Abstract
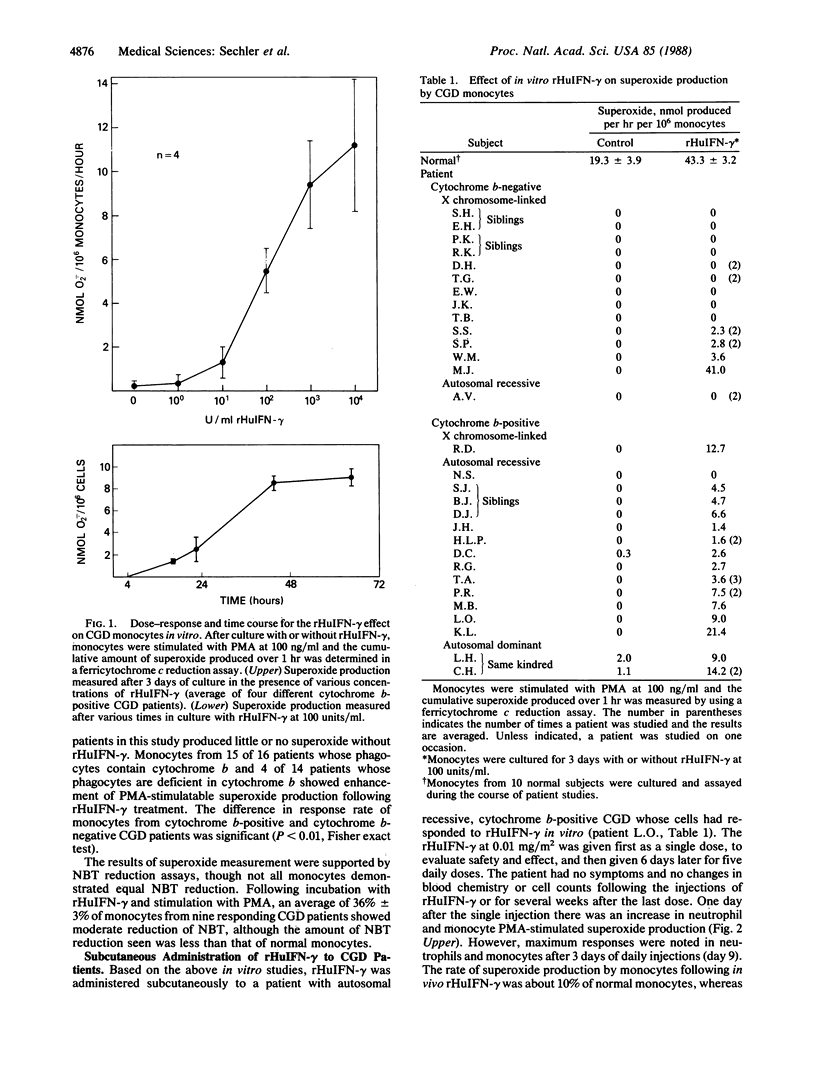
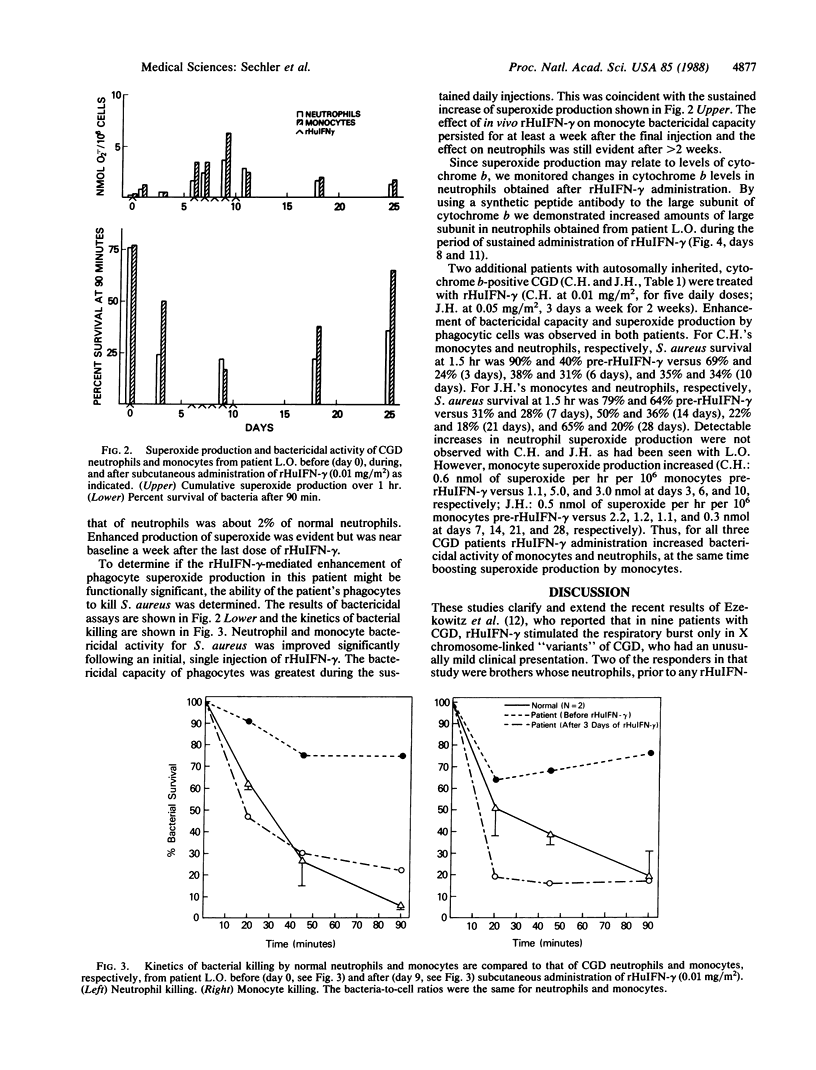
Monocytes from 19 of 30 patients with the classic phenotype of chronic granulomatous disease of childhood (CGD) responded to 3 days of treatment in culture with recombinant human interferon-gamma (rHuIFN-gamma) at 100 units/ml by producing superoxide after stimulation with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Cells from 15 of 16 patients with cytochrome b-positive CGD (15 with autosomal and 1 with X chromosome-linked inheritance) and cells from 4 of 14 patients with cytochrome b-negative CGD (13 with X chromosome-linked and 1 with autosomal recessive inheritance) responded. Subcutaneous rHuIFN-gamma (0.01-0.05 mg/m2) administered as a single dose, daily or every other day, for five or six doses to 3 patients whose phagocytes responded to rHuIFN-gamma in vitro resulted in significant improvement in phagocyte bactericidal activity against Staphylococcus aureus and increases in superoxide production. Studies on 1 patient's cells indicated the increases in superoxide production correlated with increased membrane cytochrome b. The effects of rHuIFN-gamma persisted for more than a week following cessation of therapy. Thus, we have demonstrated a partial correction in vivo of these CGD patients' phagocyte defect with rHuIFN-gamma. Moreover, the data suggest that a significant proportion of patients with CGD will respond to rHuIFN-gamma with augmentation of phagocyte microbicidal function.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur M. J., Kowalski-Saunders P., Gurney S., Tolcher R., Bull F. G., Wright R. Reduction of ferricytochrome C may underestimate superoxide production by monocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 2;98(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berton G., Zeni L., Cassatella M. A., Rossi F. Gamma interferon is able to enhance the oxidative metabolism of human neutrophils. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1276–1282. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Berkow R. L., Roberts R. L., Shurin S. B., Scott P. J. Chronic granulomatous disease due to a defect in the cytosolic factor required for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase activation. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):606–610. doi: 10.1172/JCI113360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T., Whitten D. M., Babior B. M. Defective superoxide production by granulocytes from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. N Engl J Med. 1974 Mar 14;290(11):593–597. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197403142901104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Orkin S. H., Brown R., Jesaitis A. J., Parkos C. A. The glycoprotein encoded by the X-linked chronic granulomatous disease locus is a component of the neutrophil cytochrome b complex. 1987 Jun 25-Jul 1Nature. 327(6124):717–720. doi: 10.1038/327717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezekowitz R. A., Orkin S. H., Newburger P. E. Recombinant interferon gamma augments phagocyte superoxide production and X-chronic granulomatous disease gene expression in X-linked variant chronic granulomatous disease. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1009–1016. doi: 10.1172/JCI113153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Buescher E. S., Seligmann B. E., Nath J., Gaither T., Katz P. NIH conference. Recent advances in chronic granulomatous disease. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Nov;99(5):657–674. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-5-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Fletcher M. P., Seligmann B. E., Hoffstein S., Cehrs K., Mounessa N. Human neutrophil-specific granule deficiency: a model to assess the role of neutrophil-specific granules in the evolution of the inflammatory response. Blood. 1982 Jun;59(6):1317–1329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malech H. L., Gardner J. P., Heiman D. F., Rosenzweig S. A. Asparagine-linked oligosaccharides on formyl peptide chemotactic receptors of human phagocytic cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2509–2514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P. M., Eide B., Goldsmith P., Brann M., Gierschik P., Spiegel A., Malech H. L. Detection of multiple forms of Gi alpha in HL60 cells. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 31;221(1):81–86. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80356-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Murray H. W., Wiebe M. E., Rubin B. Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):670–689. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newburger P. E., Luscinskas F. W., Ryan T., Beard C. J., Wright J., Platt O. S., Simons E. R., Tauber A. I. Variant chronic granulomatous disease: modulation of the neutrophil defect by severe infection. Blood. 1986 Oct;68(4):914–919. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno Y., Buescher E. S., Roberts R., Metcalf J. A., Gallin J. I. Reevaluation of cytochrome b and flavin adenine dinucleotide in neutrophils from patients with chronic granulomatous disease and description of a family with probable autosomal recessive inheritance of cytochrome b deficiency. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):1132–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick E., Mizel D. Rapid microassays for the measurement of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide production by macrophages in culture using an automatic enzyme immunoassay reader. J Immunol Methods. 1981;46(2):211–226. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quie P. G., White J. G., Holmes B., Good R. A. In vitro bactericidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: diminished activity in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. J Clin Invest. 1967 Apr;46(4):668–679. doi: 10.1172/JCI105568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Goff S. C., Newburger P. E., Baehner R. L., Cole F. S., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder--chronic granulomatous disease--on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):32–38. doi: 10.1038/322032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Cross A. R., Garcia R. C., Borregaard N., Valerius N. H., Soothill J. F., Jones O. T. Absence of cytochrome b-245 in chronic granulomatous disease. A multicenter European evaluation of its incidence and relevance. N Engl J Med. 1983 Feb 3;308(5):245–251. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198302033080503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segal A. W., Heyworth P. G., Cockcroft S., Barrowman M. M. Stimulated neutrophils from patients with autosomal recessive chronic granulomatous disease fail to phosphorylate a Mr-44,000 protein. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):547–549. doi: 10.1038/316547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber A. I., Borregaard N., Simons E., Wright J. Chronic granulomatous disease: a syndrome of phagocyte oxidase deficiencies. Medicine (Baltimore) 1983 Sep;62(5):286–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weening R. S., Corbeel L., de Boer M., Lutter R., van Zwieten R., Hamers M. N., Roos D. Cytochrome b deficiency in an autosomal form of chronic granulomatous disease. A third form of chronic granulomatous disease recognized by monocyte hybridization. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):915–920. doi: 10.1172/JCI111792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]