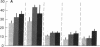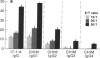Abstract
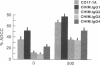
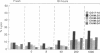
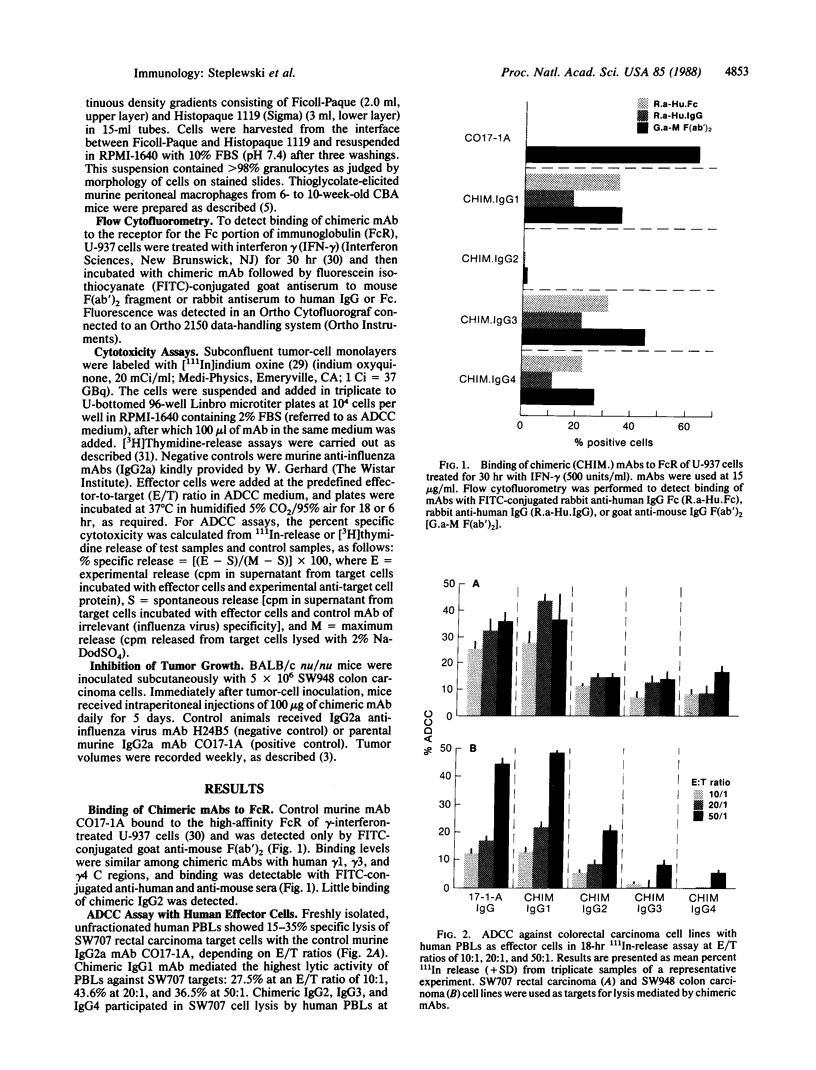
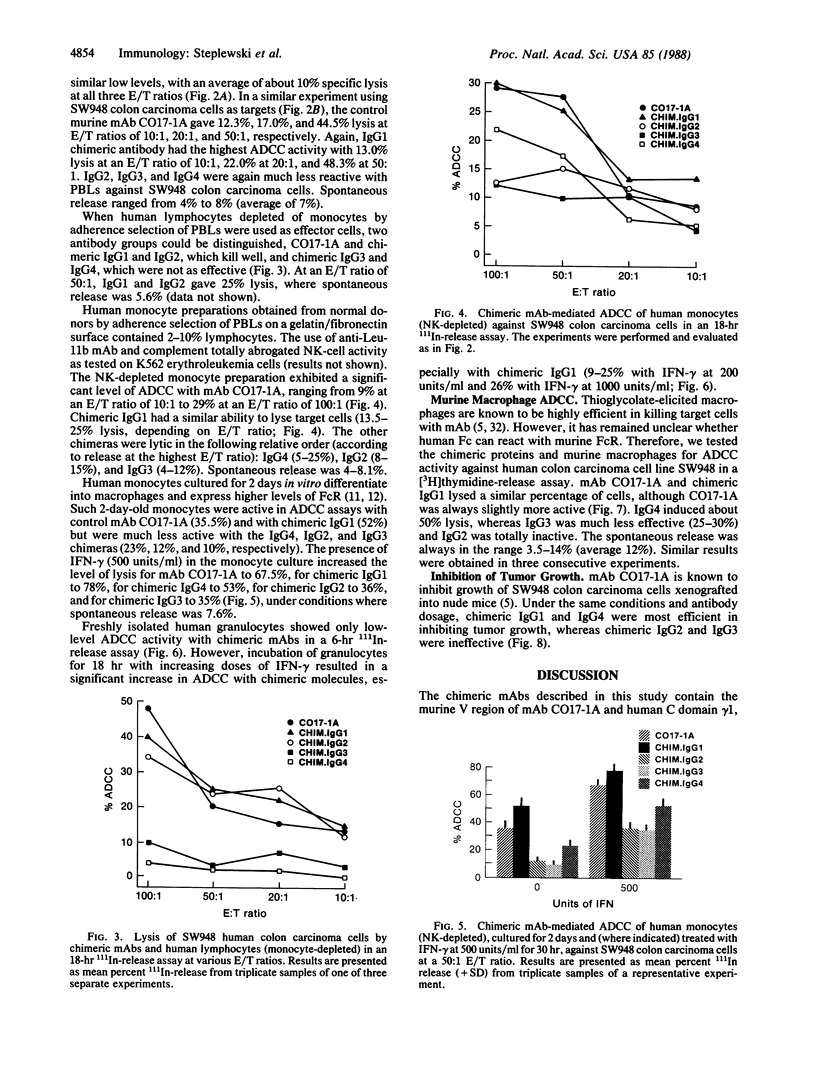
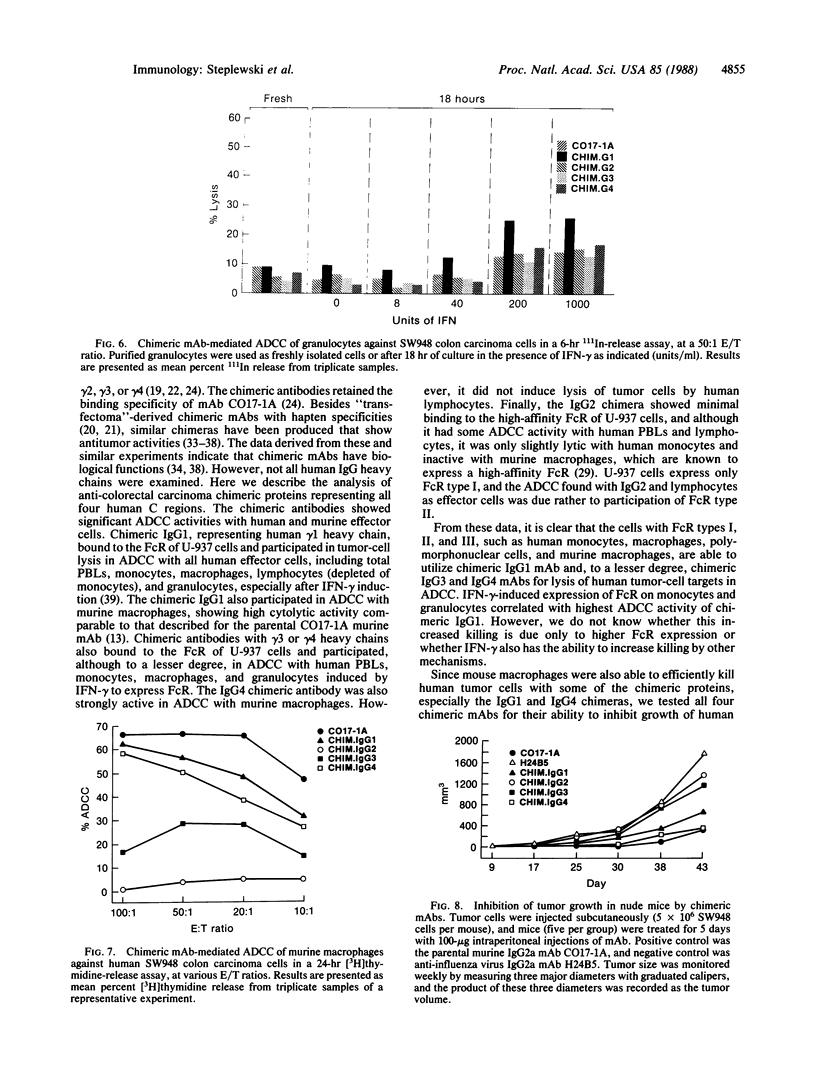
Chimeric antibodies were constructed in which the murine variable region of anti-colorectal cancer monoclonal antibody CO17-1A was joined with human gamma 1, gamma 2, gamma 3, and gamma 4 constant regions. Human-mouse chimeric proteins were compared with the parental murine IgG2a antibody CO17-1A for their ability to participate in tumor-cell destruction by human and murine effector cells in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) assays. All of the chimeric antibodies showed different degrees of ADCC with human lymphocytes, monocytes, and granulocytes and with murine macrophages. Monocytes and macrophages were able to utilize the chimeric IgG1 and, to a lesser degree, IgG4 and IgG3 antibodies to lyse tumor-cell targets in ADCC assays. The chimeric IgG1 and IgG4 antibodies were nearly as effective as the parental CO17-1A antibody in inhibiting tumor growth in nude mice. These data indicate that chimeric IgG1 antibody is superior in its antitumor activity.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Lubeck M. D., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Induction of mouse IgG2a- and IgG3-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in human monocytic cells (U937) by immune interferon. Cancer Res. 1984 Nov;44(11):5127–5131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulianne G. L., Hozumi N., Shulman M. J. Production of functional chimaeric mouse/human antibody. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):643–646. doi: 10.1038/312643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulianne G. L., Isenman D. E., Hozumi N., Shulman M. J. Biological properties of chimeric antibodies. Interaction with complement. Mol Biol Med. 1987 Feb;4(1):37–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. A., Davis G. L., Saltzgaber-Muller J., Simon P., Ho M. K., Shaw P. S., Stone B. A., Sands H., Moore G. P. Tumor-specific genetically engineered murine/human chimeric monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1987 Jul 1;47(13):3577–3583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douillard J. Y., Lehur P. A., Vignoud J., Blottière H., Maurel C., Thedrez P., Kremer M., Le Mevel B. Monoclonal antibodies specific immunotherapy of gastrointestinal tumors. Hybridoma. 1986 Jul;5 (Suppl 1):S139–S149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frödin J. E., Biberfeld P., Christensson B., Philstedt P., Sundelius S., Sylvén M., Wahren B., Koprowski H., Mellstedt H. Treatment of patients with metastasizing colo-rectal carcinoma with mouse monoclonal antibodies (Moab 17-1A): a progress report. Hybridoma. 