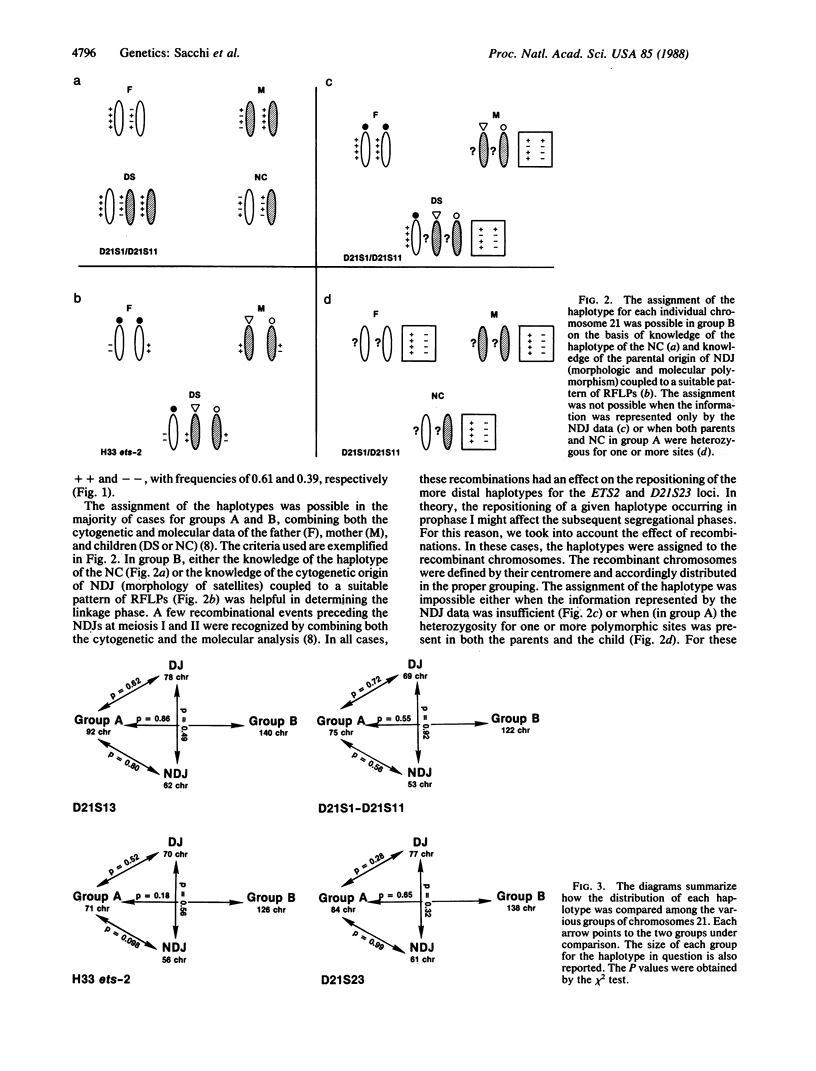
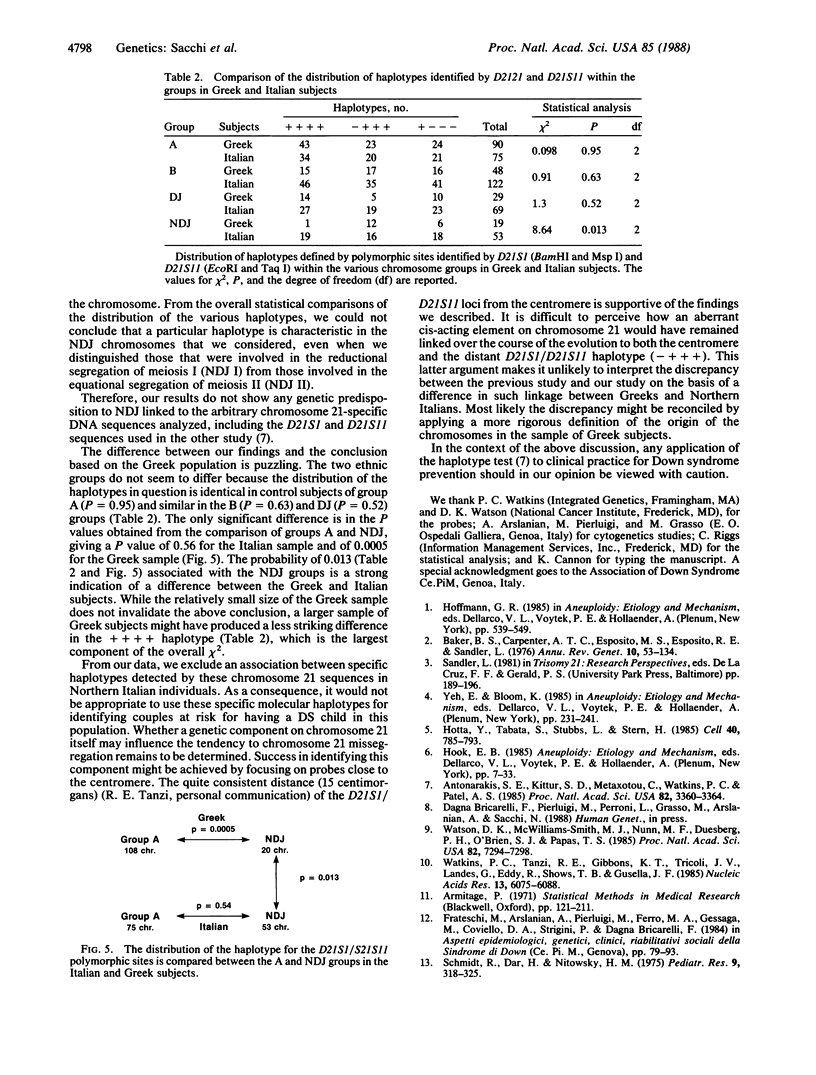
The hypothesis of a predisposition to meiotic nondisjunction for chromosome 21 carrying a specific molecular haplotype has been tested. The haplotype in question is defined by the restriction fragment length polymorphisms for the D21S1/D21S11 loci. Our results obtained on a sample of Northern Italian families with the occurrence of trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) failed to support this hypothesis, contradicting a previous study [Antonarakis, S. E., Kittur, S. D., Metaxotou, C., Watkins, P. C. & Patel, A. S. (1985) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 3360-3364]. These findings rule out an association between any specific D21S1/D21S11 haplotype (as well as other haplotypes for the D21S13, ETS2, and D21S23 loci) and a putative cis-acting genetic element favoring the meiotic missegregation of chromosome 21. For this reason, no preventive screening for couples at risk for trisomy 21 may be based on any of the haplotypes tested.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonarakis S. E., Kittur S. D., Metaxotou C., Watkins P. C., Patel A. S. Analysis of DNA haplotypes suggests a genetic predisposition to trisomy 21 associated with DNA sequences on chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3360–3364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Carpenter A. T., Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E., Sandler L. The genetic control of meiosis. Annu Rev Genet. 1976;10:53–134. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.10.120176.000413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotta Y., Tabata S., Stubbs L., Stern H. Meiosis-specific transcripts of a DNA component replicated during chromosome pairing: homology across the phylogenetic spectrum. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):785–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90338-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. C., Tanzi R. E., Gibbons K. T., Tricoli J. V., Landes G., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Gusella J. F. Isolation of polymorphic DNA segments from human chromosome 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Sep 11;13(17):6075–6088. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.17.6075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. K., McWilliams-Smith M. J., Nunn M. F., Duesberg P. H., O'Brien S. J., Papas T. S. The ets sequence from the transforming gene of avian erythroblastosis virus, E26, has unique domains on human chromosomes 11 and 21: both loci are transcriptionally active. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7294–7298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]