Abstract
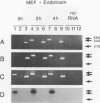
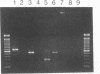
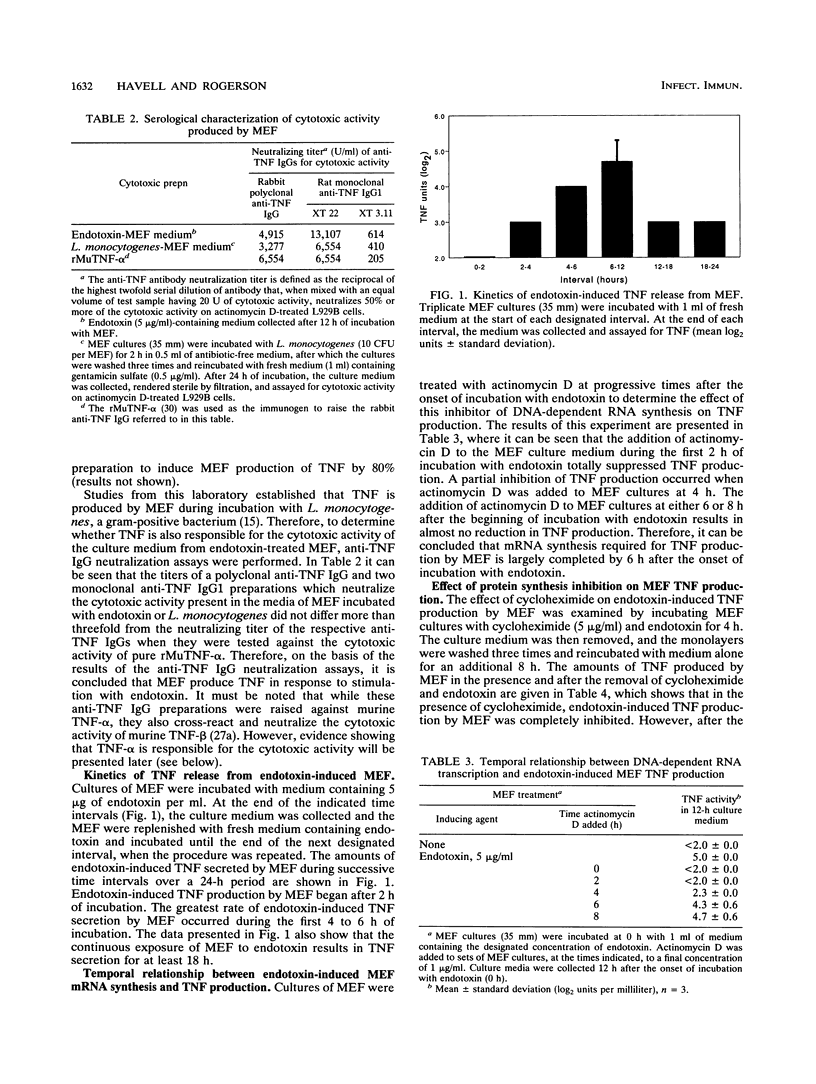
Murine embryo fibroblasts (MEF) were found to secrete tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in response to stimulation with endotoxin. Endotoxin-induced TNF production by MEF was inhibited by cycloheximide. However, reversal of the effect of this inhibitor on protein synthesis results in TNF being secreted in amounts equivalent to those produced by endotoxin-induced MEF not treated with cycloheximide. Actinomycin D treatment of MEF blocked the production of endotoxin-induced TNF. Maximal production of TNF required MEF gene transcription during the first 6 h of incubation with endotoxin. To determine whether endotoxin-induced TNF alpha (TNF-alpha) and/or TNF beta were produced by MEF, cDNA was synthesized from the total RNA isolated from endotoxin-induced MEF and amplified by the polymerase chain reaction in the presence of oligonucleotide primers specific for each cytokine. On the basis of the polymerase chain reaction analysis, it was determined that TNF-alpha mRNA levels were increased in endotoxin-induced MEF. Thus, production of TNF-alpha by fibroblasts in response to the endotoxin component of bacterial cell walls is likely to contribute to the expression of TNF-mediated effects occurring in fibroblast-rich tissues infected with gram-negative bacteria.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beutler B., Krochin N., Milsark I. W., Luedke C., Cerami A. Control of cachectin (tumor necrosis factor) synthesis: mechanisms of endotoxin resistance. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):977–980. doi: 10.1126/science.3754653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Djeu J. Y., Klein T. W., Friedman H., Stewart W. E., 2nd Induction of tumor necrosis factor by Legionella pneumophila. Infect Immun. 1987 Feb;55(2):433–437. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.2.433-437.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchard D. K., Djeu J. Y., Klein T. W., Friedman H., Stewart W. E., 2nd Protective effects of tumor necrosis factor in experimental Legionella pneumophila infections of mice via activation of PMN function. J Leukoc Biol. 1988 May;43(5):429–435. doi: 10.1002/jlb.43.5.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee D., Roberts A. D., Lowell K., Brennan P. J., Orme I. M. Structural basis of capacity of lipoarabinomannan to induce secretion of tumor necrosis factor. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):1249–1253. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.1249-1253.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross A. S., Sadoff J. C., Kelly N., Bernton E., Gemski P. Pretreatment with recombinant murine tumor necrosis factor alpha/cachectin and murine interleukin 1 alpha protects mice from lethal bacterial infection. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2021–2027. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Jan-Feb;6(1):51–95. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante A., Staugas R. E., Rowan-Kelly B., Bresatz S., Kumaratilake L. M., Rzepczyk C. M., Adolf G. R. Production of tumor necrosis factors alpha and beta by human mononuclear leukocytes stimulated with mitogens, bacteria, and malarial parasites. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3996–4003. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3996-4003.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortier A. H., Polsinelli T., Green S. J., Nacy C. A. Activation of macrophages for destruction of Francisella tularensis: identification of cytokines, effector cells, and effector molecules. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):817–825. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.817-825.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Evidence that tumor necrosis factor has an important role in antibacterial resistance. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 1;143(9):2894–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Fiers W., North R. J. The antitumor function of tumor necrosis factor (TNF), I. Therapeutic action of TNF against an established murine sarcoma is indirect, immunologically dependent, and limited by severe toxicity. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1067–1085. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Production of tumor necrosis factor during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 15;139(12):4225–4231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A., Sehgal P. B. Tumor necrosis factor-independent IL-6 production during murine listeriosis. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):756–761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havell E. A. Synthesis and secretion of interferon by murine fibroblasts in response to intracellular Listeria monocytogenes. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):787–792. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.787-792.