Abstract
Phosphoinositide (PI) 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling processes play an important role in regulating the adhesive function of integrin αIIbβ3, necessary for platelet spreading and sustained platelet aggregation. PI3K inhibitors are effective at reducing platelet aggregation and thrombus formation in vivo and as a consequence are currently being evaluated as novel antithrombotic agents. PI3K regulation of integrin αIIbβ3 activation (affinity modulation) primarily occurs downstream of Gi-coupled and tyrosine kinase-linked receptors linked to the activation of Rap1b, AKT, and phospholipase C. In the present study, we demonstrate an important role for PI3Ks in regulating the avidity (strength of adhesion) of high affinity integrin αIIbβ3 bonds, necessary for the cellular transmission of contractile forces. Using knock-out mouse models and isoform-selective PI3K inhibitors, we demonstrate that the Type Ia p110β isoform plays a major role in regulating thrombin-stimulated fibrin clot retraction in vitro. Reduced clot retraction induced by PI3K inhibitors was not associated with defects in integrin αIIbβ3 activation, actin polymerization, or actomyosin contractility but was associated with a defect in integrin αIIbβ3 association with the contractile cytoskeleton. Analysis of integrin αIIbβ3 adhesion contacts using total internal reflection fluorescence microscopy revealed an important role for PI3Ks in regulating the stability of high affinity integrin αIIbβ3 bonds. These studies demonstrate an important role for PI3K p110β in regulating the avidity of high affinity integrin αIIbβ3 receptors, necessary for the cellular transmission of contractile forces. These findings may provide new insight into the potential antithrombotic properties of PI3K p110β inhibitors.
Keywords: Cell/Adhesion, Cytoskeleton, Lipid/Phospholipid/Metabolism, Signal Transduction, Clot Retraction, Integrin avidity, PI 3-kinase, Platelet Adhesion
Introduction
Platelet adhesion and aggregation at sites of vascular injury are essential for the formation of the primary hemostatic plug and for the development of arterial thrombi (1, 2). Platelet thrombus growth is critically dependent on the adhesive function of the platelet integrin, αIIbβ3. This receptor engages multiple adhesive ligands, including von Willebrand factor, fibrinogen, and fibronectin, and is indispensable for the formation of stable platelet-platelet adhesion contacts during thrombus development. Qualitative or quantitative defects in integrin αIIbβ3 are associated with a profound defect in platelet aggregation, leading to a severe bleeding disorder. Inhibitors of integrin αIIbβ3 have been developed therapeutically, and these agents are effective at preventing arterial thrombus development in patients with the acute coronary syndromes (3).
The ligand binding function of integrin αIIbβ3 is subject to tight regulation by intracellular signaling processes that modulate the conformation of the receptor complex (affinity regulation) (4, 5). Once engaged by adhesive ligand, integrins transduce signals into the cell (outside-in signaling) necessary for cytoskeletal remodeling and clustering of integrin receptors. These latter changes are important for enhancing multivalent adhesive interactions, leading to increased strength of adhesion (avidity) (6).
Inside-out regulation appears to be a common feature of all integrins, and several well characterized signaling pathways have been linked to integrin affinity modulation. In the platelet, activating signals downstream of Gq-coupled receptors play a major role in initiating integrin αIIbβ3 activation, with phospholipase C-dependent generation of inositol polyphosphate 1,4,5-triphosphate and diacylglycerol stimulating a signaling cascade that involves CalDAGGEF-1 (7), RapIb (8), RIAM (9), Talin (10), and Kindlin3 (11). The binding of Talin and Kindlin3 to the β3 cytoplasmic tail is associated with structural reorganization of the integrin α and β cytoplasmic tails and conformational changes in the extracellular domains of the receptors, promoting high affinity interactions with multiple adhesive ligands. Maintaining integrin αIIbβ3 receptors in their high affinity state is critical for sustained platelet aggregation and thrombus development and requires the ADP purinergic receptor, P2Y12, the major Gi-coupled signaling receptor linked to the activation of PI3K3 and RapIb (12–16). PI3Ks also contribute to integrin αIIbβ3 activation by stimulating phospholipase C-dependent calcium flux, particularly downstream of tyrosine kinase-linked receptors (17–19).
The PI3Ks are classified into several distinct groups (Types I–III), based on their primary structure, mode of regulation, and substrate specificity (20, 21). PI3Ks principally transduce signals through the catalytic generation of phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) 3,4,5-trisphosphate and PtdIns 3,4-bisphosphate, two second messengers that facilitate the recruitment of pleckstrin homology domain-containing signaling proteins to the plasma membrane (22). The Type I enzymes are divided into two subtypes, Ia and Ib; Type Ia isoforms include p110α, -β, and -δ, and Type Ib includes a single isoform, p110γ.
In addition to their role in regulating integrin αIIbβ3 affinity (inside-out signaling), PI3Ks also signal downstream of integrin αIIbβ3 receptors, promoting cytoskeletal remodeling and platelet spreading (23, 24). Other platelet functional responses regulated by integrin αIIbβ3 outside-in signals include fibrin clot retraction and the platelet procoagulant response; however, the role of PI3K in these processes has not been defined.
Fibrin clot formation and subsequent retraction is typically induced by thrombin in vivo and is considered an important process to stabilize platelet thrombus formation at sites of vascular injury (25). Integrin αIIbβ3-mediated clot retraction is critically dependent on the ability of the receptors to transmit cytoskeletal contractile forces to extracellular fibrin polymers (26), a process that requires integrin αIIbβ3 outside-in signaling events that physically anchor the receptor to the actin cytoskeleton (26–28). Although PI3K signaling processes have a clearly defined role in modulating the activation (ligand binding affinity) of integrin αIIbβ3, it is currently unclear whether PI3Ks participate in subsequent integrin αIIbβ3 outside-in signaling events linked to changes in receptor avidity.
In this study, we have investigated the potential role of PI3K signaling processes in regulating the avidity of integrin αIIbβ3 receptors after they have been converted to a high affinity state by high dose thrombin. Our studies demonstrate that fully activated integrin αIIbβ3 receptors are capable of supporting irreversible platelet aggregation independent of PI3K signaling; however, these receptors have a deficit in their ability to mediate stable platelet interactions with a fibrin matrix, leading to reduced fibrin clot retraction. Our studies suggest a potentially important role for PI3K signaling processes in regulating the cytoskeletal association of integrin αIIbβ3 necessary for stable cell adhesion and the cellular transmission of contractile force. These findings may provide new mechanistic insight into the antithrombotic properties of PI3K inhibitors.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Materials
Human fibrinogen was purified from fresh frozen plasma (57). Thrombin was purchased from JPI Jones Daniels Pharmaceuticals. All other materials were from sources we have described previously (29, 30).
Animals
All procedures involving the use of C57BL/6, p110δ−/−, and p110γ−/− mice were approved by the Alfred Medical Research and Education Precinct animal ethics committee (Melbourne, Australia), under project number E/0569/2007/M. PI3K p110δ-deficient mice (p110δ−/−) and PI3K p110γ-deficient mice (p110γ−/−) were from sources described previously (29).