1986 Jul;5 (Suppl 1):S151–S161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn D. M., Steplewski Z., Herlyn M. F., Koprowski H. Inhibition of growth of colorectal carcinoma in nude mice by monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res. 1980 Mar;40(3):717–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn D., Herlyn M., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Monoclonal anti-human tumor antibodies of six isotypes in cytotoxic reactions with human and murine effector cells. Cell Immunol. 1985 Apr 15;92(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(85)90068-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn D., Herlyn M., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Monoclonal antibodies in cell-mediated cytotoxicity against human melanoma and colorectal carcinoma. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Aug;9(8):657–659. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn D., Koprowski H. IgG2a monoclonal antibodies inhibit human tumor growth through interaction with effector cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4761–4765. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn M., Steplewski Z., Herlyn D., Clark W. H., Jr, Ross A. H., Blaszczyk M., Pak K. Y., Koprowski H. Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies against human malignant melanoma. Cancer Invest. 1983;1(3):215–224. doi: 10.3109/07357908309041361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn M., Steplewski Z., Herlyn D., Koprowski H. Colorectal carcinoma-specific antigen: detection by means of monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1438–1442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. J., Steplewski Z., Matthews T. J., Hamilton T. A., Koprowski H., Adams D. O. Cytolytic interactions between murine macrophages, tumor cells, and monoclonal antibodies: characterization of lytic conditions and requirements for effector activation. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4704–4713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Steplewski Z., Mitchell K., Herlyn M., Herlyn D., Fuhrer P. Colorectal carcinoma antigens detected by hybridoma antibodies. Somatic Cell Genet. 1979 Nov;5(6):957–971. doi: 10.1007/BF01542654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Robinson R. R., Hellström K. E., Murray E. D., Jr, Chang C. P., Hellström I. Chimeric mouse-human IgG1 antibody that can mediate lysis of cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3439–3443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu A. Y., Robinson R. R., Murray E. D., Jr, Ledbetter J. A., Hellström I., Hellström K. E. Production of a mouse-human chimeric monoclonal antibody to CD20 with potent Fc-dependent biologic activity. