Abstract
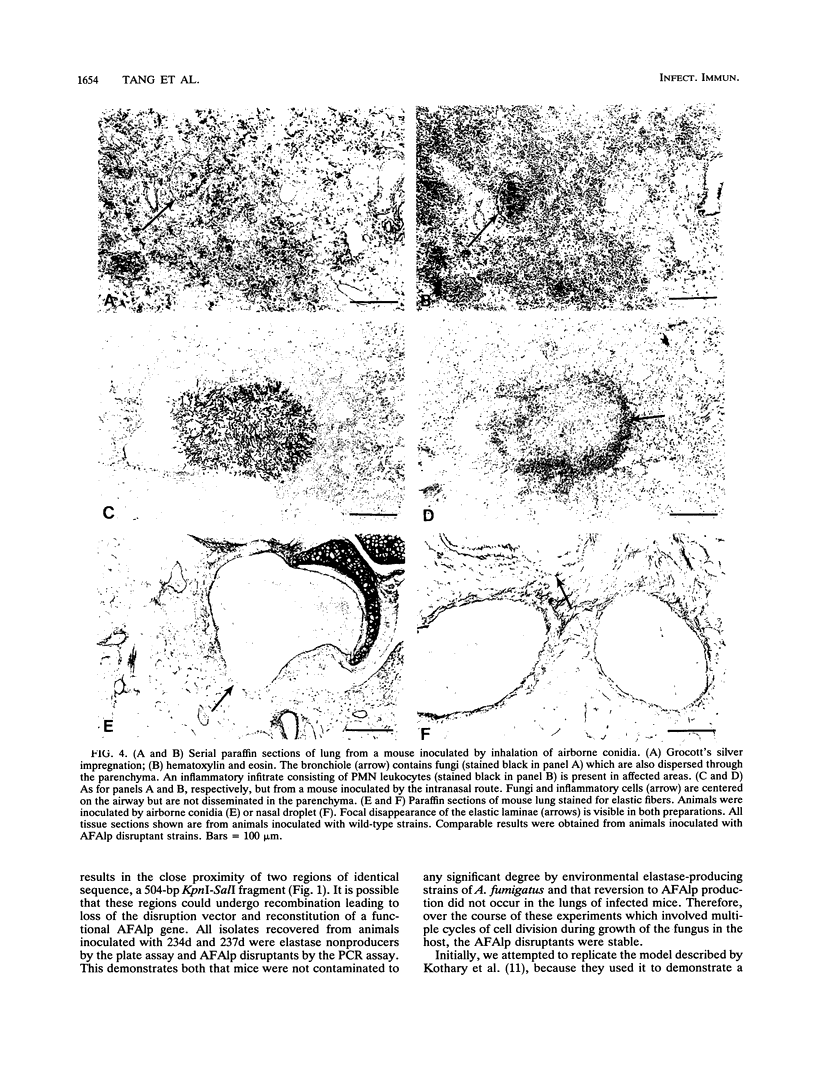
Little is known of the pathophysiology of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis (IPA), an opportunistic fungal infection usually caused by Aspergillus fumigatus. It has been suggested that the ability of the fungus to degrade elastin may aid its invasion and growth in lung tissue. We have described previously the construction of a strain of A. fumigatus in which the gene encoding an alkaline protease, AFAlp, had been disrupted (C.M. Tang, J. Cohen, and D.W. Holden, Mol. Microbiol. 6:1663-1671, 1992); this mutant is deficient in extracellular proteolytic and elastinolytic activity over a broad pH range. In this study, we compared the pathogenicity of this and another AFAlp disruptant with their isogenic, elastase-producing parental strains in two murine models of IPA. In both models, animals were inoculated via the respiratory tract. In the first model, the inoculum was delivered as airborne conidia and animals developed signs of respiratory distress within 2 to 4 days. In the second model, conidia were administered intranasally as a suspension and the disease developed over a 2-week period. No difference was observed between the wild-type and AFAlp disruptants in terms of mortality, and elastin breakdown was detected in lung tissue from animals inoculated with all four strains. We conclude that AFAlp is not a virulence determinant in these models of IPA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aufauvre-Brown A., Cohen J., Holden D. W. Use of randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers to distinguish isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Nov;30(11):2991–2993. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.11.2991-2993.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cove D. J. The induction and repression of nitrate reductase in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 11;113(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen D., Leong S. A., Wilson L. J., Henner D. J. Transformation of Aspergillus nidulans with the hygromycin-resistance gene, hph. Gene. 1987;57(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutler J. E. Putative virulence factors of Candida albicans. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:187–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning D. W., Ward P. N., Fenelon L. E., Benbow E. W. Lack of vessel wall elastolysis in human invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Infect Immun. 1992 Dec;60(12):5153–5156. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.12.5153-5156.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon D. M., Polak A., Walsh T. J. Fungus dose-dependent primary pulmonary aspergillosis in immunosuppressed mice. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1452–1456. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1452-1456.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frosco M., Chase T., Jr, Macmillan J. D. Purification and properties of the elastase from Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect Immun. 1992 Mar;60(3):728–734. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.3.728-734.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerson S. L., Talbot G. H., Hurwitz S., Strom B. L., Lusk E. J., Cassileth P. A. Prolonged granulocytopenia: the major risk factor for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis in patients with acute leukemia. Ann Intern Med. 1984 Mar;100(3):345–351. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-100-3-345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaton-Ogay K., Suter M., Crameri R., Falchetto R., Fatih A., Monod M. Nucleotide sequence of a genomic and a cDNA clone encoding an extracellular alkaline protease of Aspergillus fumigatus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Apr 15;71(2):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90506-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kothary M. H., Chase T., Jr, Macmillan J. D. Correlation of elastase production by some strains of Aspergillus fumigatus with ability to cause pulmonary invasive aspergillosis in mice. Infect Immun. 1984 Jan;43(1):320–325. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.1.320-325.