Collection of Blood and Preparation of Platelet-rich Plasma and Washed Platelets
All procedures involving the collection of human and mouse blood were approved by the Monash University Standing Committee on Ethics in Research involving Humans (Project CF07/0125–2007/0005) and the Alfred Medical Research and Education Precinct animal ethics committee (Standard Operating Procedure 19, collection of whole blood from mice), respectively. Isolation of human platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and preparation of washed platelets were performed as described previously (31).
Platelet Aggregation
Washed platelets (3.0 × 108/ml) were incubated with vehicle (DMSO, 0.001%), LY294002 (25 μm), TGX221 (0.5 μm), and/or receptor antagonists/inhibitors of ADP and TxA2 signaling (100 μm MRS2179, 10 μm AR-C69931MX, 0.2 units/ml apyrase, 10 μm indomethacin) prior to stimulation with the indicated agonist concentrations. All aggregations were initiated by stirring the suspensions at 950 rpm for 10 min at 37 °C in a four-channel automated platelet analyzer (AggRAM, Helena Laboratories). Platelet aggregation was defined as percentage change in light transmission.
Clot Retraction
Clot retraction in both citrated PRP and washed platelets isolated from human or mouse (p110γ+/+, p110γ−/−) whole blood (supplemented with 0.5 mg/ml purified fibrinogen) was performed as previously described (32). In some experiments, PRP/washed platelets were preincubated with pan-PI3K inhibitors (25 μm LY294002, 100 nm wortmannin, PRP) or PI3K isoform-specific inhibitors (0.5 μm TGX221, 0.5 μm D-010, 3.0 μm AS252424) and/or ADP/TxA2 antagonists for 10 min at 37 °C. For studies using PRP, inhibitors were used at 4 times the indicated concentrations. Clot formation was initiated by the addition of thrombin (1–10 units/ml), and retraction was observed over the indicated time course at room temperature. The extent of clot retraction was expressed as the volume of serum extruded from the clot as a percentage of the total reaction volume, minus data obtained from c7E3 Fab/ aggrastat-pretreated platelets. In experiments using washed platelets and purified fibrinogen, clots were typically less stable (particularly when treated with PI3K inhibitors), making quantification of extruded serum unreliable. In these studies, the percentage of clot retraction was assessed as the percentage change in two-dimensional surface area of the clot and expressed as follows: 0 = 0%, 1 = <10%, 2 = 10–25%, 3 = 25–50%, 4 = 50–75%, 5 = 75–90%, and 6 = >90% reduction in clot surface area.
Microscopic Analysis of Clot Retraction
Washed platelets treated with either vehicle (DMSO, 0.001%) or wortmannin (100 nm) were supplemented with 0.25 mg/ml fibrinogen containing 10% Oregon Green-labeled fibrinogen. Platelets were placed on glass slides blocked with 2% bovine serum albumin and stimulated with 1 unit/ml thrombin. The process of clot retraction was visualized in real time using both differential interference contrast (DIC) microscopy and epifluorescence microscopy using an inverted Olympus microscope with a ×100 (1.4 numerical aperture) oil immersion objective.
Measurement of Integrin αIIbβ3 Activation
Integrin αIIbβ3 activation was assessed by flow cytometry (FACSCalibur, BD Biosciences), using a fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated PAC-1 monoclonal antibody, as described previously (29).
HPLC-based Phospholipid Analysis
Washed platelets were labeled with inorganic [32P]H3PO4 (1.0 mCi/ml), as described previously (33), and stimulated with thrombin (1 unit/ml) for the indicated time period. Lipids were extracted and separated by HPLC according to a modified method of Stephens et al. (34). PI peaks co-eluting with commercially available PtdIns 3,4-bisphosphate standards were integrated and normalized to the total lipid applied.
Quantification of Cytoskeleton-associated Integrin αIIbβ3
Fractionation of the 15,000 × g Triton X-100-insoluble cytoskeletal fraction from platelets in retracting clots was performed according to the methods of Fox (35) and Osdoit and Rosa (36). The cytoskeletal content of integrin αIIbβ3 was determined by Western blot analysis using an anti-αIIb (SZ22) monoclonal antibody (Immunotech), quantified using densitometry, and corrected for total protein loading relative to actin.
Analysis of Platelet Adhesion and Spreading on Fibrinogen Matrices
Acid-washed microcapillary slides were incubated with hexamethyldisilazane for 15 min, prior to incubating with human fibrinogen (0.2–100 μg/ml) for 2 h at room temperature. Prior to use, slides were blocked with bovine serum albumin (2%). Washed human platelets (5.0 × 107/ml) treated with vehicle (DMSO, 0.001%), LY294002 (25 μm), TGX221 (0.5 μm), and/or ADP/TxA2 antagonists were allowed to interact with fibrinogen (0.2–100 μg/ml)-coated microslides in the presence or absence of 1 unit/ml thrombin, and adhesion and spreading were imaged in real time using DIC microscopy (×63 magnification; Leica TCS SP; Leica, Heidelberg, Germany) and recorded for off-line analysis, using PowerDVD. Note that platelets exhibiting only filopodal extensions were classified as not spread.
Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence (TIRF) Microscopy
The Olympus total internal reflection system was used with minor modifications (37). For a more detailed description of TIRF microscopy, see Truskey (38). Light from a helium/neon laser (543 nm) was introduced into the back focal plane of an Olympus IX81 inverted microscope (equipped with shuttered DIC optics) via a single-mode optical fiber using a 70/30 beam splitter to allow for epifluorescence illumination using a Sutter DG4 light source coupled via a liquid light guide. This configuration allows for rapid consecutive switching between DIC, epifluorescent illumination, and TIRF laser illumination. The TIRF laser was focused at the back focal plane of a high numerical aperture objective lens (Apo100XOHR; numerical aperture 1.65; Olympus), and acquisition was performed using multidimensional data acquisition in Metamorph version 6.0 (39).
Measurement of the Stability of Integrin αIIbβ3 Adhesion Contacts
Washed platelets (5 × 107/ml) pretreated with vehicle (DMSO, 0.001%), LY294002 (25 μm), or TGX221 (0.5 μm) were perfused into hexamethyldisilazane-pretreated glass capillaries coated with various concentrations of fibrinogen (0.2–100 μg/ml) and allowed to adhere under static conditions for ∼5 min, prior to the application of flow (1800 s−1). Stable platelet adhesion was visualized using DIC microscopy and recorded in real time for off-line analysis. The number of platelets per field pre- and postshear application was quantified and expressed as percentage of stable platelet adhesion relative to presheared levels of adhesion.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical significance between multiple treatment groups was analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance with Dunnett's multiple comparison test. Statistical significance between multiple treatment groups over time was performed using two-way analysis of variance, with Bonferroni post-tests. Statistical significance between two treatment groups was analyzed using an unpaired Student's t test with two-tailed p values (Prism software, GraphPad Software for Science, San Diego, CA) (ns, not significant; p > 0.05; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001). Data are presented as means ± either S.E. or S.D. (where indicated), where n is the number of independent experiments performed.