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3521–3526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobuglio A. F., Saleh M., Peterson L., Wheeler R., Carrano R., Huster W., Khazaeli M. B. Phase I clinical trial of CO17-1A monoclonal antibody. Hybridoma. 1986 Jul;5 (Suppl 1):S117–S123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubeck M. D., Kimoto Y., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Killing of human tumor cell lines by human monocytes and murine monoclonal antibodies. Cell Immunol. 1988 Jan;111(1):107–117. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubeck M. D., Steplewski Z., Baglia F., Klein M. H., Dorrington K. J., Koprowski H. The interaction of murine IgG subclass proteins with human monocyte Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1985 Aug;135(2):1299–1304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. L., Johnson M. J., Herzenberg L. A., Oi V. T. Chimeric human antibody molecules: mouse antigen-binding domains with human constant region domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6851–6855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison S. L. Transfectomas provide novel chimeric antibodies. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1202–1207. doi: 10.1126/science.3929380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura Y., Yokoyama M., Araki K., Ueda R., Kudo A., Watanabe T. Recombinant human-mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody specific for common acute lymphocytic leukemia antigen. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 15;47(4):999–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Kobayashi M., Rossi M. E., Anegon I., Trinchieri G. Immune interferon enhances functional properties of human granulocytes: role of Fc receptors and effect of lymphotoxin, tumor necrosis factor, and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 1;138(3):765–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahagan B. G., Dorai H., Saltzgaber-Muller J., Toneguzzo F., Guindon C. A., Lilly S. P., McDonald K. W., Morrissey D. V., Stone B. A., Davis G. L. A genetically engineered murine/human chimeric antibody retains specificity for human tumor-associated antigen. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):1066–1074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears H. F., Atkinson B., Mattis J., Ernst C., Herlyn D., Steplewski Z., Häyry P., Koprowski H. Phase-I clinical trial of monoclonal antibody in treatment of gastrointestinal tumours. Lancet. 1982 Apr 3;1(8275):762–765. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91811-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears H. F., Herlyn D., Herlyn M., Grotzinger P. J., Steplewski Z., Gerhard W., Koprowski H. Ex vivo perfusion of a tumor-containing colon with monoclonal antibody. J Surg Res. 1981 Aug;31(2):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(81)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears H. F., Herlyn D., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Effects of monoclonal antibody immunotherapy on patients with gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma. J Biol Response Mod. 1984;3(2):138–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sears H. F., Herlyn D., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Initial trial use of murine monoclonal antibodies as immunotherapeutic agents for gastrointestinal adenocarcinoma. Hybridoma. 1986 Jul;5 (Suppl 1):S109–S115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw D. R., Khazaeli M. B., Sun L. K., Ghrayeb J., Daddona P. E., McKinney S., LoBuglio A. F. Characterization of a mouse/human chimeric monoclonal antibody (17-1A) to a colon cancer tumor-associated antigen. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4534–4538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindelar W. F., Maher M. M., Herlyn D., Sears H. F., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Trial of therapy with monoclonal antibody 17-1A in pancreatic carcinoma: preliminary results. Hybridoma. 1986 Jul;5 (Suppl 1):S125–S132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steplewski Z., Herlyn D., Maul G., Koprowski H. Hypothesis: macrophages as effector cells for human tumor destruction mediated by monoclonal antibody. Hybridoma. 1983;2(1):1–5. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1983.2.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steplewski Z., Lubeck M. D., Koprowski H. Human macrophages armed with murine immunoglobulin G2a antibodies to tumors destroy human cancer cells. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):865–867. doi: 10.1126/science.6879183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L. K., Curtis P., Rakowicz-Szulczynska E., Ghrayeb J., Chang N., Morrison S. L., Koprowski H. Chimeric antibody with human constant regions and mouse variable regions directed against carcinoma-associated antigen 17-1A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):214–218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundström C., Nilsson K. Establishment and characterization of a human histiocytic lymphoma cell line (U-937). Int J Cancer. 1976 May 15;17(5):565–577. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurin J., Thurin M., Kimoto Y., Herlyn M., Lubeck M. D., Elder D. E., Smereczynska M., Karlsson K. A., Clark W. M., Jr, Steplewski Z. Monoclonal antibody-defined correlations in melanoma between levels of GD2 and GD3 antigens and antibody-mediated cytotoxicity. Cancer Res. 1987 Mar 1;47(5):1229–1233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]