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Edman J. C., Wickes B. L. Genetic association of mating types and virulence in Cryptococcus neoformans. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):602–605. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.602-605.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwon-Chung K. J., Lehman D., Good C., Magee P. T. Genetic evidence for role of extracellular proteinase in virulence of Candida albicans. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):571–575. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.571-575.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamy B., Moutaouakil M., Latge J. P., Davies J. Secretion of a potential virulence factor, a fungal ribonucleotoxin, during human aspergillosis infections. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1811–1815. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald F., Odds F. C. Virulence for mice of a proteinase-secreting strain of Candida albicans and a proteinase-deficient mutant. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Feb;129(2):431–438. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-2-431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyaji M., Nishimura K. Relationship between proteolytic activity of Aspergillus fumigatus and the fungus invasiveness of mouse brain. Mycopathologia. 1977 Dec 31;62(3):161–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00444109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod M., Paris S., Sarfati J., Jaton-Ogay K., Ave P., Latgé J. P. Virulence of alkaline protease-deficient mutants of Aspergillus fumigatus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Jan 1;106(1):39–46. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monod M., Togni G., Rahalison L., Frenk E. Isolation and characterisation of an extracellular alkaline protease of Aspergillus fumigatus. J Med Microbiol. 1991 Jul;35(1):23–28. doi: 10.1099/00222615-35-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PIGGOTT W. R., EMMONS C. W. Device for inhalation exposure of animals to spores. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1960 Apr;103:805–806. doi: 10.3181/00379727-103-25677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichard U., Büttner S., Eiffert H., Staib F., Rüchel R. Purification and characterisation of an extracellular serine proteinase from Aspergillus fumigatus and its detection in tissue. J Med Microbiol. 1990 Dec;33(4):243–251. doi: 10.1099/00222615-33-4-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. C., Bode R. B., McCuan-Kirsch C. M. Elastase production in clinical isolates of Aspergillus. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988 Jul;10(3):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0732-8893(88)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross I. K., De Bernardis F., Emerson G. W., Cassone A., Sullivan P. A. The secreted aspartate proteinase of Candida albicans: physiology of secretion and virulence of a proteinase-deficient mutant. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Apr;136(4):687–694. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-4-687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spreadbury C. L., Krausz T., Pervez S., Cohen J. Invasive aspergillosis: clinical and pathological features of a new animal model. J Med Vet Mycol. 1989;27(1):5–15. doi: 10.1080/02681218980000021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. J., Schäfer W. Cutinase is not required for fungal pathogenicity on pea. Plant Cell. 1992 Jun;4(6):621–629. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.6.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang C. M., Cohen J., Holden D. W. An Aspergillus fumigatus alkaline protease mutant constructed by gene disruption is deficient in extracellular elastase activity. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jun;6(12):1663–1671. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00891.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi H., Ogawa Y., Murakami S., Ishida Y., Murakami K., Masaki A., Kawabe H., Arimura H., Nakano E., Motai H. A full length cDNA clone for the alkaline protease from Aspergillus oryzae: structural analysis and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):33–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00261154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]