RESULTS
Inhibition of PI3K Selectively Inhibits Clot Retraction in Thrombin-stimulated Platelets
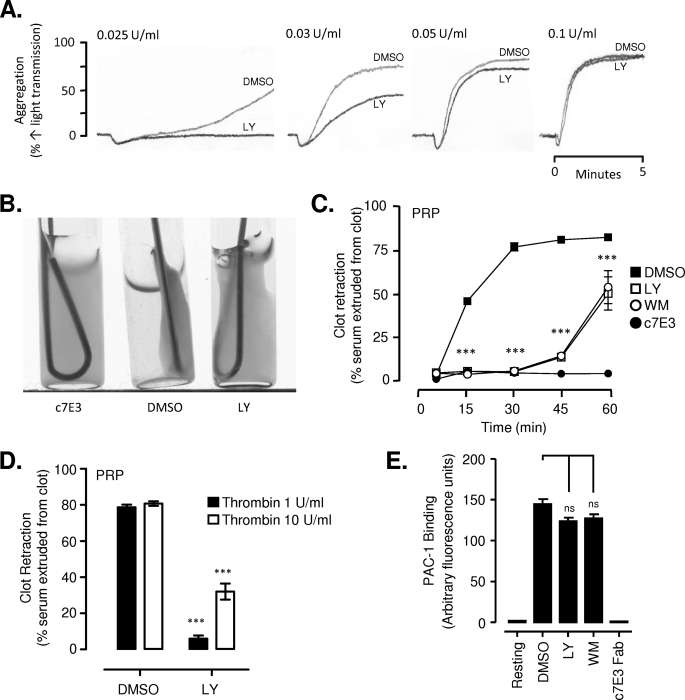
PI3Ks have a well defined role in promoting sustained integrin αIIbβ3 activation downstream of Gi-coupled receptors, necessary for stable platelet aggregation and spreading (12–14, 16, 29, 40). The effects of PI3K inhibitors on these functional platelet responses are most evident at lower agonist concentrations, with platelet stimulation by potent agonists, such as thrombin, overcoming the platelet-inhibitory effects of PI3K antagonists (29, 41). Consistent with this, preincubating platelets with the pan-PI3K inhibitors, LY294002 (25 μm; Fig. 1A) or wortmannin (100 nm; data not shown), reduced platelet aggregation induced by low dose thrombin (0.025–0.05 unit/ml); however, above 0.1 units/ml, neither LY294002 nor wortmannin had a significant inhibitory effect on the rate, extent, or stability of thrombin-stimulated platelet aggregation. Similarly, inhibition of PI3K reduced lamellipodium formation and platelet spreading on a high density fibrinogen matrix in the absence of thrombin, a defect that was completely reversed by pretreating platelets with high dose thrombin (supplemental Fig. 1). In contrast, inhibition of PI3K had a marked inhibitory effect on fibrin clot retraction stimulated by high dose thrombin (1 unit/ml) (Fig. 1, B and C). In control platelets, ∼75% retraction was observed 30 min after the addition of thrombin (1 unit/ml) compared with <10% clot retraction in platelets pretreated with LY294002 (25 μm; Fig. 1C); however, after 90 min, full clot retraction occurred (supplemental Fig. 2A). This inhibitory effect of PI3K inhibitors was observed with washed platelets and PRP and occurred at thrombin concentrations as high as 10 units/ml (Fig. 1D and supplemental Fig. 2A). In control studies, we confirmed that this defect in clot retraction was unlikely to be due to changes in integrin αIIbβ3 affinity because the rate and extent of integrin αIIbβ3 activation induced by 1 unit/ml thrombin (using the activation-specific anti-integrin αIIbβ3 monoclonal antibody PAC-1), was no different in the presence or absence of PI3K inhibitors (Fig. 1E). These studies demonstrate that PI3K plays an important role in regulating the contractile function of thrombin-stimulated platelets independent of changes in integrin αIIbβ3 ligand binding affinity.
FIGURE 1.
Selective role for PI3K in clot retraction. Washed platelets or those in plasma (PRP) were pretreated with vehicle (DMSO), LY294002 (LY) (washed, 25 μm; PRP, 100 μm), wortmannin (WM) (washed, 100 nm; PRP, 400 nm), or the integrin αIIbβ3 antagonist (c7E3 Fab, 50 μg/ml). A, washed platelets (3 × 108/ml) were stimulated with increasing concentrations of thrombin (0.025–0.1 unit/ml) under stirring conditions, and the extent of platelet aggregation was examined as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Shown are representative tracings of at least three independent experiments. B–D, PRP was stimulated with increasing concentrations of thrombin (1–10 units/ml), and the extent of clot retraction was examined over time, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” B, clot retraction in PRP stimulated by 1 unit/ml thrombin, after 30 min, representative of at least three independent experiments. C, quantification of clot retraction over time, induced by stimulation of PRP with 1 unit/ml thrombin. Results represent the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments, each performed in duplicate. D, quantification of the percentage (%) clot retraction in washed platelets and PRP stimulated with the indicated concentrations of thrombin after 30 min. Results represent the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments, performed in triplicate. E, washed platelets (5 × 107/ml) were stimulated with 1 unit/ml thrombin, and the level of integrin αIIbβ3 activation was measured by flow cytometry using an activation-specific anti-integrin αIIbβ3 antibody (PAC-1). Results represent the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. C–E, not significant (ns), p > 0.05; ***, p < 0.001).
PI3K Inhibition Impairs Clot Retraction Independent of Platelet-released ADP and TxA2
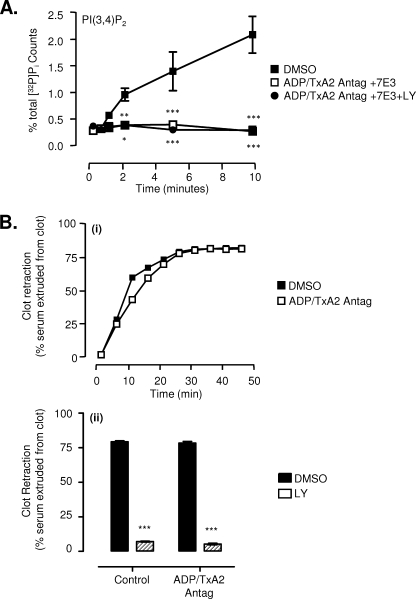
PI3K activation in thrombin-stimulated platelets requires platelet co-stimulation by ADP (42) as well as integrin αIIbβ3 outside-in signaling (43). Consistent with this, pretreating platelets with combined ADP, TxA2, and integrin αIIbβ3 antagonists completely eliminated thrombin-stimulated PI3K activation, as evidenced by a failure to generate the PI3K lipid second messenger, PtdIns 3,4-bisphosphate (Fig. 2A). These results support previous findings that thrombin stimulation of platelets through Gq- and G13-coupled protease-activated receptors is insufficient to induce significant PI3K activation (42, 44). To investigate whether the reduction in thrombin-stimulated clot retraction by PI3K inhibitors was dependent on released ADP or TxA2, washed platelets or PRP were pretreated with ADP/TxA2 antagonists prior to platelet stimulation with thrombin. Analysis of the rate and extent of fibrin clot retraction revealed minimal contribution for ADP and TxA2 in enhancing clot retraction (Fig. 2B, i). Moreover, PI3K inhibitors produced a similar defect in clot retraction in platelets pretreated with ADP/TxA2 antagonists compared with untreated controls (Fig. 2B, ii), confirming that the effects of PI3K inhibition were not dependent on platelet co-stimulation by these agonists. Collectively, these studies suggest that the PI3K signaling processes regulating fibrin clot retraction are unlikely to be occurring directly downstream of the thrombin protease-activated receptors or ADP/TxA2 (inside-out signaling) but more likely occur downstream of integrin αIIbβ3.
