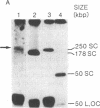
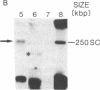
Abstract
Amplification of genes can sometimes be detected by molecular hybridization but not by cytogenetic methods, suggesting that in some cases the units of amplification may be too small to be detected by light microscopy. The experiments reported here investigate whether submicroscopic amplification units are present in early passages of the human tumor cell lines HL-60 and COLO 320. The results show that such cells do contain submicroscopic, extrachromosomal, supercoiled circular molecules harboring MYC genes. The molecules in HL-60 are approximately 250 kilobase pairs (kbp), while those in COLO 320 are 120-160 kbp. The extrachromosomal molecules in HL-60 are shown to replicate semiconservatively and approximately once in one cell cycle. We propose that these submicroscopic elements are precursors of double-minute chromosomes, the usual extrachromosomal manifestation of gene amplification, since both are structurally similar and replicate autonomously.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A., Lindahl T. Epstein-Barr virus genomes with properties of circular DNA molecules in carrier cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1477–1481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Schwab M., Lin C. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Homogeneously staining chromosomal regions contain amplified copies of an abundantly expressed cellular oncogene (c-myc) in malignant neuroendocrine cells from a human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1707–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Schwab M. Oncogene amplification in tumor cells. Adv Cancer Res. 1986;47:235–281. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ardeshir F., Giulotto E., Zieg J., Brison O., Liao W. S., Stark G. R. Structure of amplified DNA in different Syrian hamster cell lines resistant to N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2076–2088. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur G. M., Seeger R. C., Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Amplification of N-myc in untreated human neuroblastomas correlates with advanced disease stage. Science. 1984 Jun 8;224(4653):1121–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.6719137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll S. M., Gaudray P., De Rose M. L., Emery J. F., Meinkoth J. L., Nakkim E., Subler M., Von Hoff D. D., Wahl G. M. Characterization of an episome produced in hamster cells that amplify a transfected CAD gene at high frequency: functional evidence for a mammalian replication origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1740–1750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. K. A new chromosome region possibly derived from double minutes in an in vitro transformed epithelial cell line. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1980;27(1):2–7. doi: 10.1159/000131458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. K. Double minutes and homogeneously staining regions: gene amplification in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:21–59. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.000321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M., Fried M. Large inverted duplications are associated with gene amplification. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamkalo B. A., Farnham P. J., Johnston R., Schimke R. T. Ultrastructural features of minute chromosomes in a methotrexate-resistant mouse 3T3 cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1126–1130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin J. L., Milbrandt J. D., Heintz N. H., Azizkhan J. C. DNA sequence amplification in mammalian cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;90:31–82. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R. Eucaryotic DNA: organization of the genome for replication. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Schimke R. T. Amplification and loss of dihydrofolate reductase genes in a Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;1(12):1069–1076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.12.1069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Zehnbauer B. A., Brodeur G. M., Seeger R. C., Trent J. M., Meltzer P. S., Vogelstein B. Amplification units containing human N-myc and c-myc genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1031–1035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney J. E., Hamlin J. L. Isolation of the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain from methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):569–577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B. J., Lai E., Hamkalo B. A., Hood L., Attardi G. Novel submicroscopic extrachromosomal elements containing amplified genes in human cells. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):434–437. doi: 10.1038/327434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Killary A. M., Fournier R. E., Wahl G. M. Unstable and stable CAD gene amplification: importance of flanking sequences and nuclear environment in gene amplification. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1415–1424. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meselson M., Stahl F. W. THE REPLICATION OF DNA IN ESCHERICHIA COLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Jul 15;44(7):671–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.7.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passananti C., Davies B., Ford M., Fried M. Structure of an inverted duplication formed as a first step in a gene amplification event: implications for a model of gene amplification. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1697–1703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02420.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn L. A., Moore G. E., Morgan R. T., Woods L. K. Cell lines from human colon carcinoma with unusual cell products, double minutes, and homogeneously staining regions. Cancer Res. 1979 Dec;39(12):4914–4924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Stark G. R. Charomids: cosmid vectors for efficient cloning and mapping of large or small restriction fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8664–8668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T., Sherwood S. W., Hill A. B., Johnston R. N. Overreplication and recombination of DNA in higher eukaryotes: potential consequences and biological implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C. W., Krolewski J. J., Rush M. G. Selective trapping of circular double-stranded DNA molecules in solidifying agarose. Plasmid. 1982 May;7(3):263–270. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(82)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Clark G. M., Wong S. G., Levin W. J., Ullrich A., McGuire W. L. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987 Jan 9;235(4785):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.3798106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Gene amplification. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:447–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J., Meltzer P., Rosenblum M., Harsh G., Kinzler K., Mashal R., Feinberg A., Vogelstein B. Evidence for rearrangement, amplification, and expression of c-myc in a human glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):470–473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Robert de Saint Vincent B., DeRose M. L. Effect of chromosomal position on amplification of transfected genes in animal cells. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):516–520. doi: 10.1038/307516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint Vincent B. R., Delbrück S., Eckhart W., Meinkoth J., Vitto L., Wahl G. The cloning and reintroduction into animal cells of a functional CAD gene, a dominant amplifiable genetic marker. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):267–277. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90410-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]