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfgott D. C., May L. T., Sthoeger Z., Tamm I., Sehgal P. B. Bacterial lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin) enhances expression and secretion of beta 2 interferon by human fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1300–1309. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofsli E., Lamvik J., Nissen-Meyer J. Evidence that tumour necrosis factor (TNF) is not constitutively present in vivo. The association of TNF with freshly isolated monocytes reflects a rapid in vitro production. Scand J Immunol. 1988 Oct;28(4):435–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1988.tb01473.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jablons D. M., Mulé J. J., McIntosh J. K., Sehgal P. B., May L. T., Huang C. M., Rosenberg S. A., Lotze M. T. IL-6/IFN-beta-2 as a circulating hormone. Induction by cytokine administration in humans. J Immunol. 1989 Mar 1;142(5):1542–1547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindler V., Sappino A. P., Grau G. E., Piguet P. F., Vassalli P. The inducing role of tumor necrosis factor in the development of bactericidal granulomas during BCG infection. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90676-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köck A., Schwarz T., Kirnbauer R., Urbanski A., Perry P., Ansel J. C., Luger T. A. Human keratinocytes are a source for tumor necrosis factor alpha: evidence for synthesis and release upon stimulation with endotoxin or ultraviolet light. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le J. M., Weinstein D., Gubler U., Vilcek J. Induction of membrane-associated interleukin 1 by tumor necrosis factor in human fibroblasts. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 1;138(7):2137–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiby D. A., Fortier A. H., Crawford R. M., Schreiber R. D., Nacy C. A. In vivo modulation of the murine immune response to Francisella tularensis LVS by administration of anticytokine antibodies. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.84-89.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastroeni P., Arena A., Costa G. B., Liberto M. C., Bonina L., Hormaeche C. E. Serum TNF alpha in mouse typhoid and enhancement of a Salmonella infection by anti-TNF alpha antibodies. Microb Pathog. 1991 Jul;11(1):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90091-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Burrowes C. E., Cybulsky M. I., Dinarello C. A. Acute inflammation and a Shwartzman-like reaction induced by interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Synergistic action of the cytokines in the induction of inflammation and microvascular injury. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):463–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano Y., Onozuka K., Terada Y., Shinomiya H., Nakano M. Protective effect of recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha in murine salmonellosis. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1935–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennica D., Hayflick J. S., Bringman T. S., Palladino M. A., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the cDNA for murine tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6060–6064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picarella D. E., Kratz A., Li C. B., Ruddle N. H., Flavell R. A. Insulitis in transgenic mice expressing tumor necrosis factor beta (lymphotoxin) in the pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10036–10040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spriggs D. R., Imamura K., Rodriguez C., Sariban E., Kufe D. W. Tumor necrosis factor expression in human epithelial tumor cell lines. J Clin Invest. 1988 Feb;81(2):455–460. doi: 10.1172/JCI113341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner S. J., Libby P. Human vascular smooth muscle cells. Target for and source of tumor necrosis factor. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 1;142(1):100–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner-Felmayer G., Werner E. R., Fuchs D., Hausen A., Reibnegger G., Wachter H. Tetrahydrobiopterin-dependent formation of nitrite and nitrate in murine fibroblasts. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1599–1607. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Magee D. M., Bonewald L. F., Smith J. G., Bleicker C. A., Byrne G. I., Schachter J. A role in vivo for tumor necrosis factor alpha in host defense against Chlamydia trachomatis. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1572–1576. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1572-1576.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckerman S. H., Evans G. F., Guthrie L. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms involved in the differential expression of LPS-induced IL-1 and TNF mRNA. Immunology. 1991 Aug;73(4):460–465. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]