FIGURE 2.
PI3K regulates clot retraction in an ADP/TxA2-independent manner. A, washed human platelets were pretreated with vehicle (DMSO) or with ADP/TxA2 antagonists (as described under “Experimental Procedures”) in combination with the integrin αIIbβ3 antagonist c7E3 Fab (50 μg/ml) (ADP/TxA2 Antag + 7E3), alone or in combination with LY294002 (25 μm) (ADP/TxA2 Antag + 7E3 + LY). The level of PtdIns 3,4-bisphosphate production over a 10-min period was measured following stimulation of platelets with 1 unit/ml thrombin, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” These results represent the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments. B, PRP pretreated with vehicle (DMSO), ADP/TxA2 antagonists (see “Experimental Procedures”), and/or LY294002 (25 μm) were stimulated with 1 unit/ml thrombin. The extent of clot retraction was quantified over time (i) or after 30 min (ii), as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Results are taken from one representative of three independent experiments (each performed in duplicate) (i) or represent the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments (ii) (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001).
Type Ia PI3K p110β Isoform Regulates Thrombin-induced Clot Retraction
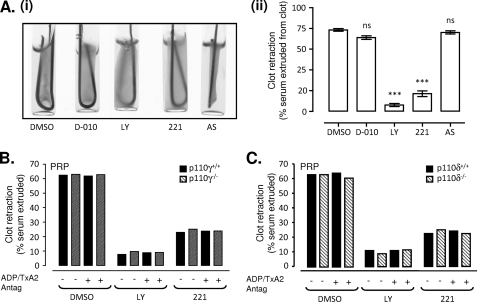
To examine the specific PI3K isoforms regulating thrombin-induced clot retraction, isoform-selective PI3K inhibitors and specific knock-out mouse models were employed. Selective inhibition of p110β with the pharmacological antagonist TGX221 (29) significantly reduced thrombin-induced clot retraction to a similar, albeit slightly reduced, extent as LY294002 (Fig. 3A and supplemental Fig. 2A) or wortmannin (data not shown). In contrast, pharmacological inhibition of p110δ (D-010) or p110γ (AS252424) was without effect (Fig. 3A). Consistent with this, the rate and extent of thrombin-stimulated clot retraction was no different in p110γ+/+ and p110γ−/− mice, and in both genotypes, clot retraction was inhibited to a similar extent by either LY294002 or TGX221 (Fig. 3, B and C, and supplemental Fig. 2, B and C). These results suggest a major role for the Type IA PI3K p110β in regulating thrombin-stimulated clot retraction.
FIGURE 3.
PI3K p110β is the major isoform involved in thrombin-induced integrin αIIbβ3-mediated clot retraction. A–C, washed human platelets (3 × 108/ml) (A) or those derived from either p110γ+/+, p110γ−/−, p110δ+/+, or p110δ−/− mice (2.5 × 108/ml) (B and C) were preincubated with vehicle alone (DMSO) or various PI3K isoform inhibitors (pan-PI3K, LY294002 (LY; 25 μm); p110β, TGX221 (221; 0.5 μm); p110δ, D-010 (0.5 μm); or p110γ, AS252424 (AS; 1 μm)). Pretreated platelets were supplemented with 0.5 mg/ml fibrinogen prior to stimulation with 1 unit/ml thrombin, and the extent of clot retraction was quantified as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Images depicted in A (i) represent one representative of three independent experiments, quantified in A (ii) (mean ± S.E., n = 3; not significant (ns), p > 0.05; ***, p < 0.001). In B and C, clot retraction was examined in the presence or absence of ADP/TxA2 antagonists, and results are representative of three independent experiments.
Inhibition of PI3K Retards Integrin αIIbβ3 Translocation to the Platelet Cytoskeleton in Retracting Clots
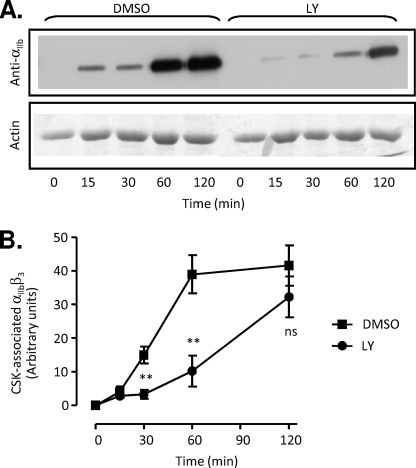
To gain insight into the mechanisms by which PI3K regulates clot retraction, we examined several processes that are required for this functional platelet response, including myosin light chain phosphorylation (necessary for actomyosin contractility), F-actin polymerization, and the cytoskeletal association of integrin αIIbβ3 receptors. The degree of platelet contractility has previously been demonstrated to correlate closely with the rate and extent of myosin light chain phosphorylation (45). Analysis of myosin light chain phosphorylation in thrombin-stimulated platelets revealed no significant effect of PI3K inhibitors on the kinetics of myosin light chain phosphorylation (supplemental Fig. 3A). Similarly F-actin polymerization, which is critical for the transmission of contractile tension to the fibrin clot, was also unaffected by PI3K inhibition (supplemental Fig. 3B). Analysis of integrin αIIbβ3 association with the Triton X-100-insoluble cytoskeleton of platelets revealed a time-dependent increase in integrin αIIbβ3-cytoskeletal association, commencing within 15 min of thrombin stimulation and maximal by 120 min (Fig. 4, A and B). Significantly, this translocation was delayed in LY292004 (Fig. 4, A and B) and wortmannin-treated platelets (data not shown), with the delay in cytoskeletal association correlating with the time-dependent defect in clot retraction (compare with Fig. 1C). Overall, these findings indicate that PI3K promotes the cytoskeletal association of integrin αIIbβ3 receptors, necessary for the cellular transmission of contractile forces.
FIGURE 4.
PI3K inhibition delays the translocation of integrin αIIbβ3 to the platelet cytoskeleton. A and B, washed platelets were pretreated with either vehicle (DMSO) or LY294002 (LY; 25 μm), prior to stimulating with 1 unit/ml thrombin in the presence of purified fibrinogen (0.5 mg/ml). Platelets were lysed at the indicated times, and the cytoskeletal fraction was isolated and analyzed for integrin αIIbβ3 translocation, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The anti-αIIb immunoblot (top) and corresponding actin loading control (bottom) in A are representative of three independent experiments, quantified in B by performing densitometry on anti-αIIb (SZ22) immunoblots, followed by correction for total protein loading based on actin levels. These results represent the mean ± S.E., n = 3 (**, p < 0.005; not significant (ns), p > 0.05).
Real-time Analysis of Platelet Adhesion and Retraction of Fibrin Clots
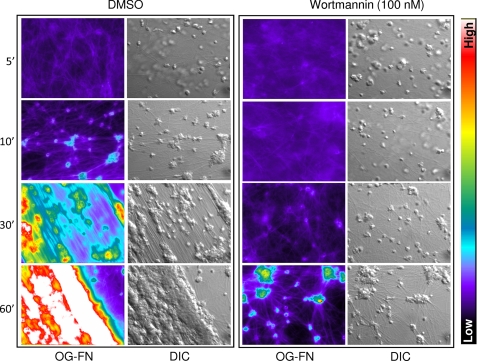
To gain further insight into the effect of PI3K inhibitors on the clot retraction process, microscopic examination of the dynamic interactions between activated platelets and fibrin was performed. For these studies, washed platelets, in the presence of fluorescently labeled fibrinogen, were stimulated with 1.0 unit/ml thrombin, and the formation and subsequent retraction of fibrin polymers were visualized in real time by DIC and epifluorescence (Oregon Green-labeled fibrinogen) microscopy. In control samples, the addition of thrombin triggered the formation of microscopically visible fibrin strands (Fig. 5, DMSO) that rapidly associated with activated platelets. By 10 min post-stimulation, platelet aggregates (satellites) formed between numerous bundles of interconnected fibrin polymers (Fig. 5, DMSO, 10′). These aggregates actively reorganized fibrin polymers into parallel sheets in a time-dependent manner (Fig. 5, DMSO, 30′), themselves clustering into larger satellites. Platelet satellite formation and fibrin polymer reorganization were completely inhibited by the integrin αIIbβ3 blocking antibody c7E3 Fab (50 μg/ml; data not shown). Wortmannin inhibition of PI3K significantly delayed the interaction of activated platelets with fibrin polymers, resulting in unstable platelet adhesion contacts. As a consequence, the subsequent development of small platelet satellites and fibrin bundles were significantly delayed (up to 30–60 min post-thrombin stimulation) (Fig. 5). These findings suggest that the inhibition of PI3K reduces the development of stable high affinity integrin αIIbβ3 adhesion contacts with fibrin polymers, undermining subsequent force generation on the fibrin clot.
FIGURE 5.
Microscopic analysis of the role of PI3K in platelet-mediated clot retraction. Washed platelets were pretreated with either vehicle (DMSO) or wortmannin (100 nm) and supplemented with 0.25 mg/ml fibrinogen containing 10% Oregon Green-labeled fibrinogen (OG-FGN). Platelets were stimulated with 1 unit/ml thrombin, and the process of clot retraction was visualized in real time using both DIC microscopy and epifluorescence microscopy (Oregon Green-labeled fibrinogen), as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Images are taken from one representative of three independent experiments. Note that the colored side bar indicates the intensity of fluorescence wherein the warmer colors (red/white) depict higher levels of fluorescence intensity and colder colors (blue/black) indicate a lower level of fluorescence intensity.
PI3K Strengthens High Affinity Integrin αIIbβ3 Adhesion Contacts
To investigate further the role of PI3K in regulating the stability of high affinity integrin αIIbβ3 adhesion contacts, platelet adhesion experiments were performed on an immobilized fibrinogen matrix. Platelet adhesion to fibrinogen is exclusively mediated though integrin αIIbβ3 adhesive bonds, leading to the generation of outside-in signals that induce cytoskeletal remodeling, leading to the extension of numerous filopodia and broad lamellipodial sheets (46). Consistent with previous studies, the ability of platelets to adhere and spread on an immobilized fibrinogen matrix in the absence of platelet co-stimulation by soluble agonists was found to be critically dependent on the matrix ligand density (47) (data not shown). For example, at fibrinogen coating concentrations between 10 and 50 μg/ml, stable platelet adhesion and spreading was readily observed, even in the presence of ADP/TxA2 antagonists. However, at fibrinogen coating concentrations below 5 μg/ml, platelet adhesion was typically less stable, with spreading observed in only a small proportion of adherent platelets. In contrast, in the presence of thrombin, platelet adhesion and spreading occurred rapidly on low density fibrinogen matrices (0.2–5 μg/ml) (supplemental Fig. 4). These findings suggest that a threshold matrix density is required for low affinity αIIbβ3 receptors (in the absence of soluble agonist co-stimulation) to transduce activation signals that promote stable platelet adhesion and spreading.
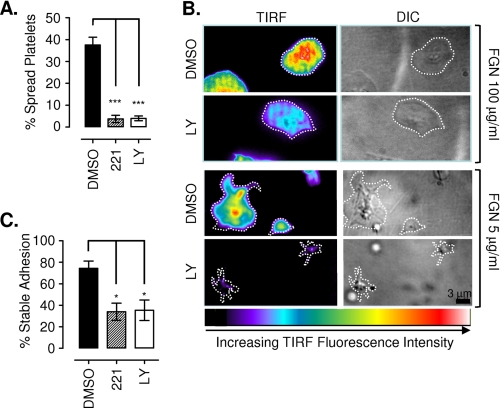
To gain insight into the effects of PI3K inhibitors on platelet adhesion dynamics as a function of matrix density, we performed real-time DIC microscopy. Analysis of platelet adhesion and spreading revealed that washed platelets treated with PI3K inhibitors were slow to develop firm adhesion contacts with the fibrinogen matrix, even at high matrix coating concentrations (10–100 μg/ml) (data not shown). PI3K inhibitor-treated platelets developed numerous filopodial extensions, many of which formed transient adhesion contacts with the matrix; however, adhesion contacts with the main cell body developed slowly relative to untreated controls. In contrast, in the presence of thrombin, both control and PI3K-inhibited platelets developed rapid stable adhesion contacts with the fibrinogen surface (through both filopodial extensions and the main cell body), leading to circumferentially uniform lamellipodial extensions that promoted isotropic full platelet spreading (data not shown). Notably, at low matrix densities (≤5 μg/ml), thrombin (1 unit/ml) was unable to overcome the adhesion and spreading defect associated with PI3K inhibition (platelets treated with LY294002 or the p110β-selective inhibitor TGX221) (Fig. 6A). Under these conditions, thrombin-stimulated platelets extended numerous transient filopodia; however, neither the filopodia nor main cell body was able to form stable adhesion contacts with the matrix, preventing subsequent firm platelet adhesion and lamellipodial generation (Fig. 6A and supplemental Fig. 4).
FIGURE 6.
PI3K plays an important role in strengthening high affinity integrin αIIbβ3 adhesive contacts. Washed human platelets were preincubated with vehicle alone (DMSO), LY294002 (LY; 25 μm), wortmannin (100 nm), or TGX221 (221; 0.5 μm) prior to stimulation with 1 unit/ml thrombin and application to immobilized fibrinogen (0.2–100 μg/ml). A, platelet-fibrinogen interactions under static conditions were recorded in real time for off-line analysis, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Results are expressed as percentage of spread platelets and represent the mean ± S.E. of three independent experiments, with five random fields of view analyzed per experiment (***, p < 0.001). B, thrombin-stimulated DiIC12-labeled platelets were allowed to interact with an immobilized fibrinogen matrix (5–100 μg/ml) and observed using TIRF microscopy and DIC microscopy in real time as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Images were taken 10 min post-stimulation and are representative of three independent experiments. Note that the pseudocolor scale is representative of raw TIRF fluorescence intensity, with black/blue indicative of platelet membrane regions at the periphery of the evanescent field (∼100 nm from the coverslip surface) and red/white indicative of platelet membrane within ∼12–15 nm of the coverslip surface. C, thrombin-stimulated platelets were gently perfused (150 s−1) into fibrinogen-coated (2.0 μg/ml) microslides and allowed to interact for 5 min under static conditions prior to perfusion of Tyrode's buffer at 1800 s−1 for 5 min. The number of adherent platelets in the field of view before and after shear application was quantified, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Results are expressed as percentage of stable adhesion (mean ± S.E., n = 3; *, p < 0.05).
To investigate the impact of PI3K inhibitors on the formation of platelet adhesion contacts in more detail, we employed TIRF microscopy, a technique that is ideally suited for the analysis of cell adhesion “footprints” that form within 100 nm of the matrix surface (39). In control studies, thrombin-stimulated platelets were observed to rapidly form single point contacts with the fibrinogen matrix (5 μg/ml), followed by rapid symmetric extension of lamellipodial sheets, leading to robust isotropic platelet spreading (supplemental Video 1). Significantly, these fully spread platelets exhibited relatively symmetric adhesion contacts, typified by a homogenous and relatively intense TIRF footprint, indicative of tight coupling to the fibrinogen surface (Fig. 6B). In contrast, platelets treated with the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 initially formed single point contacts with the fibrinogen surface equivalent to controls but were apparently incapable of initiating platelet spreading (Fig. 6B). LY294002-treated platelet adhesion was typified by the formation of multiple loosely adherent filopodial extensions undergoing rapid turnover. Significantly, the central platelet body appeared to be entirely incapable of forming firm adhesion contacts with the substrate, as signified by a highly unstable and very low intensity TIRF footprint (Fig. 6B and supplemental Video 1). Analysis of the adhesive strength of these platelets by exposing the adhering platelets to sudden increases in hemodynamic shear forces (from 0 to 1800 s−1) resulted in >60% detachment of thrombin-stimulated platelets (in the presence of the PI3K inhibitor LY294002 or the p110β-selective inhibitor TGX221) relative to ∼20% of controls (Fig. 6C). Taken together, these results demonstrate an important role for PI3K in promoting the formation of stable high affinity integrin αIIbβ3 adhesive bonds.
DISCUSSION
PI3K signaling processes have a well defined role in regulating the affinity status of integrin αIIbβ3, particularly downstream of Gi- and tyrosine kinase-coupled receptors. The studies presented here have defined a key role for PI3K in regulating the avidity of integrin αIIbβ3 adhesion contacts (i.e. stability of adhesion) following platelet stimulation by high dose thrombin. We have demonstrated that PI3K-dependent increases in integrin avidity are important for allowing high affinity integrin adhesive bonds to transmit cytoskeletal contractile forces and to maintain stable platelet adhesion in a shear field. Moreover, we have demonstrated that these abnormalities in platelet contractile function were not due to alterations in integrin αIIbβ3 ligand binding affinity, actin polymerization, or myosin light chain phosphorylation but appeared to be due to a selective defect in the ability of integrin αIIbβ3 to anchor to the contractile cytoskeleton. These findings define an important role for PI3K in regulating the cellular transmission of contractile force.
An unexpected finding from the current study was the important role of PI3K in promoting the stable adhesion of thrombin-stimulated platelets. It has previously been demonstrated by others (47) and confirmed here that defects in platelet adhesion and spreading of PI3K inhibitor-treated platelets can be overcome by platelet co-stimulation with soluble agonists. Our imaging studies have demonstrated that high affinity integrin αIIbβ3 adhesion contacts are highly unstable on fibrin polymers and on a low density fibrinogen substrate in the absence of PI3K signaling. Potential explanations for these findings require consideration of the factors regulating integrin avidity. In general, the overall strength of adhesion is dictated by the intrinsic binding kinetics of individual ligand-receptor bonds (affinity) as well as the total number of bonds (valency) (6). Several factors influence valency, including the density of both receptors and ligands at the adhesive surface, the geometric arrangement of these surfaces, and the mobility of the receptor and/or ligand. In the case of integrins, these receptors can move within the plane of the lipid bilayer, in part through cytoskeleton-dependent changes in receptor distribution (6). With respect to our findings, it is likely that the defect in platelet adhesion stability is related to alterations in total number of bonds (valency), because affinity regulation of individual integrin αIIbβ3 bonds was unaltered by PI3K inhibitors in thrombin-stimulated platelets.
Of the potential mechanisms by which PI3K signaling could regulate valency, one possibility is that PI3K is regulating integrin receptor distribution as a result of changes in cytoskeletal reorganization. One hypothesis is that inhibition of PI3K interferes with the initial stabilization of platelet-fibrin cross-linking by preventing clustering of integrin adhesive bonds. This is consistent with our findings that PI3K inhibitors reduce the cytoskeletal association of integrin receptors, a process that is essential for the ability of actin cables to cluster integrins into focal adhesion-like complexes and transmit contractile forces to extracellular matrices (48). Such a possibility would be consistent with findings in nucleated cells in which PI3K signaling processes promote clustering of integrin αVβ1 (in human umbilical vein endothelial cells), αLβ2 (in leukocytes), and α6β4 (in breast cell carcinoma), leading to enhanced receptor avidity (49–53).
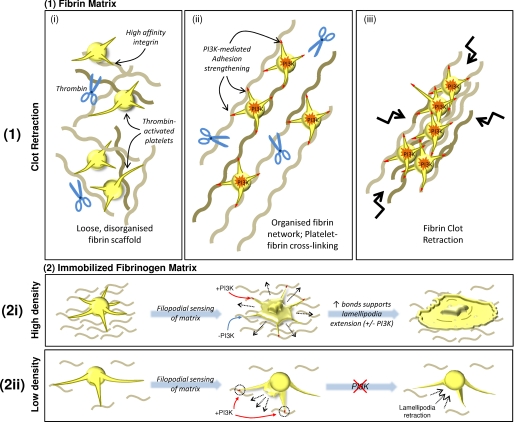
An alternative model, suggested by our DIC microscopy and TIRFM findings, is that PI3K inhibition may interfere with the development of stable adhesion contacts by interfering with the development of stable “lamellae-type” membrane extensions. For example, we have observed that filopodial extensions from the surface of thrombin-stimulated platelets promote the formation of stable adhesive interactions with a low density fibrinogen matrix. Typically, formation of stable filopodial adhesion contacts is followed by the development of lamellae that serve to promote the development of new integrin adhesion contacts at the leading edge of the cell (54). Thus, it is likely that defects in lamellae extension, as a result of PI3K inhibition, would decrease the redistribution of high affinity integrin αIIbβ3 adhesive bonds to regions of sparse ligand density. This could be the case during the early stages of fibrin clot retraction, wherein individual fibrin strands are randomly and sparsely distributed in three-dimensional space, limiting the ability of integrin receptors to cross-link the fibrin scaffold (Fig. 7). Presumably, under conditions of high ligand density (such as a high density fibrinogen substrate), the projection of discrete lamellipodial sheets becomes less critical for the lateral extension and formation of new integrin bonds. In this latter situation, the platelet develops circumferentially uniform membrane extensions that are insensitive to the effects of PI3K inhibitors, thereby promoting isotropic platelet spreading.
FIGURE 7.
Proposed model for PI3K-mediated regulation of adhesion strengthening and cellular retraction of fibrin polymers. 1, during early phases of platelet-mediated clot retraction, thrombin-activated platelets form adhesive contacts with sparse fibrin polymers. Although high in affinity, due to a low matrix density, these adhesive contacts are relatively unstable and inefficient in transmitting platelet contractile forces. The activation of PI3K strengthens integrin adhesion contacts (as depicted by red-tipped filopodia), potentially through integrin redistribution, enabling efficient transmission of platelet contractile forces to the fibrin clot, leading to fibrin polymer reorganization and subsequent clot retraction. 2, the requirement for PI3K-mediated adhesion strengthening is also evident in thrombin-stimulated platelets adhering to immobilized fibrinogen. In the presence of a high density fibrinogen matrix (2i), numerous high affinity integrin contacts are formed rapidly and simultaneously. The number of adhesive contacts formed with the high density matrix at any one time, both by the main platelet body and subsequently by tips of extended filopodia, provide enough adhesive support to facilitate isotropic extension of lamellipodia, even in the absence of PI3K signaling. However, under conditions of low matrix density (2ii), the main platelet body is unable to form multiple stable contacts with the matrix, resulting in transient adhesive episodes (as demonstrated in supplemental Video 1). As with platelets on a high density matrix, filopodia are extended; however, due to low matrix density, these filopodia form unstable contacts, instead requiring PI3K-mediated adhesion strengthening to stabilize adhesion, and enable directed extension of lamellipodia between adjacent filopodial extensions. In the absence of PI3K signaling, the unstable nature of these adhesion contacts results in the formation of short lamellipodia that are transiently extended and retracted into the main cell body, resulting in an inability of the platelet to fully spread.
Based on our analysis of PI3K lipid products and the effects of ADP receptor antagonists, our studies suggest that the major role for PI3K signaling in regulating fibrin clot retraction occurs downstream of integrin αIIbβ3. It has previously been well established (42, 43) and confirmed in the present study, that the dominant pathways promoting PI3K activation in thrombin-stimulated platelets involve ADP-dependent stimulation of the P2Y12 receptor and ligand-induced integrin αIIbβ3 “outside-in” signaling. The P2Y12 receptor is the target of the thienopyridine group of antithrombotic drugs and promotes platelet activation in part through the Gi-dependent activation of PI3K p110β (16). PI3K p110β activation also occurs directly downstream of tyrosine kinase-linked receptors adhesion receptors, including integrin αIIbβ3 (29, 55), and as shown in the current study, complete blockade of ADP stimulation of platelets in combination with integrin αIIbβ3 inhibitors effectively eliminates all PI3K lipid product generation downstream of thrombin protease-activated receptors. Thus, it is unlikely that the inhibition of clot retraction observed in the current study can be explained by protease-activated receptor signaling defects linked to inside-out integrin αIIbβ3 activation. Similarly, our findings that ADP receptor antagonists had no significant impact on the rate and extent of thrombin-stimulated clot retraction suggest that PI3K signaling primarily occurs downstream of integrin αIIbβ3 and is necessary for the cytoskeletal association of the receptor complex and for outside-in changes in integrin αIIbβ3 avidity.
Inhibition of PI3K p110β produces a marked defect in platelet aggregate stability and thrombus formation that is particularly apparent under conditions of high shear stress (29). Part of the antithrombotic effect of these inhibitors relates to the important role of PI3K signaling in sustaining integrin αIIbβ3 activation downstream of Gi- and tyrosine kinase-linked receptors (16, 55). The studies presented here suggest that PI3K may also promote thrombus stability by enhancing the avidity of high affinity integrin αIIbβ3 receptors, necessary for shear-resistant platelet adhesion and fibrin clot retraction. The importance of platelet contractility in supporting thrombus growth and stability has recently been confirmed in myosin II-deficient mouse platelets and following microinjection of platelet contractility inhibitors at sites of vascular injury in vivo (30, 56). Recent experimental evidence has suggested that there are two temporally distinct phases of platelet contraction relevant to thrombus stability. The first of these involves the transmission of contractile forces between platelets (independent of fibrin formation) during the initial stages of thrombus development (30). The second involves the transmission of forces to developing fibrin polymers, a process that occurs at a later stage of thrombus development and is likely to play a key role in regulating stability of the secondary hemostatic plug. Interestingly, in preliminary studies, we have found that PI3K inhibitors appear to have minimal impact on the transmission of contractile forces between platelets during initial thrombus formation,4 a finding that may partially explain the lack of an inhibitory effect of these inhibitors on the formation of the primary platelet hemostatic plug (16, 29).
In summary, these studies demonstrate that PI3K not only plays an important role in maintaining integrin αIIbβ3 receptors in a high affinity state (through inside-out signaling) but also regulates the avidity of these activated receptors via transmission of outside-in signals. This bidirectional signaling function of PI3K may help explain the antithrombotic effectiveness of PI3Kβ inhibitors.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Imala Alwis for technical assistance and Professor Hatem Salem for helpful discussions.
This work was supported by grants from the National Heart Foundation of Australia and the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia.

The on-line version of this article (available at http://www.jbc.org) contains supplemental Figs. 1–4 and Video 1.
A. Ono, S. M. Schoenwaelder, and S. P. Jackson, unpublished observations.
- PI3K
- phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- PtdIns
- phosphatidylinositol
- DIC
- differential interference contrast
- PRP
- platelet-rich plasma
- RIAM
- Rap1b-interacting adaptor molecule
- TxA2
- thromboxane A2
- TIRF
- total internal reflection fluorescence
- HPLC
- high pressure liquid chromatography.
REFERENCES
- 1.Jackson S. P. (2007) Blood 109, 5087–5095 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ruggeri Z. M., Mendolicchio G. L. (2007) Circ. Res. 100, 1673–1685 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bhatt D. L., Topol E. J. (2003) Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2, 15–28 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Banno A., Ginsberg M. H. (2008) Biochem. Soc. Trans. 36, 229–234 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Coller B. S., Shattil S. J. (2008) Blood 112, 3011–3025 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Carman C. V., Springer T. A. (2003) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 547–556 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Crittenden J. R., Bergmeier W., Zhang Y., Piffath C. L., Liang Y., Wagner D. D., Housman D. E., Graybiel A. M. (2004) Nat. Med. 10, 982–986 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M., Smyth S. S., Schoenwaelder S. M., Fischer T. H., White G. C., 2nd (2005) J. Clin. Invest. 115, 680–687 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Han J., Lim C. J., Watanabe N., Soriani A., Ratnikov B., Calderwood D. A., Puzon-McLaughlin W., Lafuente E. M., Boussiotis V. A., Shattil S. J., Ginsberg M. H. (2006) Curr. Biol. 16, 1796–1806 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Petrich B. G., Marchese P., Ruggeri Z. M., Spiess S., Weichert R. A., Ye F., Tiedt R., Skoda R. C., Monkley S. J., Critchley D. R., Ginsberg M. H. (2007) J. Exp. Med. 204, 3103–3111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Moser M., Nieswandt B., Ussar S., Pozgajova M., Fässler R. (2008) Nat. Med. 14, 325–330 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Trumel C., Payrastre B., Plantavid M., Hechler B., Viala C., Presek P., Martinson E. A., Cazenave J. P., Chap H., Gachet C. (1999) Blood 94, 4156–4165 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bertoni A., Tadokoro S., Eto K., Pampori N., Parise L. V., White G. C., Shattil S. J. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 25715–25721 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kauffenstein G., Bergmeier W., Eckly A., Ohlmann P., Léon C., Cazenave J. P., Nieswandt B., Gachet C. (2001) FEBS Lett. 505, 281–290 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lova P., Paganini S., Sinigaglia F., Balduini C., Torti M. (2002) J. Biol. Chem. 277, 12009–12015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Schoenwaelder S. M., Ono A., Sturgeon S., Chan S. M., Mangin P., Maxwell M. J., Turnbull S., Mulchandani M., Anderson K., Kauffenstein G., Rewcastle G. W., Kendall J., Gachet C., Salem H. H., Jackson S. P. (2007) J. Biol. Chem. 282, 28648–28658 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Gratacap M. P., Payrastre B., Viala C., Mauco G., Plantavid M., Chap H. (1998) J. Biol. Chem. 273, 24314–24321 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guinebault C., Payrastre B., Sultan C., Mauco G., Breton M., Levy-Toledano S., Plantavid M., Chap H. (1993) Biochem. J. 292, 851–856 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pasquet J. M., Bobe R., Gross B., Gratacap M. P., Tomlinson M. G., Payrastre B., Watson S. P. (1999) Biochem. J. 342, 171–177 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Vanhaesebroeck B., Leevers S. J., Panayotou G., Waterfield M. D. (1997) Trends Biochem. Sci. 22, 267–272 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Vanhaesebroeck B., Waterfield M. D. (1999) Exp. Cell Res. 253, 239–254 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wymann M. P., Pirola L. (1998) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1436, 127–150 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hartwig J. H. (2007) in Platelets, 2nd Ed. (Michelson A. ed) Academic Press, Inc., New York [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jackson S. P., Yap C. L., Anderson K. E. (2004) Biochem. Soc. Trans. 32, 387–392 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Crawley J. T., Zanardelli S., Chion C. K., Lane D. A. (2007) J. Thromb. Haemost. 5, Suppl. 1, 95–101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cohen I., Gerrard J. M., White J. G. (1982) J. Cell Biol. 93, 775–787 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cohen I., Burk D. L., White J. G. (1989) Blood 73, 1880–1887 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Carr M. E., Jr., Carr S. L., Hantgan R. R., Braaten J. (1995) Thromb. Haemost. 73, 499–505 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Jackson S. P., Schoenwaelder S. M., Goncalves I., Nesbitt W. S., Yap C. L., Wright C. E., Kenche V., Anderson K. E., Dopheide S. M., Yuan Y., Sturgeon S. A., Prabaharan H., Thompson P. E., Smith G. D., Shepherd P. R., Daniele N., Kulkarni S., Abbott B., Saylik D., Jones C., Lu L., Giuliano S., Hughan S. C., Angus J. A., Robertson A. D., Salem H. H. (2005) Nat. Med. 11, 507–514 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ono A., Westein E., Hsiao S., Nesbitt W. S., Hamilton J. R., Schoenwaelder S. M., Jackson S. P. (2008) Blood 112, 90–99 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schoenwaelder S. M., Yuan Y., Josefsson E. C., White M. J., Yao Y., Mason K. D., O'Reilly L. A., Henley K. J., Ono A., Hsiao S., Willcox A., Roberts A. W., Huang D. C., Salem H. H., Kile B. T., Jackson S. P. (2009) Blood 114, 663–666 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schoenwaelder S. M., Kulkarni S., Salem H. H., Imajoh-Ohmi S., Yamao-Harigaya W., Saido T. C., Jackson S. P. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272, 24876–24884 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Maxwell M. J., Yuan Y., Anderson K. E., Hibbs M. L., Salem H. H., Jackson S. P. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 32196–32204 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Stephens L. R., Eguinoa A., Erdjument-Bromage H., Lui M., Cooke F., Coadwell J., Smrcka A. S., Thelen M., Cadwallader K., Tempst P., Hawkins P. T. (1997) Cell 89, 105–114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Fox J. E. (1993) Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 344, 175–185 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Osdoit S., Rosa J. P. (2001) J. Biol. Chem. 276, 6703–6710 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ohara-Imaizumi M., Nishiwaki C., Kikuta T., Nagai S., Nakamichi Y., Nagamatsu S. (2004) Biochem. J. 381, 13–18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Truskey G. A., Burmeister J. S., Grapa E., Reichert W. M. (1992) J. Cell Sci. 103, 491–499 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Nesbitt W. S., Westein E., Tovar-Lopez F. J., Tolouei E., Mitchell A., Fu J., Carberry J., Fouras A., Jackson S. P. (2009) Nat. Med. 15, 665–673 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lova P., Paganini S., Hirsch E., Barberis L., Wymann M., Sinigaglia F., Balduini C., Torti M. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 131–138 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Watanabe N., Nakajima H., Suzuki H., Oda A., Matsubara Y., Moroi M., Terauchi Y., Kadowaki T., Suzuki H., Koyasu S., Ikeda Y., Handa M. (2003) Blood 102, 541–548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Selheim F., Idsøe R., Fukami M. H., Holmsen H., Vassbotn F. S. (1999) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 263, 780–785 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Payrastre B., Missy K., Trumel C., Bodin S., Plantavid M., Chap H. (2000) Biochem. Pharmacol. 60, 1069–1074 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kim S., Foster C., Lecchi A., Quinton T. M., Prosser D. M., Jin J., Cattaneo M., Kunapuli S. P. (2002) Blood 99, 3629–3636 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Bromberg M. E., Sevy R. W., Daniel J. L., Salganicoff L. (1985) Am. J. Physiol. 249, C297–C303 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Shattil S. J. (1999) Thromb. Haemost. 82, 318–325 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Jirousková M., Jaiswal J. K., Coller B. S. (2007) Blood 109, 5260–5269 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Burridge K., Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M. (1996) Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 12, 463–518 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Krauss K., Altevogt P. (1999) J. Biol. Chem. 274, 36921–36927 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Gilcrease M. Z., Zhou X., Welch K. (2004) Cancer Res. 64, 7395–7398 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Dormond O., Ponsonnet L., Hasmim M., Foletti A., Rüegg C. (2004) Thromb. Haemost. 92, 151–161 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Jones S. L., Wang J., Turck C. W., Brown E. J. (1998) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 95, 9331–9336 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lynch L., Vodyanik P. I., Boettiger D., Guvakova M. A. (2005) Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 51–63 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Nobes C. D., Hall A. (1995) Cell 81, 53–62 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Canobbio I., Stefanini L., Cipolla L., Ciraolo E., Gruppi C., Balduini C., Hirsch E., Torti M. (2009) Blood 114, 2193–2196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Léon C., Eckly A., Hechler B., Aleil B., Freund M., Ravanat C., Jourdain M., Nonne C., Weber J., Tiedt R., Gratacap M. P., Severin S., Cazenave J. P., Lanza F., Skoda R., Gachet C. (2007) Blood 110, 3183–3191 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Jakobsen E., Kierulf P. (1973) Thromb. Res. 3, 145–159 [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.